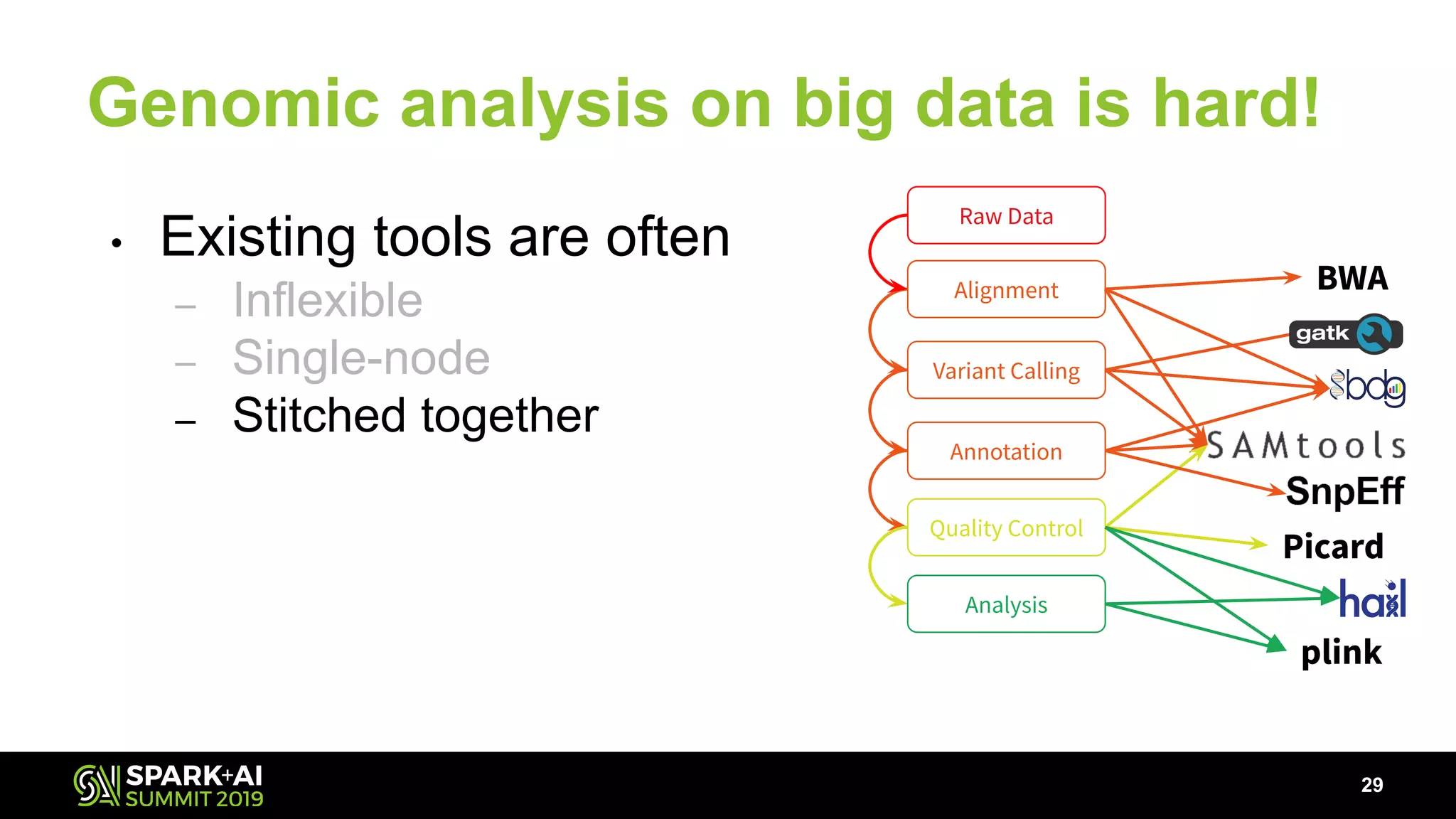
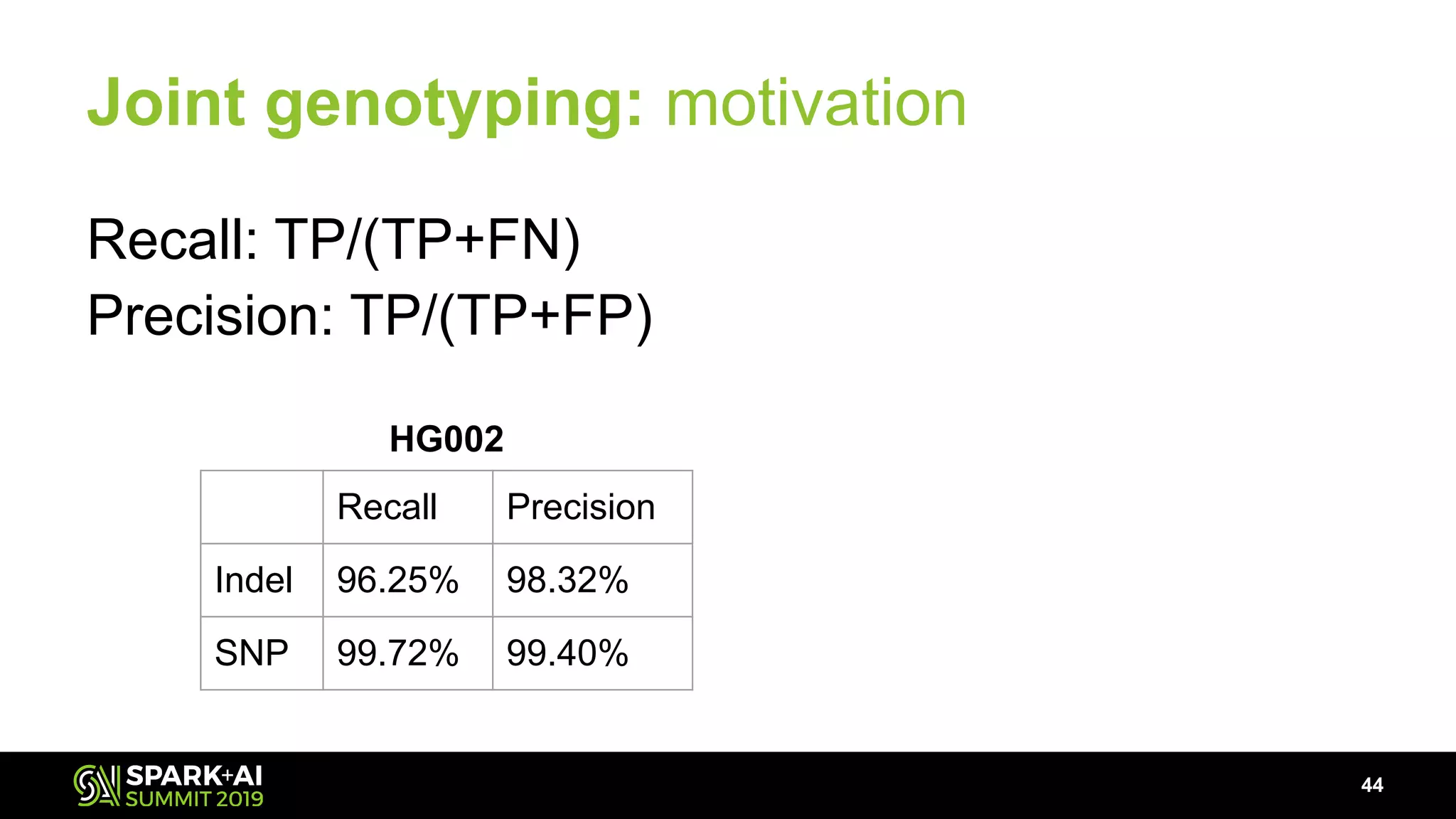
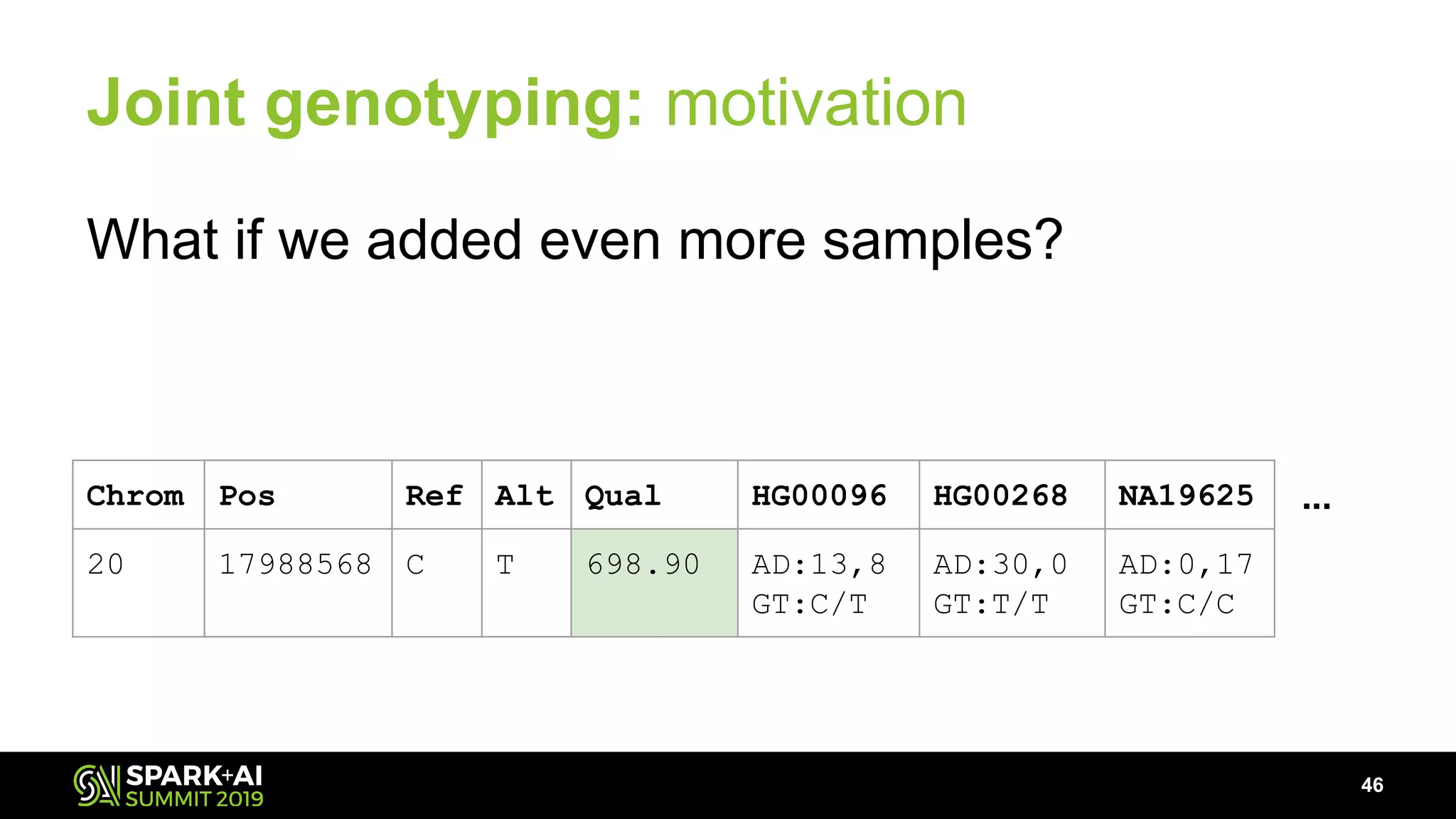
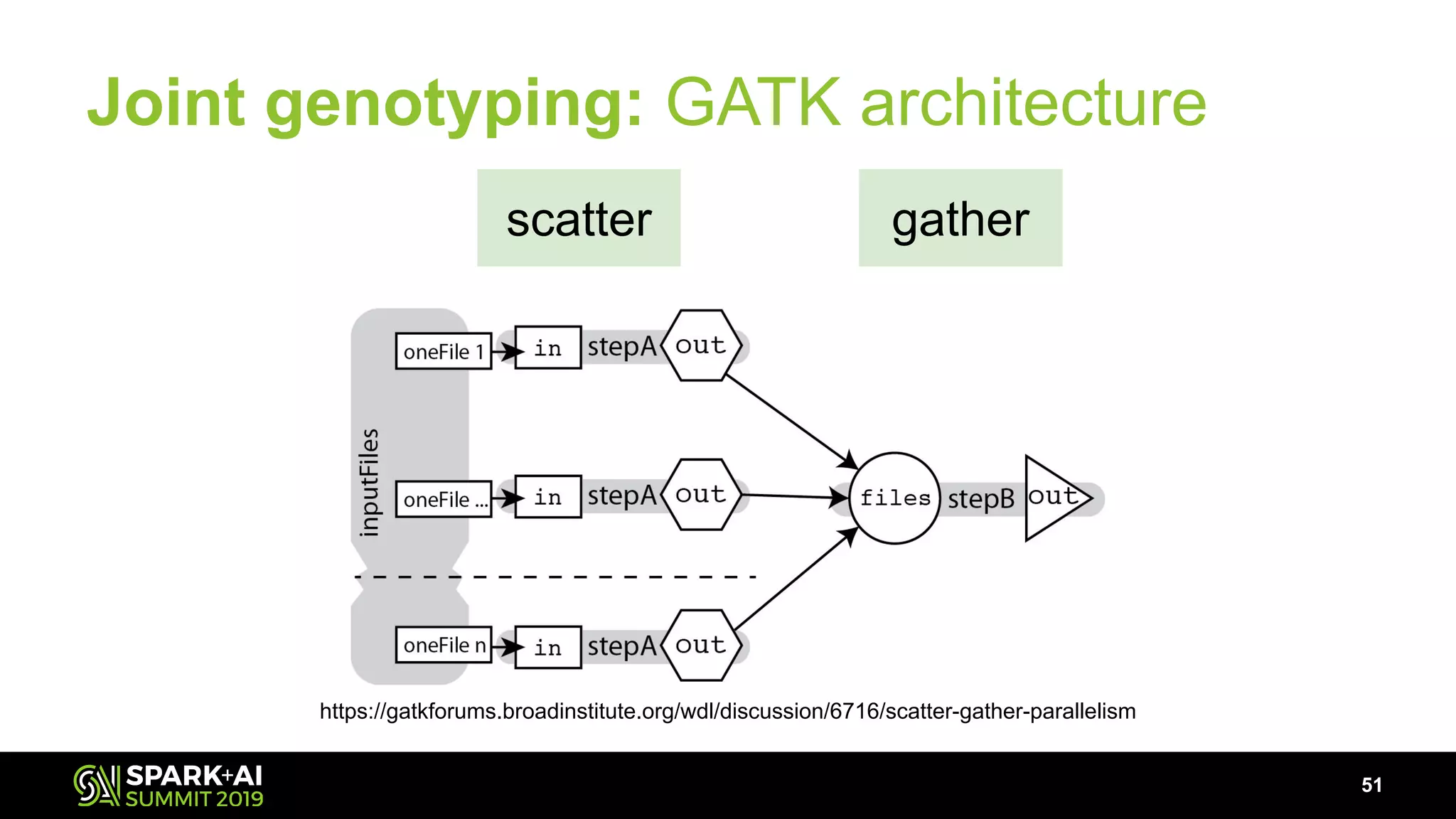
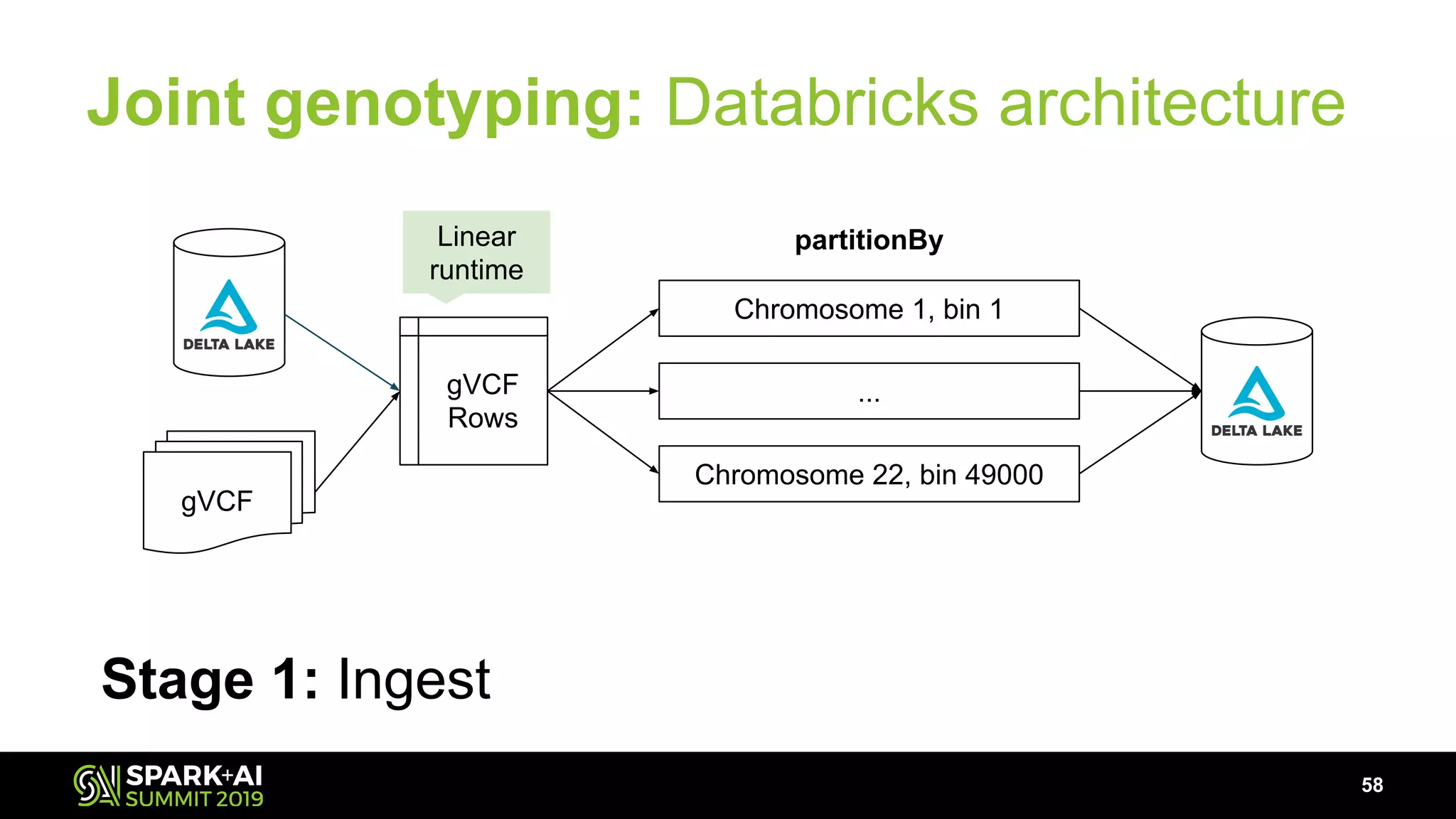
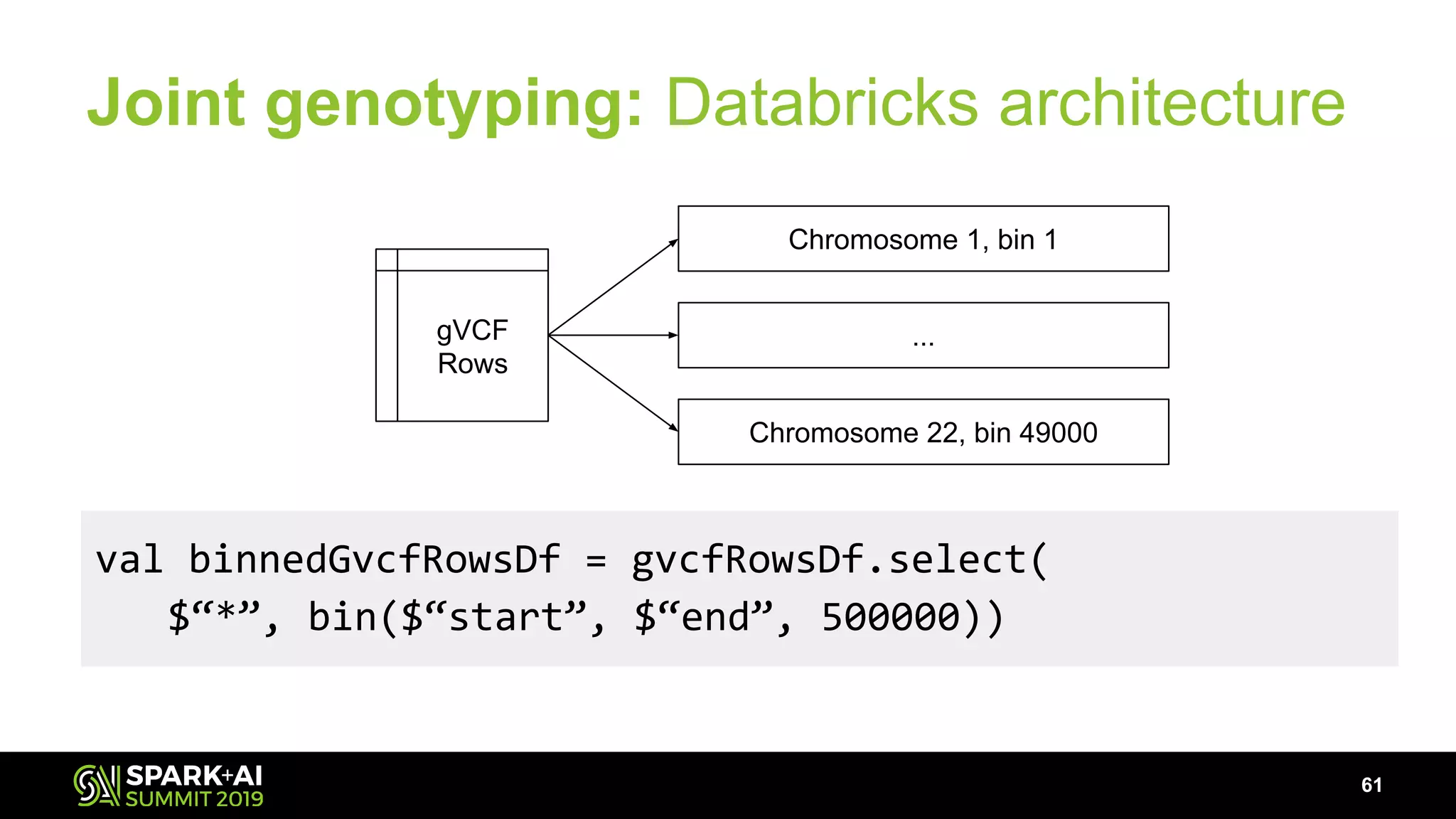
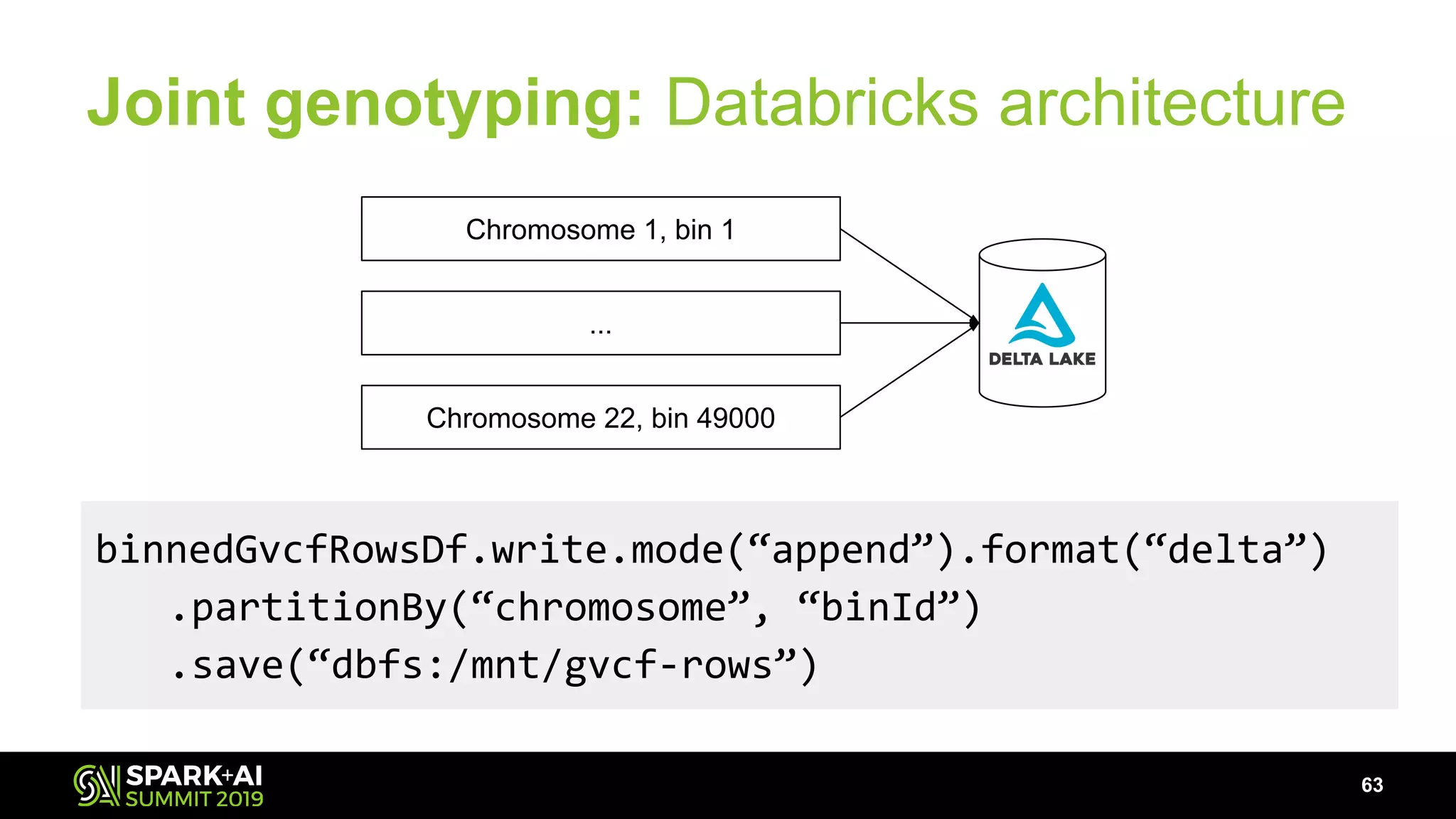
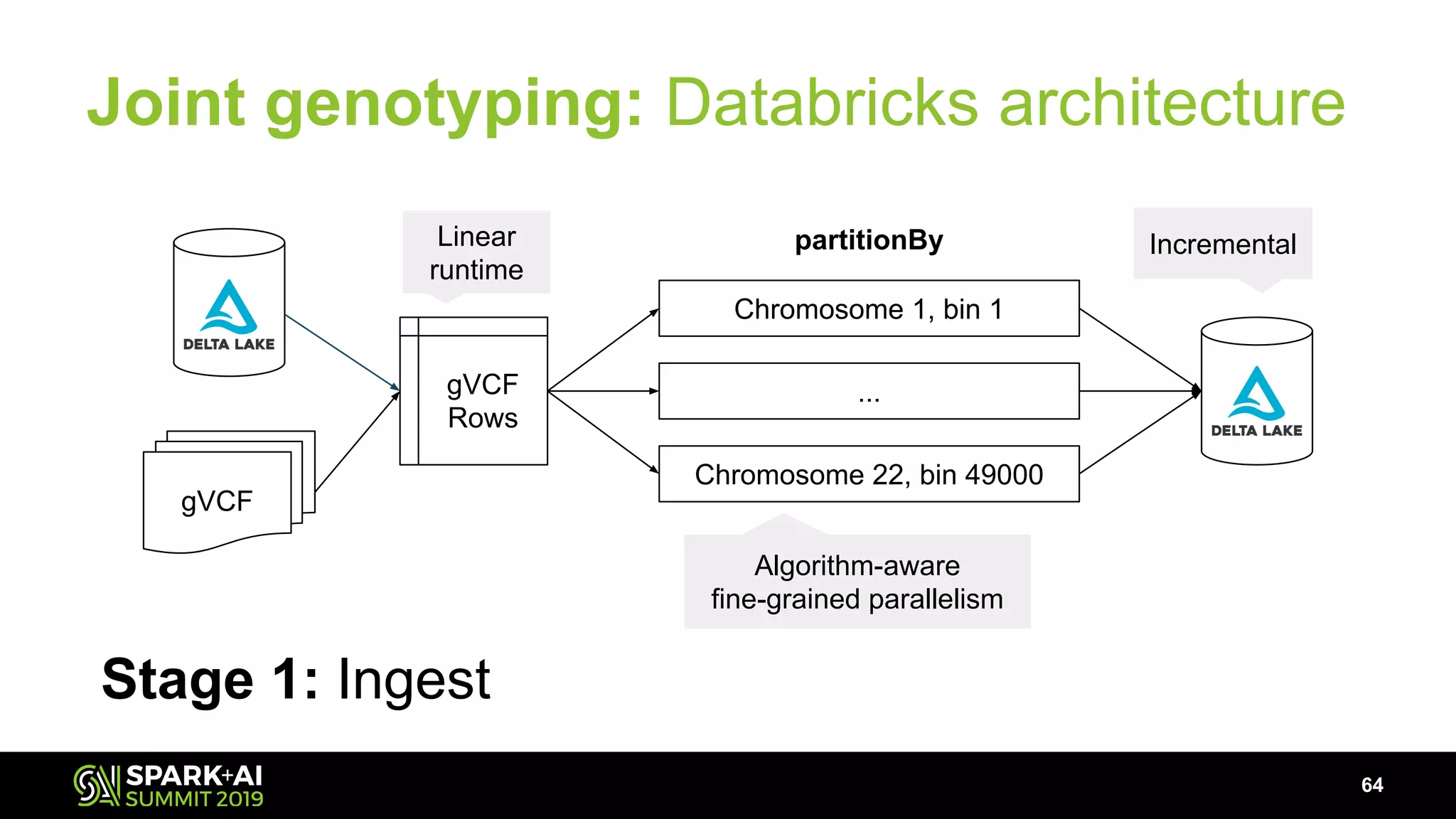
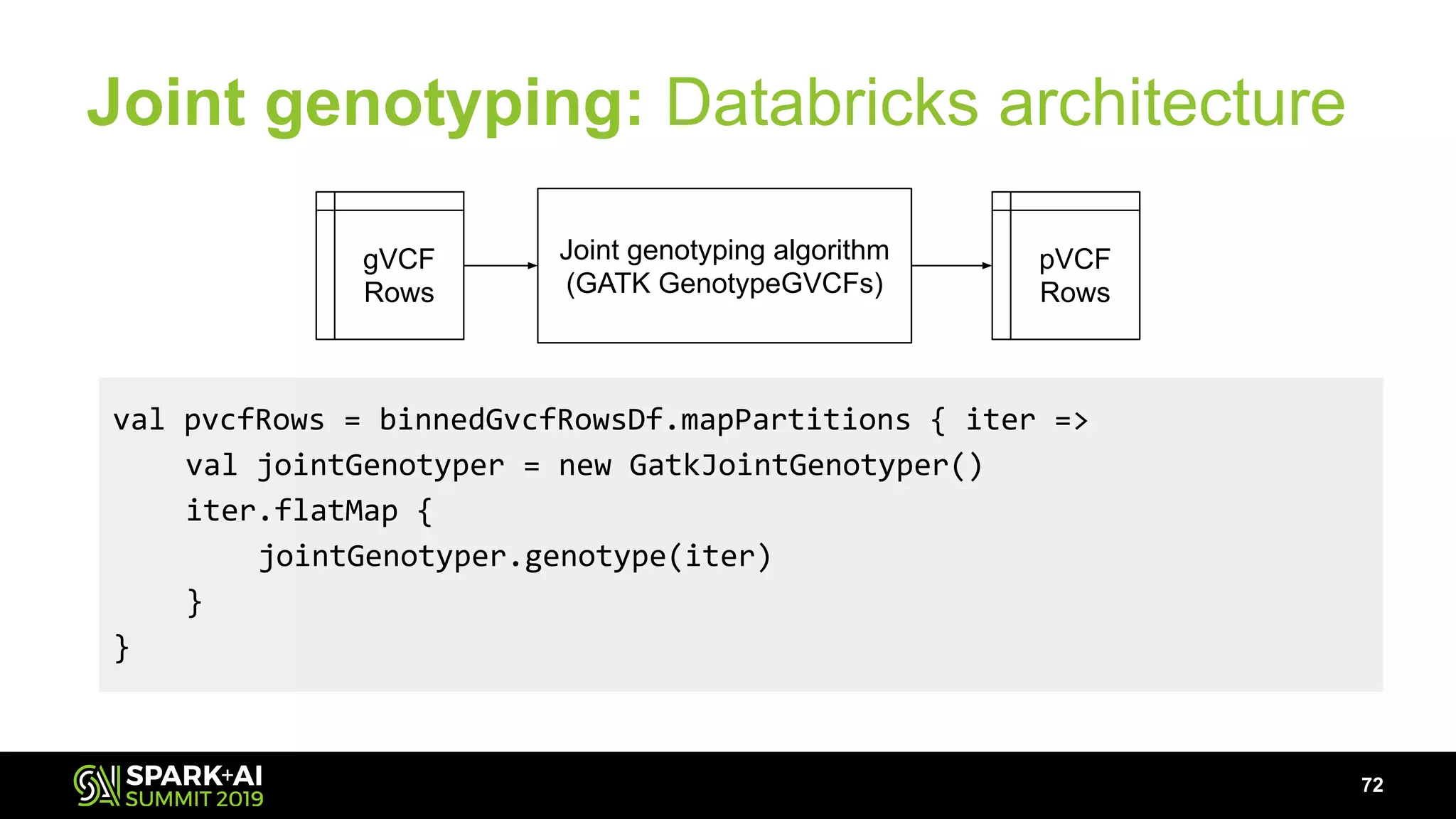
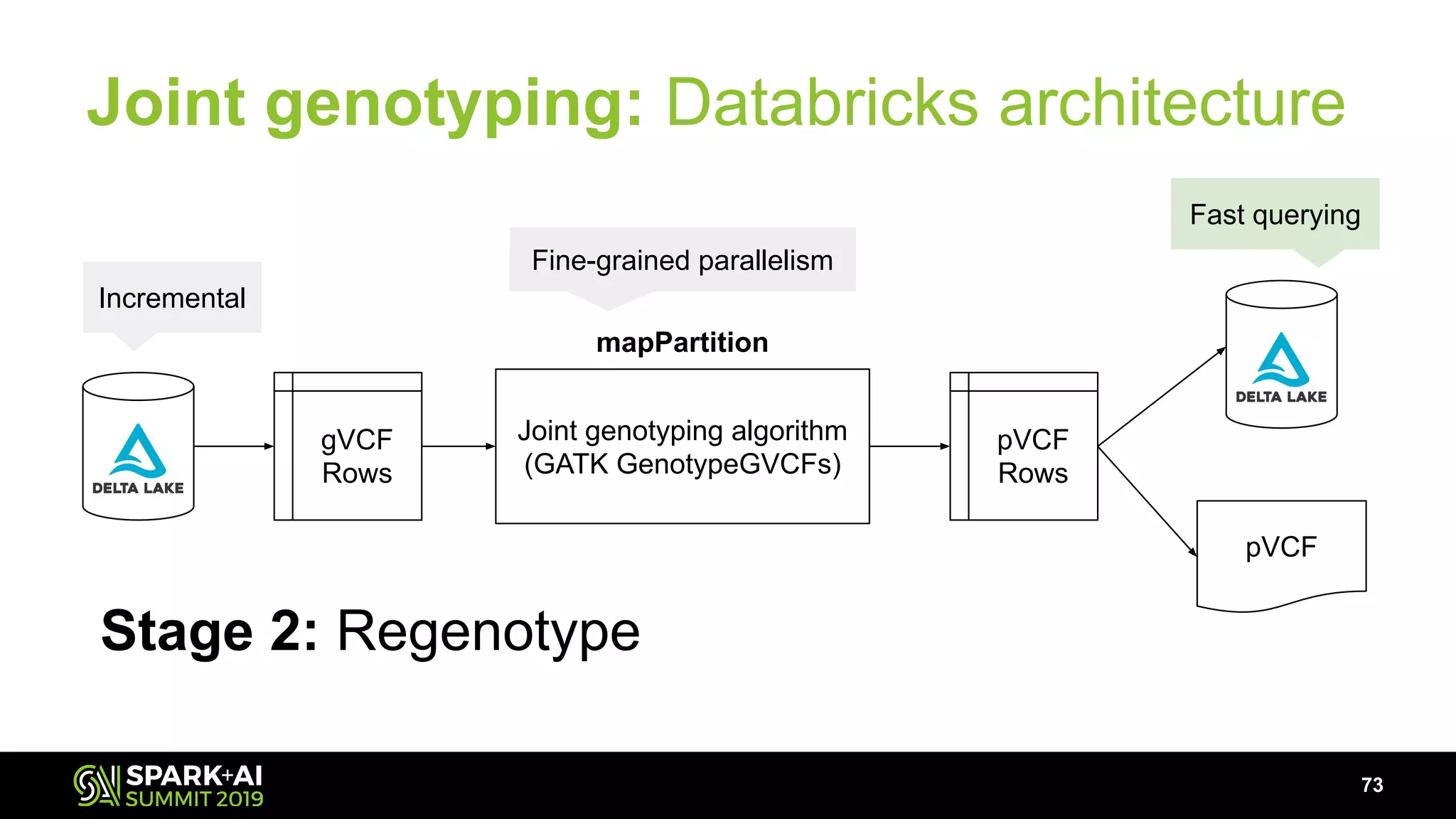
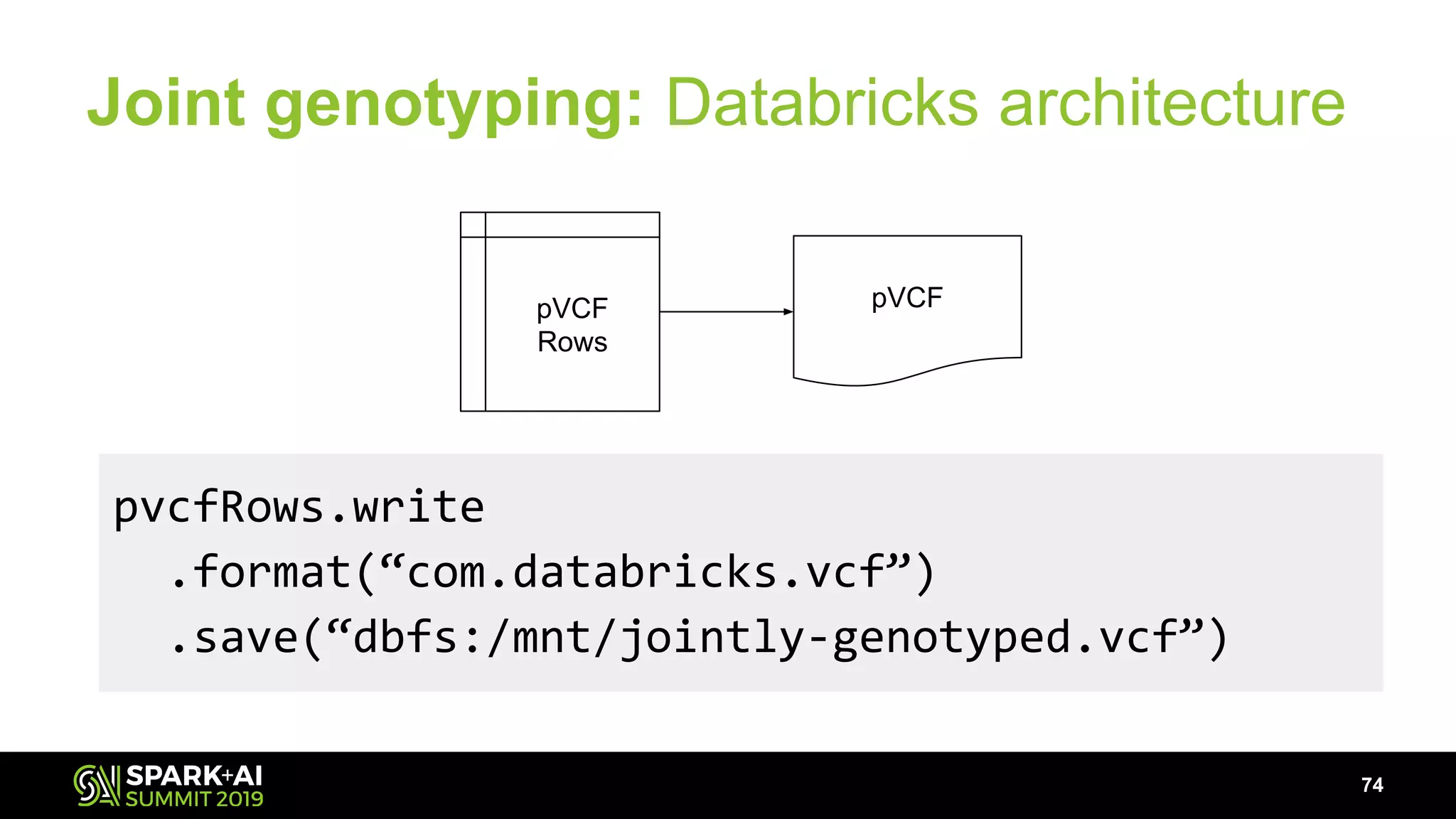
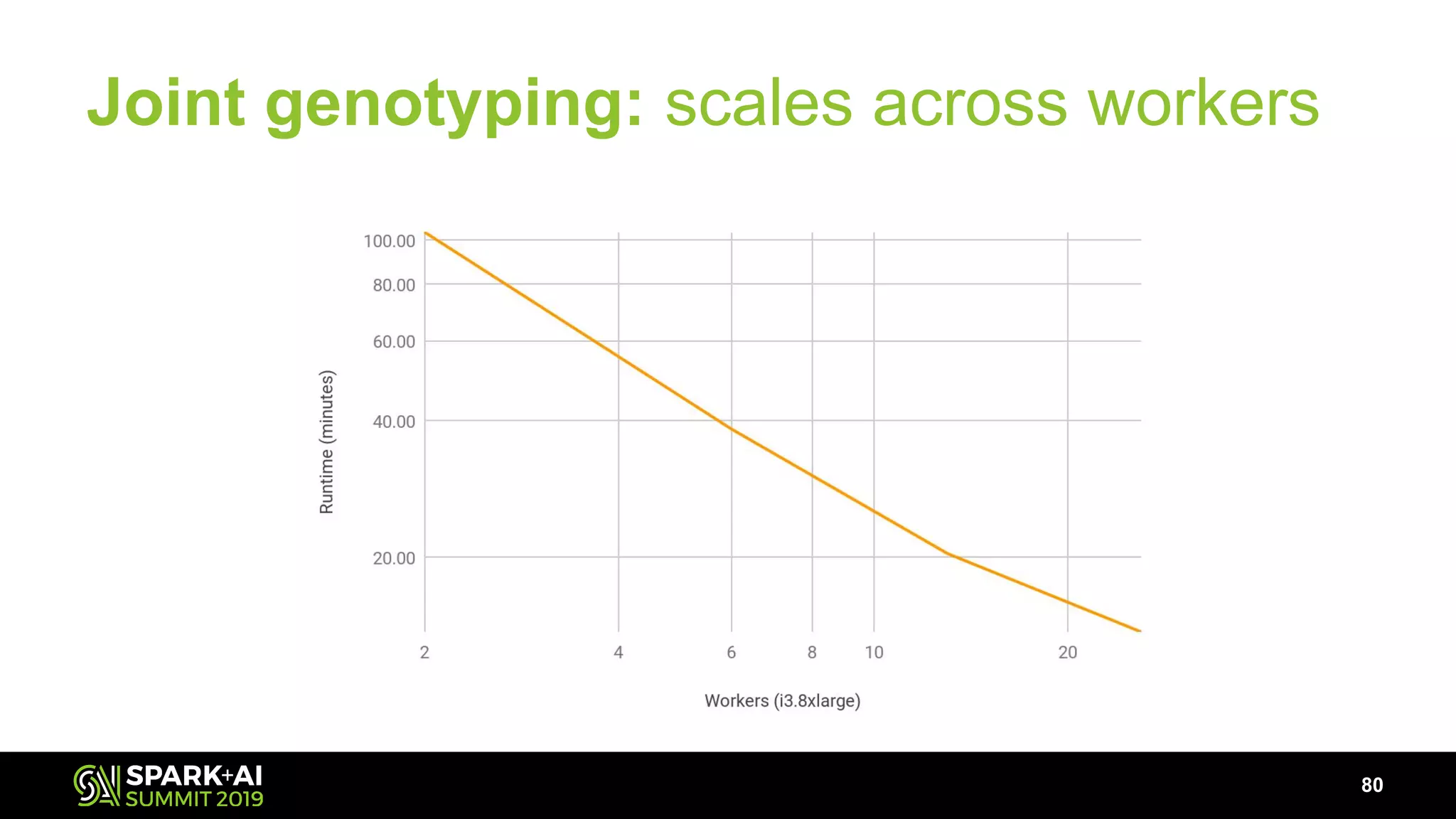
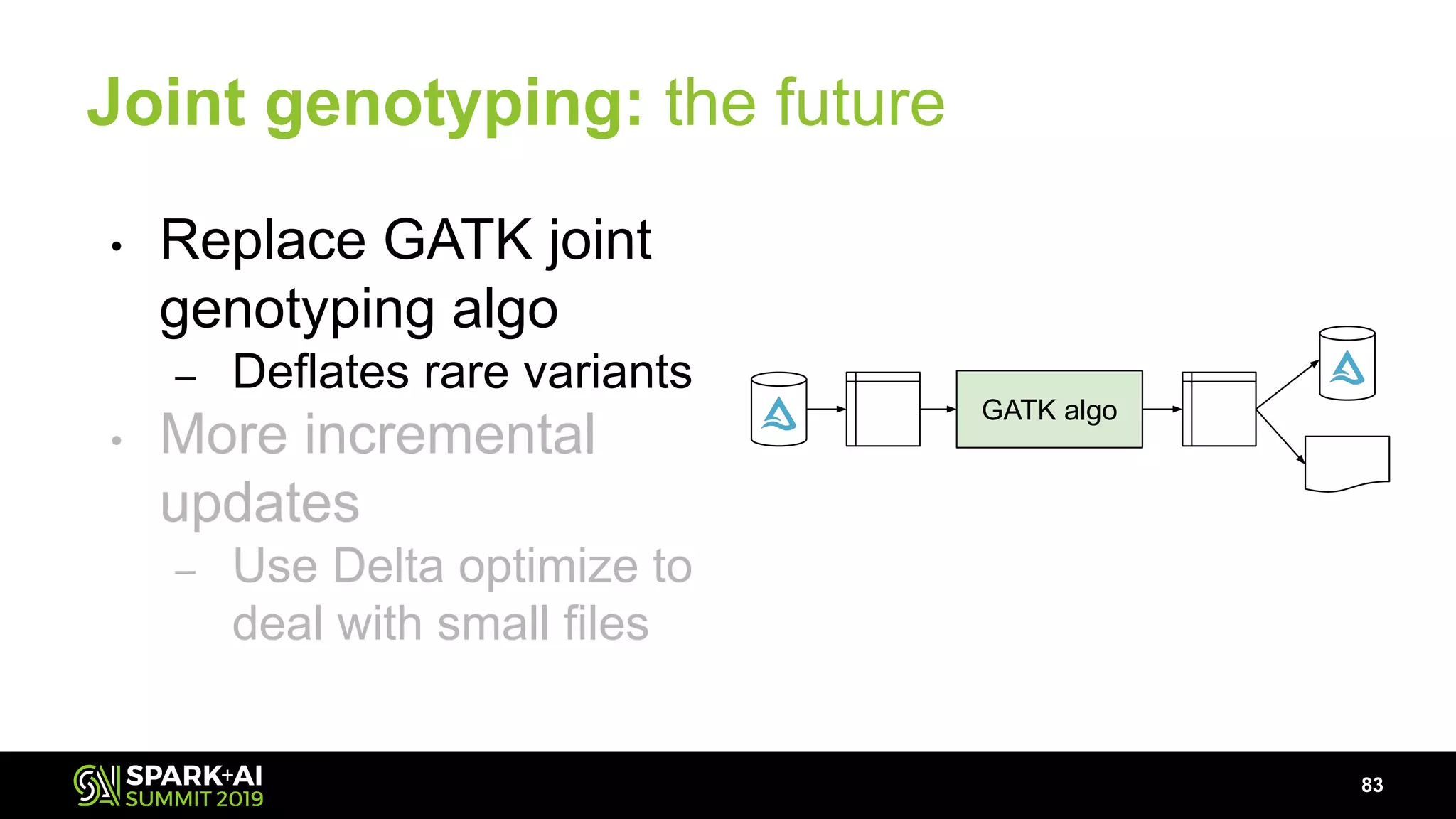
The document discusses advancements in genomics and healthcare, highlighting the case of a 6-year-old boy who was cured of a rare genetic condition through genomic sequencing and stem cell transplantation. It explores the challenges of genomic data analysis, emphasizing the need for efficient processing techniques, particularly using Databricks for joint genotyping. The presentation outlines the potential of big genomic data to accelerate drug discovery, optimize treatment, and reduce healthcare costs.