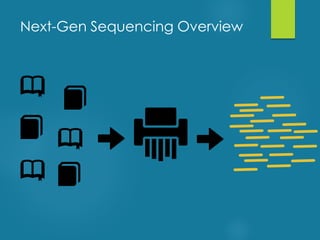
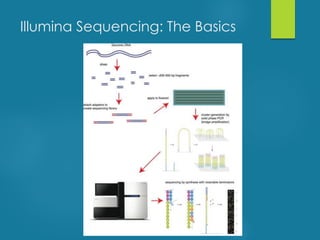
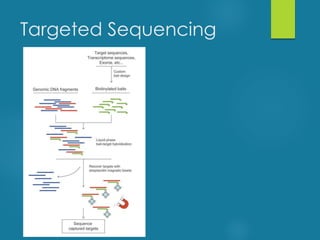
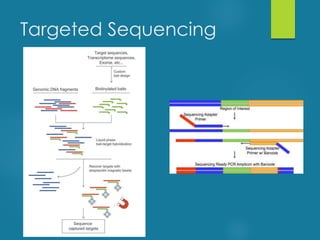
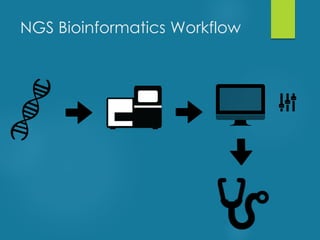
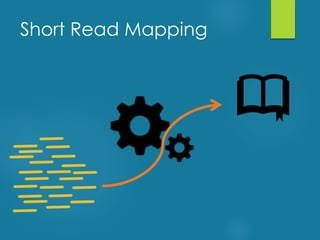
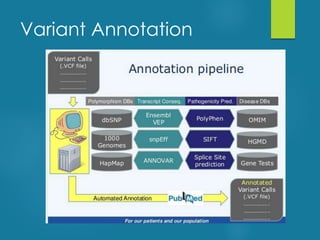
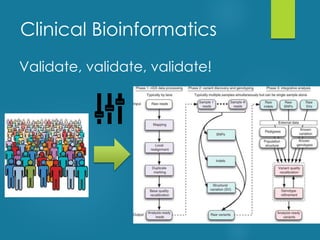
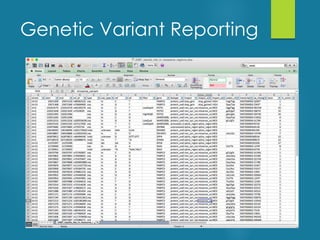
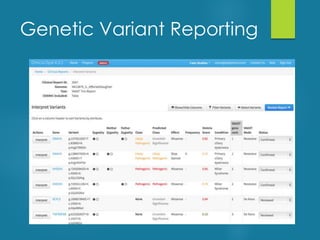
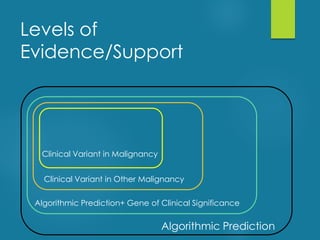
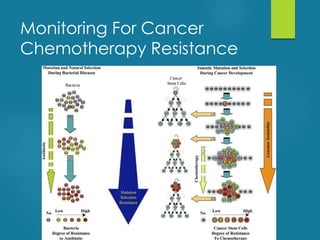
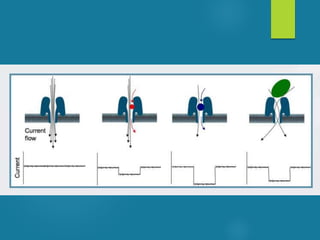
This document discusses next-generation sequencing and its applications in genomics and pathology. It begins with an overview of common NGS terms and technologies. It then covers the typical NGS analysis workflow including quality control, mapping reads to a reference genome, variant calling and annotation. Challenges such as data storage, sharing and reporting are also addressed. The document concludes that clinical sequencing is becoming established but requires ongoing collaboration between pathologists, geneticists and bioinformaticians to realize its potential.