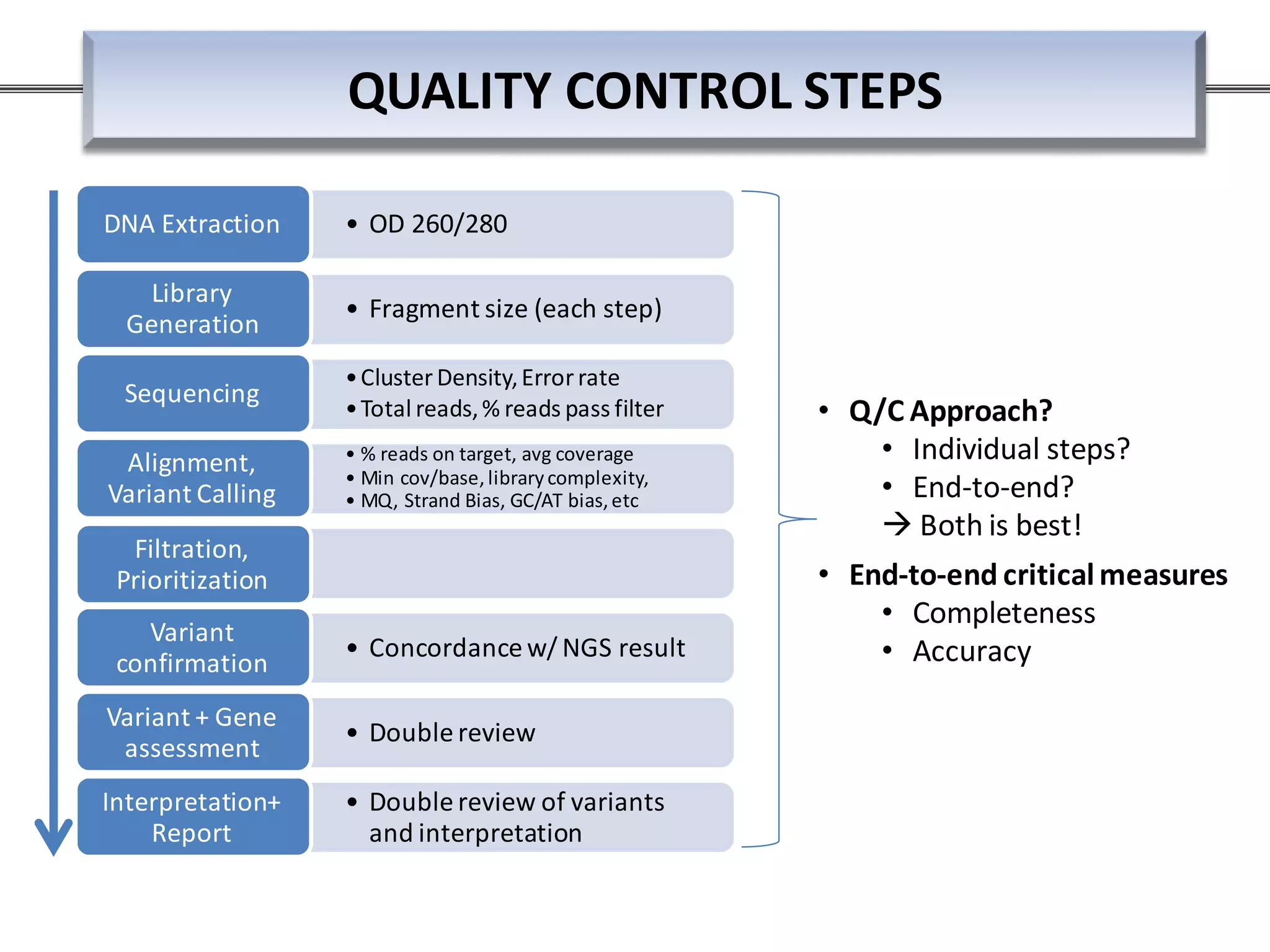
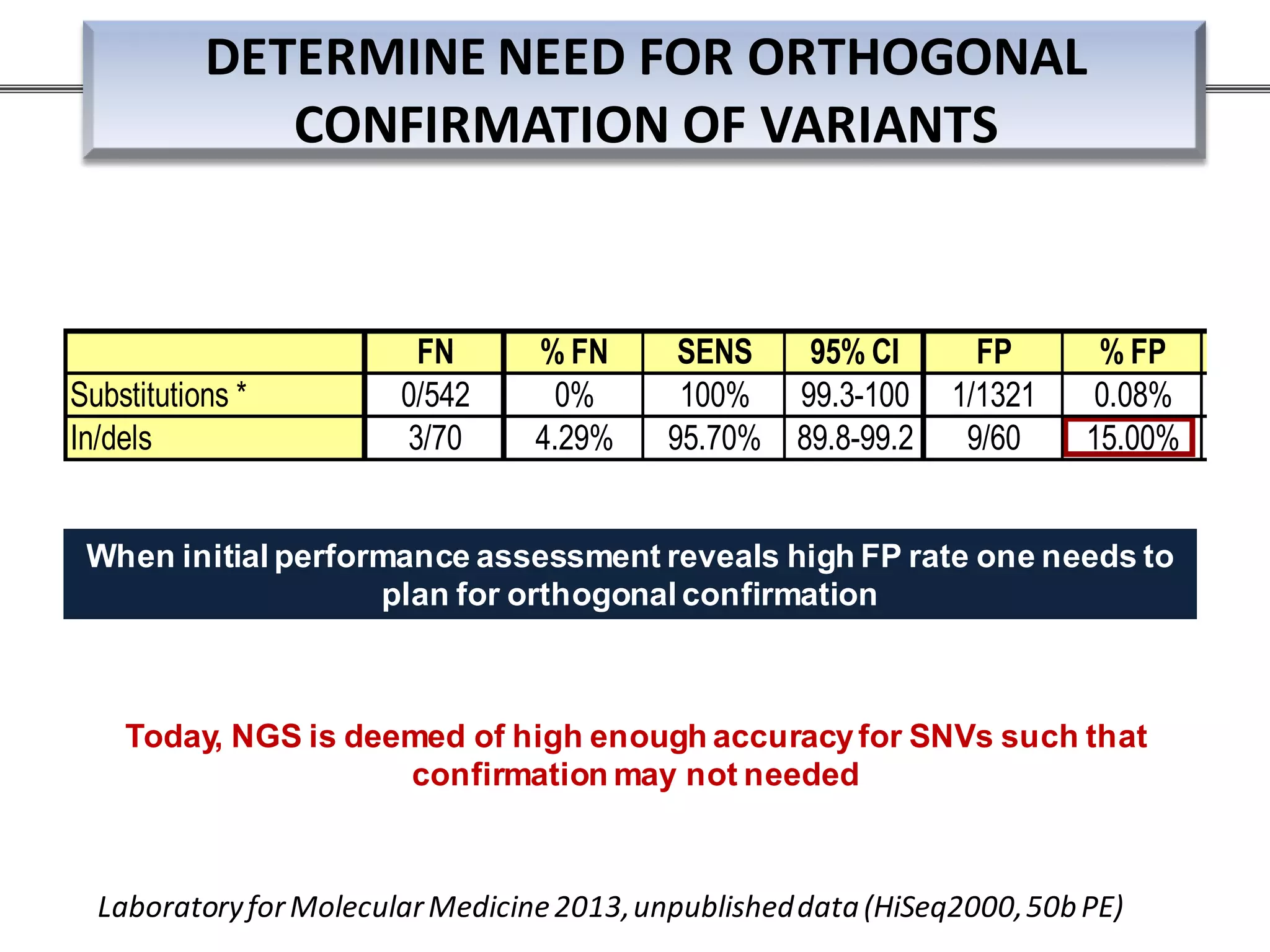
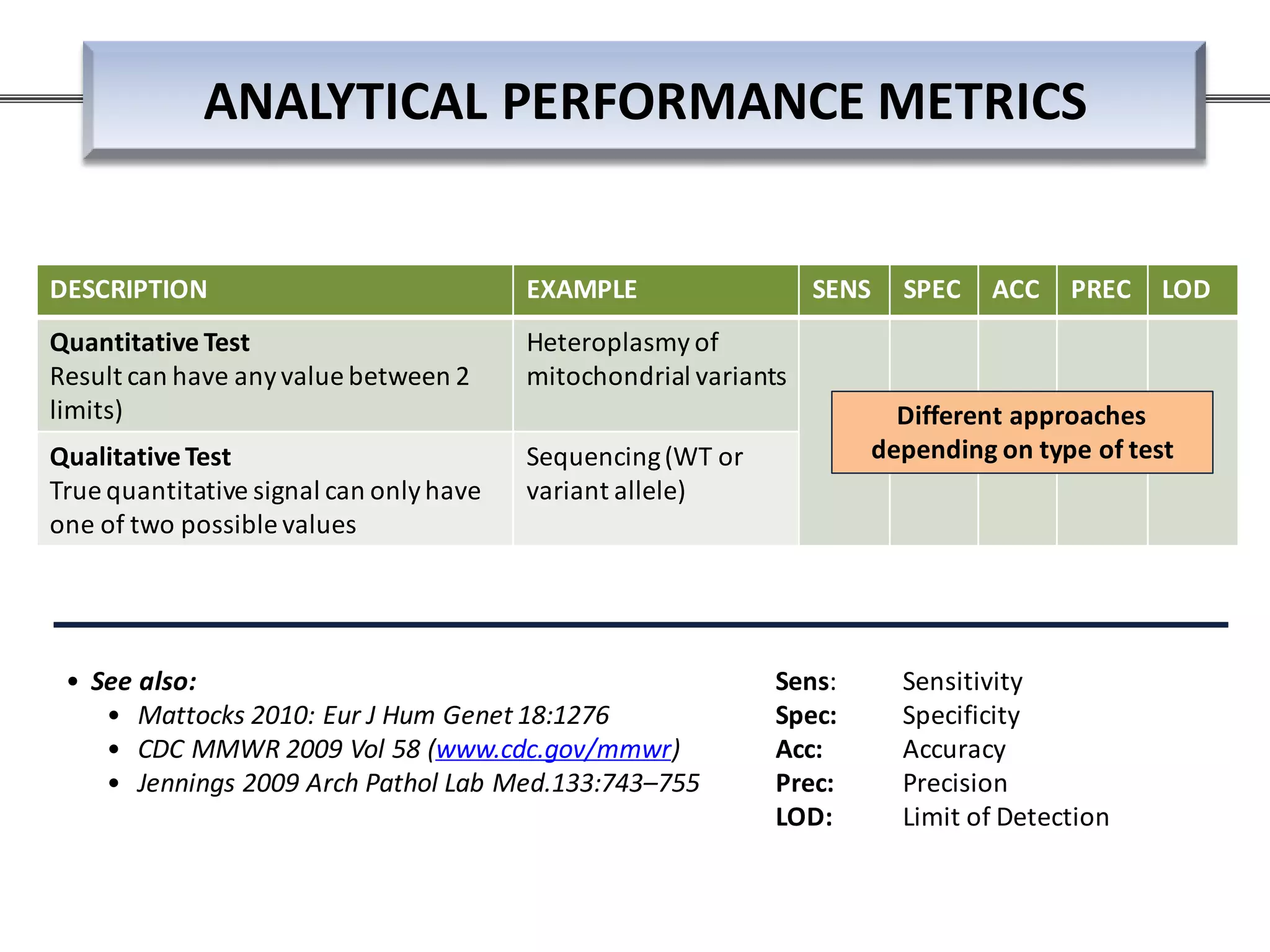
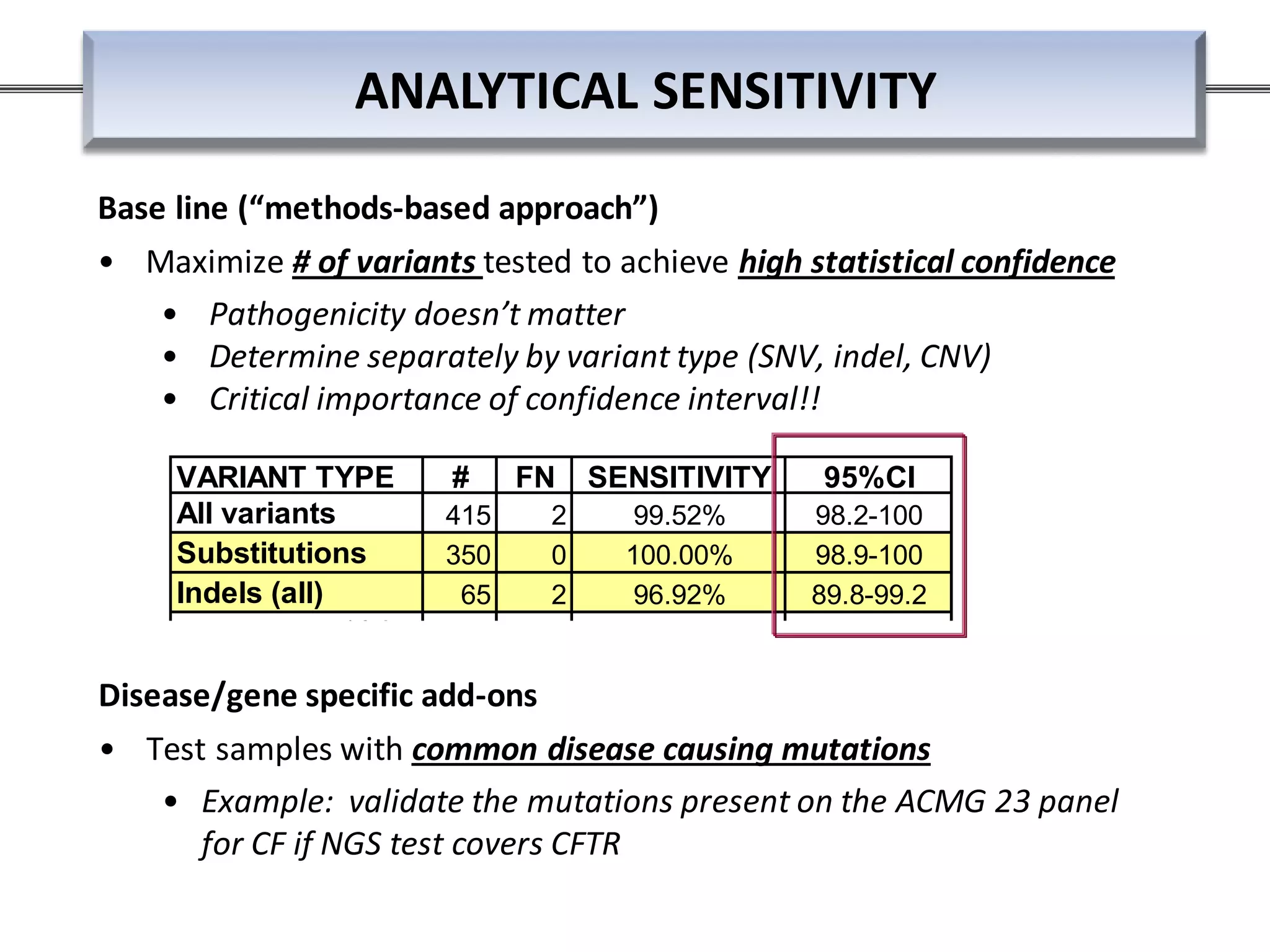
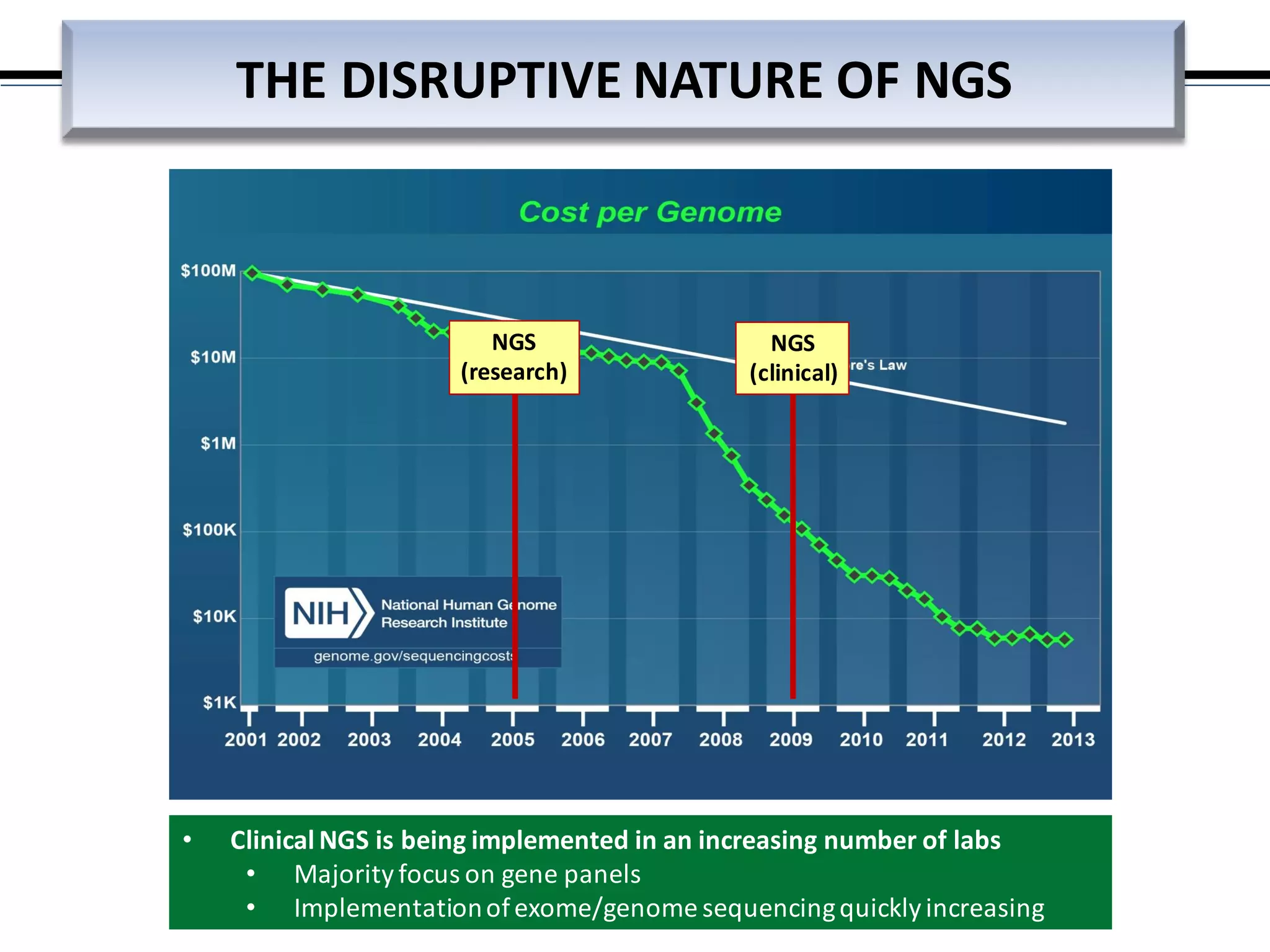
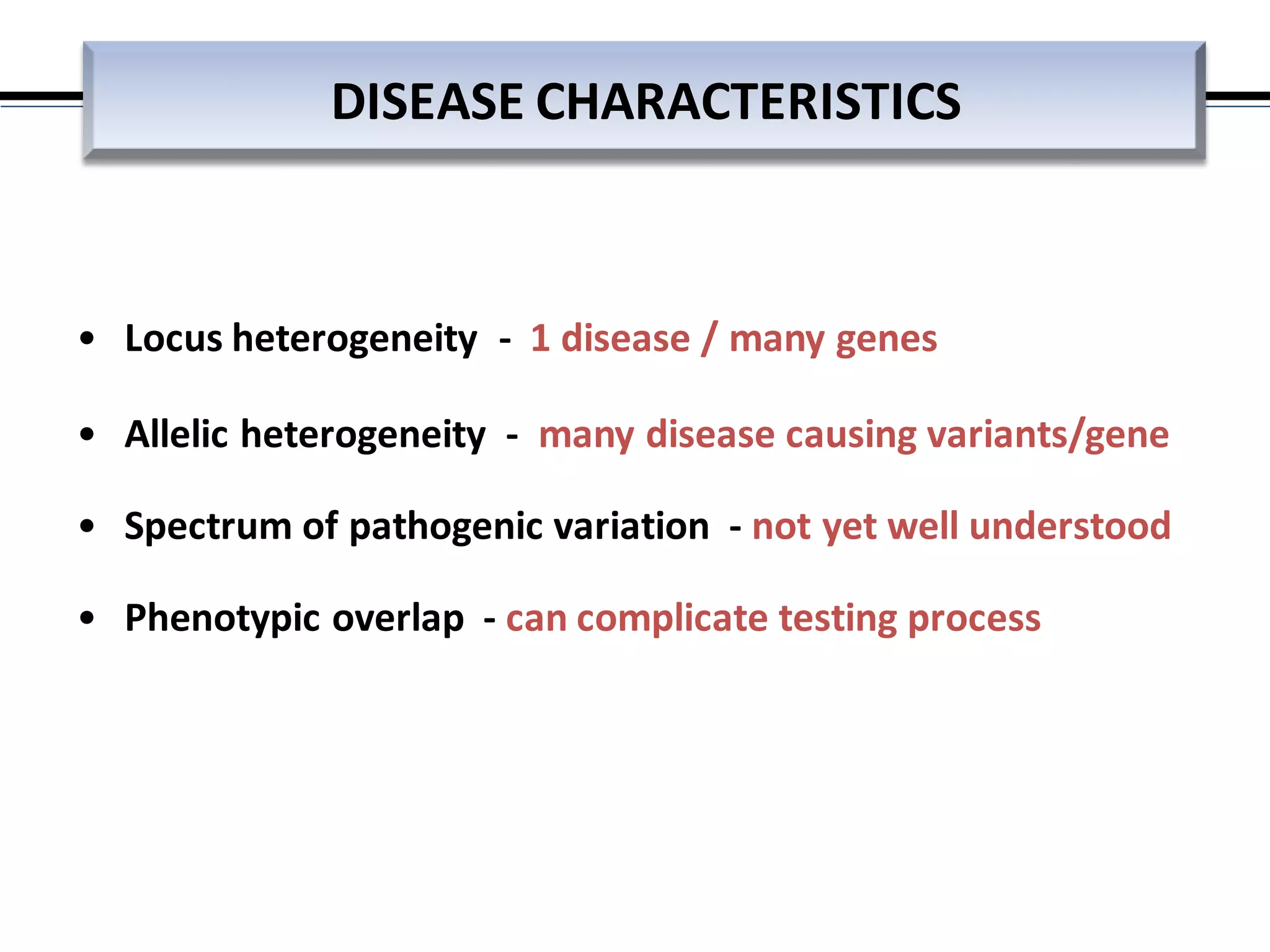
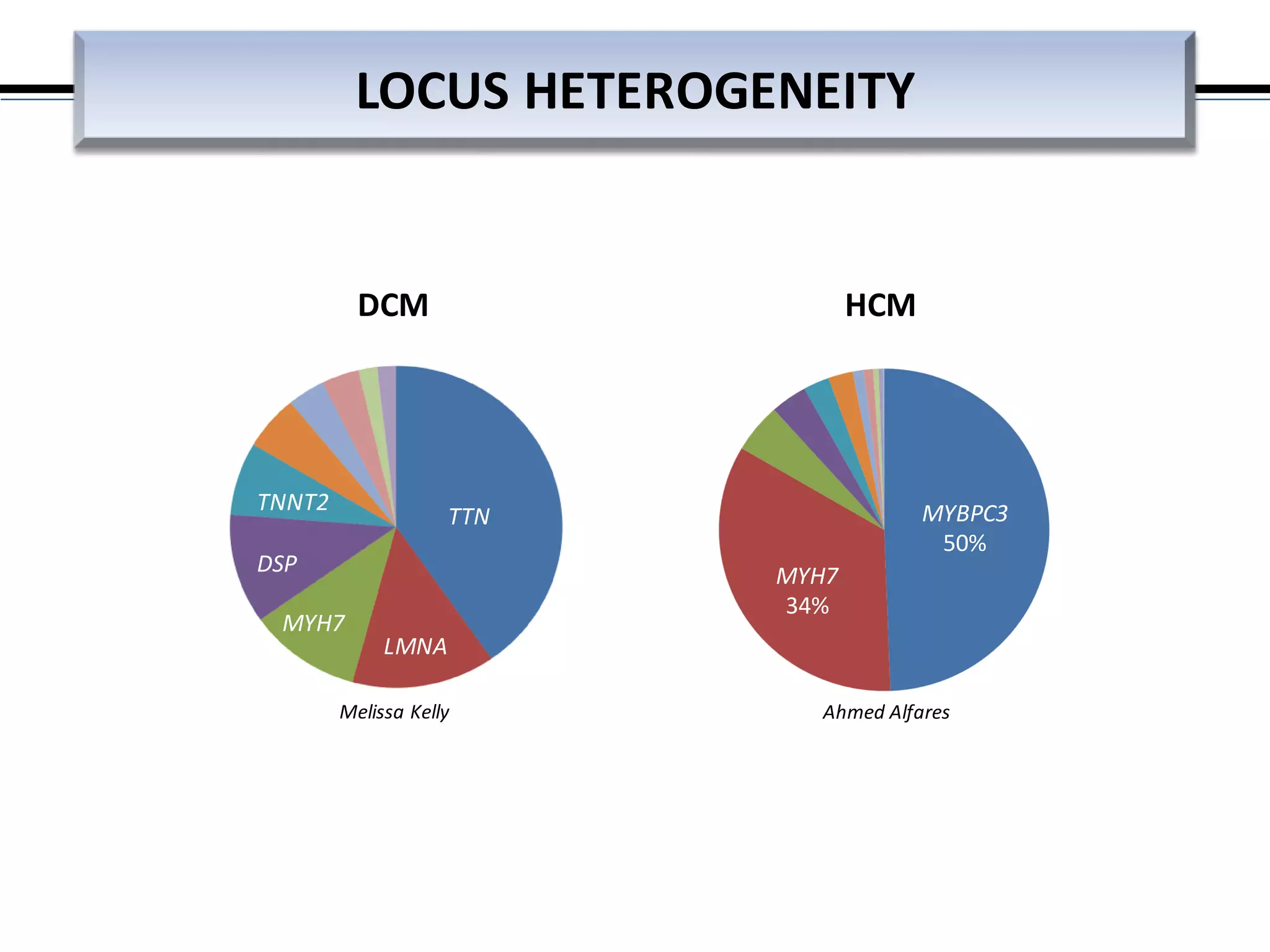
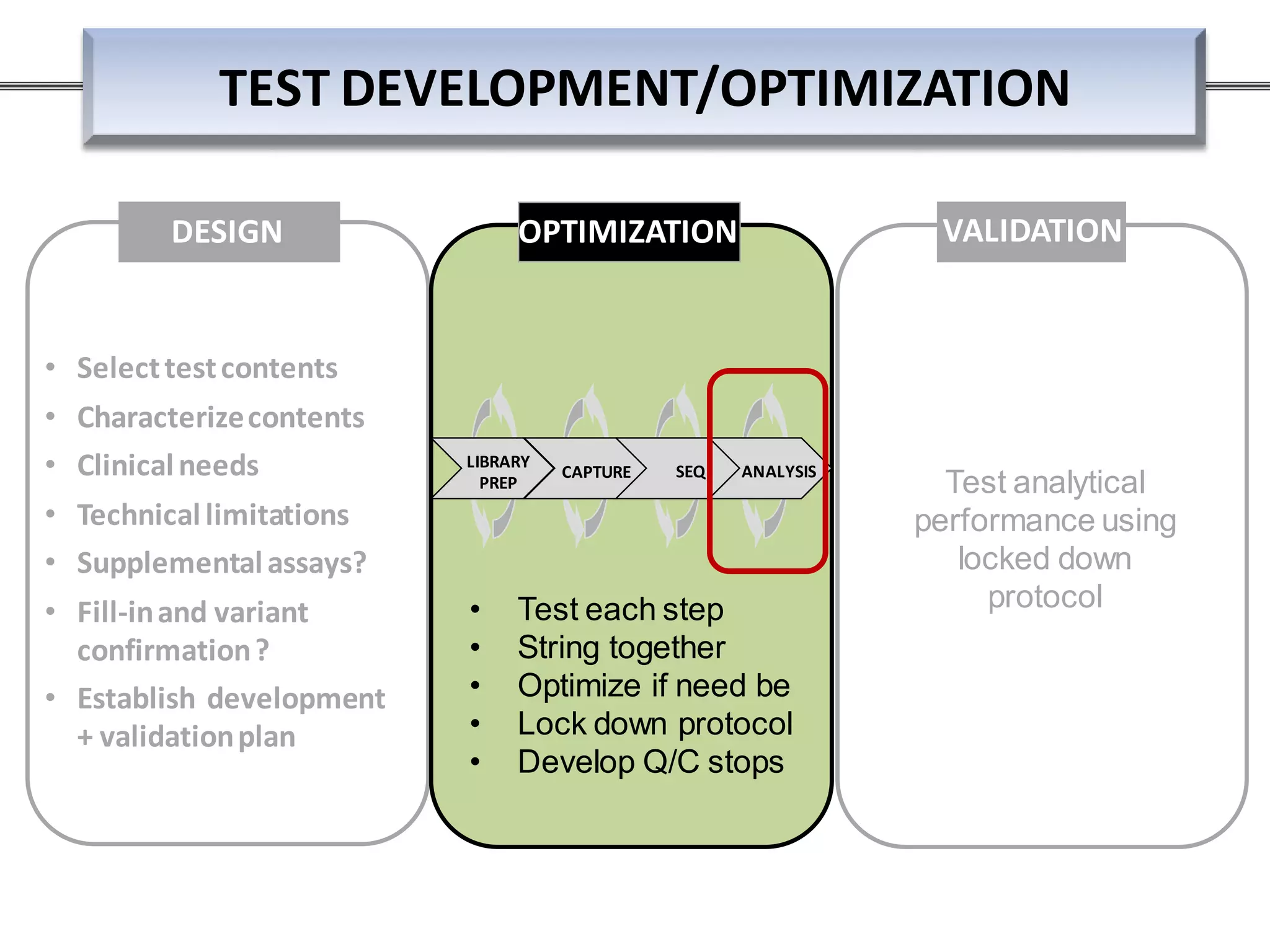
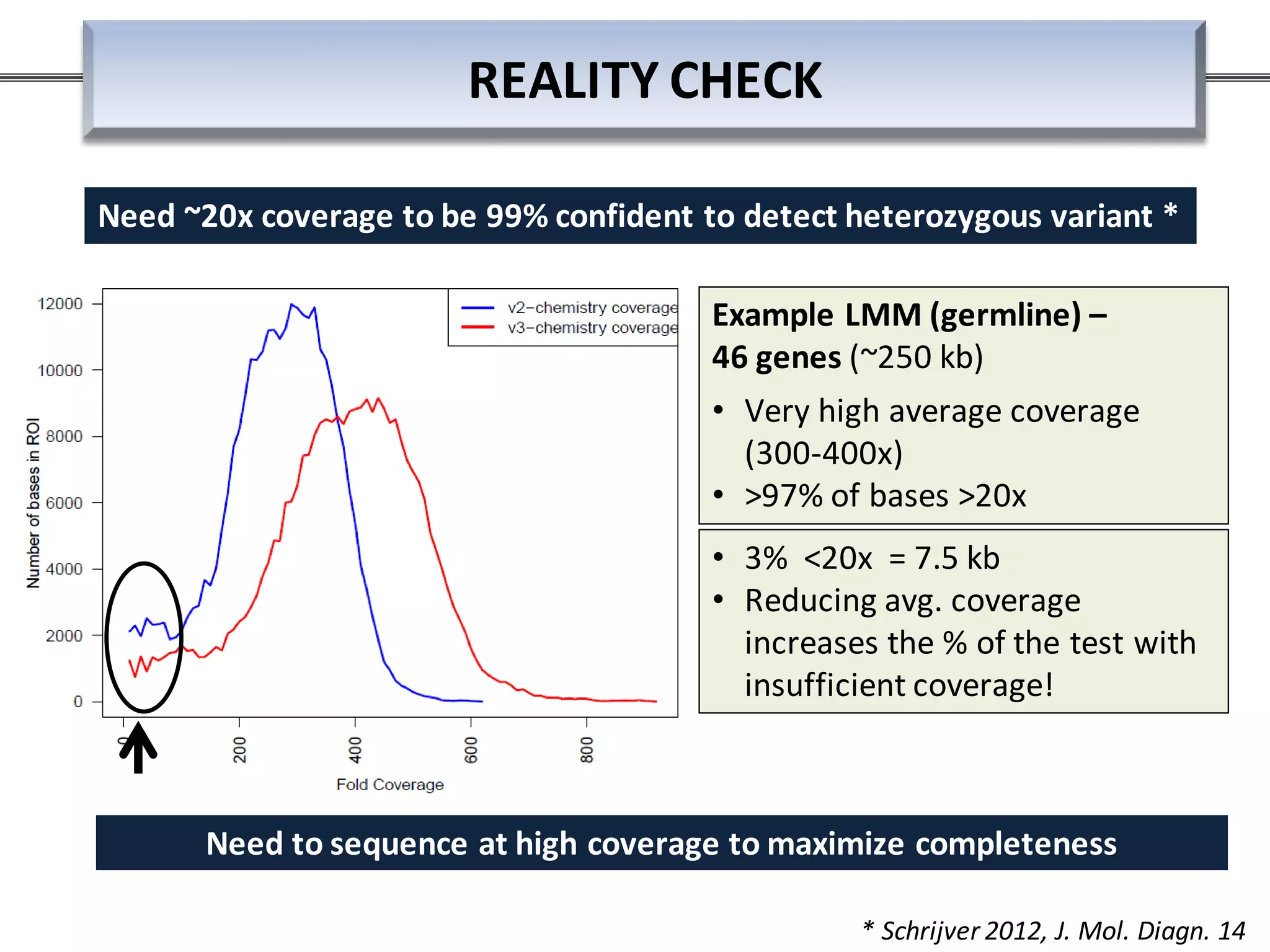
This webinar discussed the implementation and impact of next-generation sequencing (NGS) in clinical settings, focusing on its use for inherited disorders and gene panels. It addressed the complexities of NGS, including technical limitations, the importance of bioinformatics, and challenges related to variant interpretation. The presentation emphasized the need for improved testing workflows and standards within the genomics community to enhance clinical diagnostic accuracy.





















![TTN_EX155
c.31709T>C
[SB= -10.01]
TTN_EX45A
c.15318T>C
[SB= -146.03]
TTN_EX157
c.31861A>G
[SB= -855.52]
LMNA_EX10
c.*4C>T
[SB= -106.6]
TAZ_EX10
c.718G>C
[SB= -3536.45]
TTN_EX37
c.8887A>C
[SB= 8.04]
TTN_EX37
c.8887A>C
[SB= 14.07]
TTN_EX37
c.8887A>C
[SB= 17.08]
HOM
HET
203 samples; n=1455 variants: NGS + Sanger TRUE POS FALSE POS
ANALYSIS THRESHOLDS – ALLELIC FRACTION
• Need large “truth sets”
• Until recentlythere was none labs could obtain pre-test development
• Data shown here generated from launching NGS pipeline w/o any
threshold (2011)
• very high overhead for confirmatorytesting till truth set established
via Sanger confirmation
• Now have some communityresources: NIST’s NA12878 high
confidence regions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prom-9440-001ngsintheclinicbirgitfunkeqiagenslidedeckwebinar01-160420151031/75/NGS-in-Clinical-Research-Meet-the-NGS-Experts-Series-Part-1-35-2048.jpg)