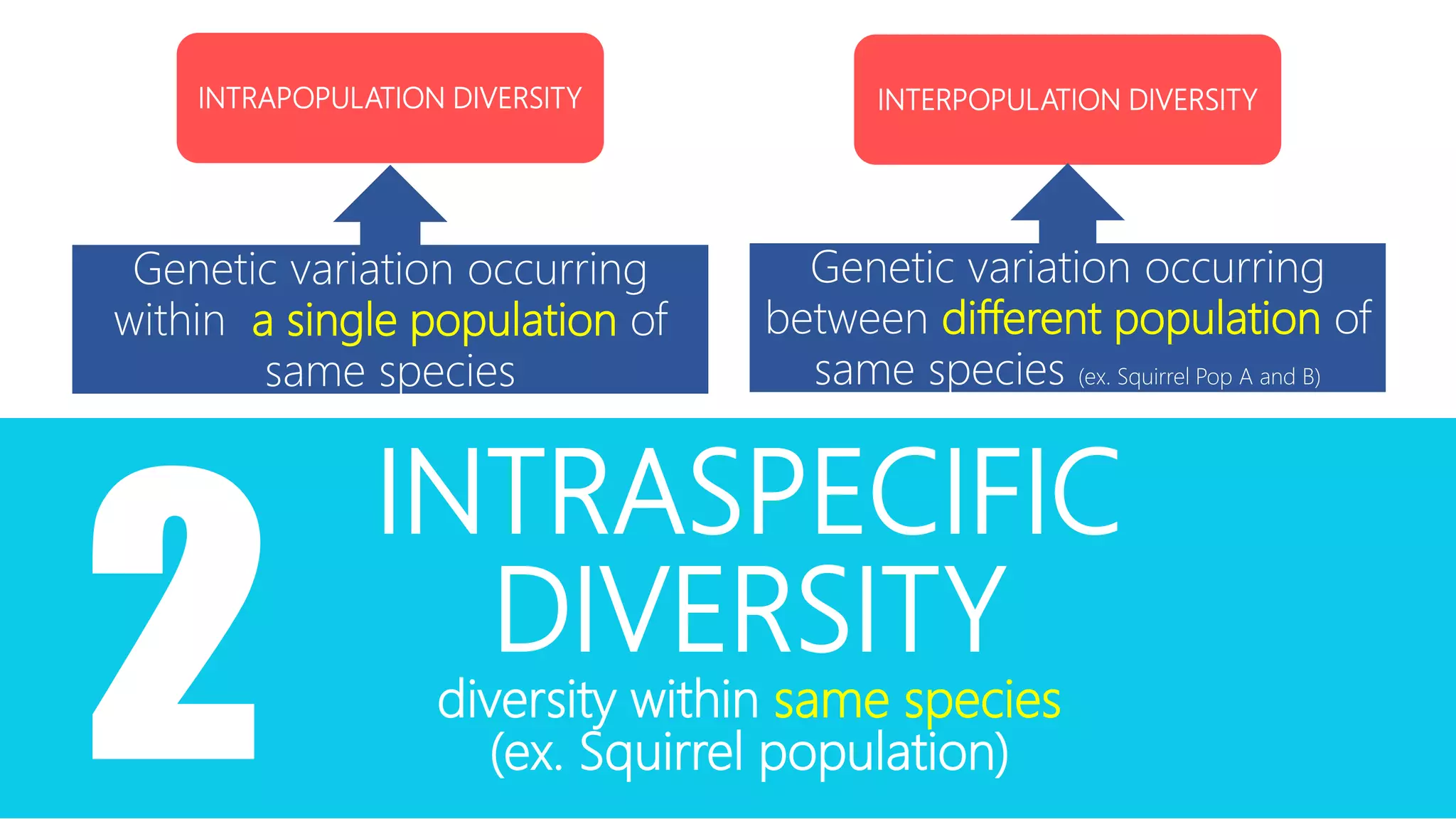
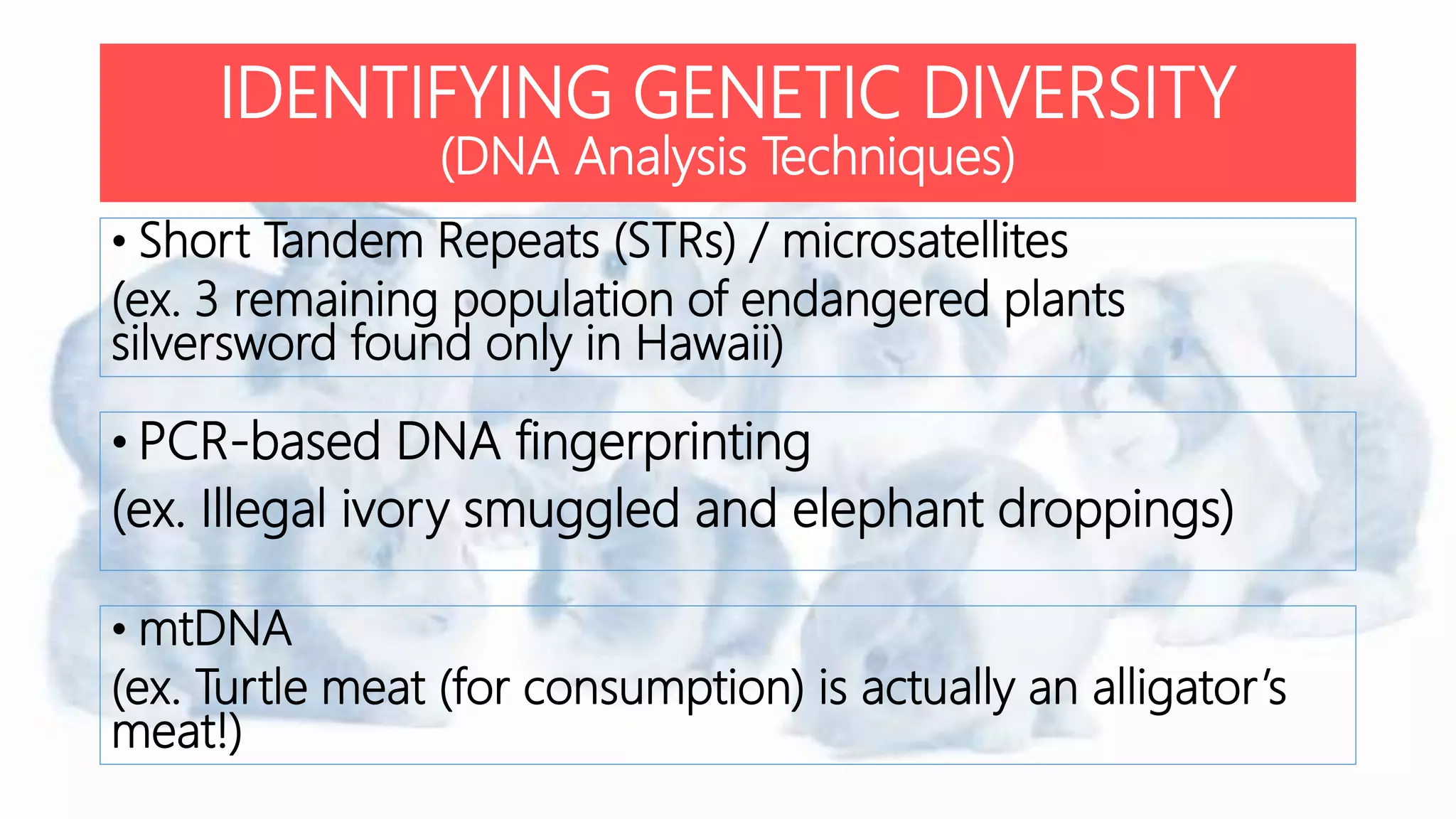
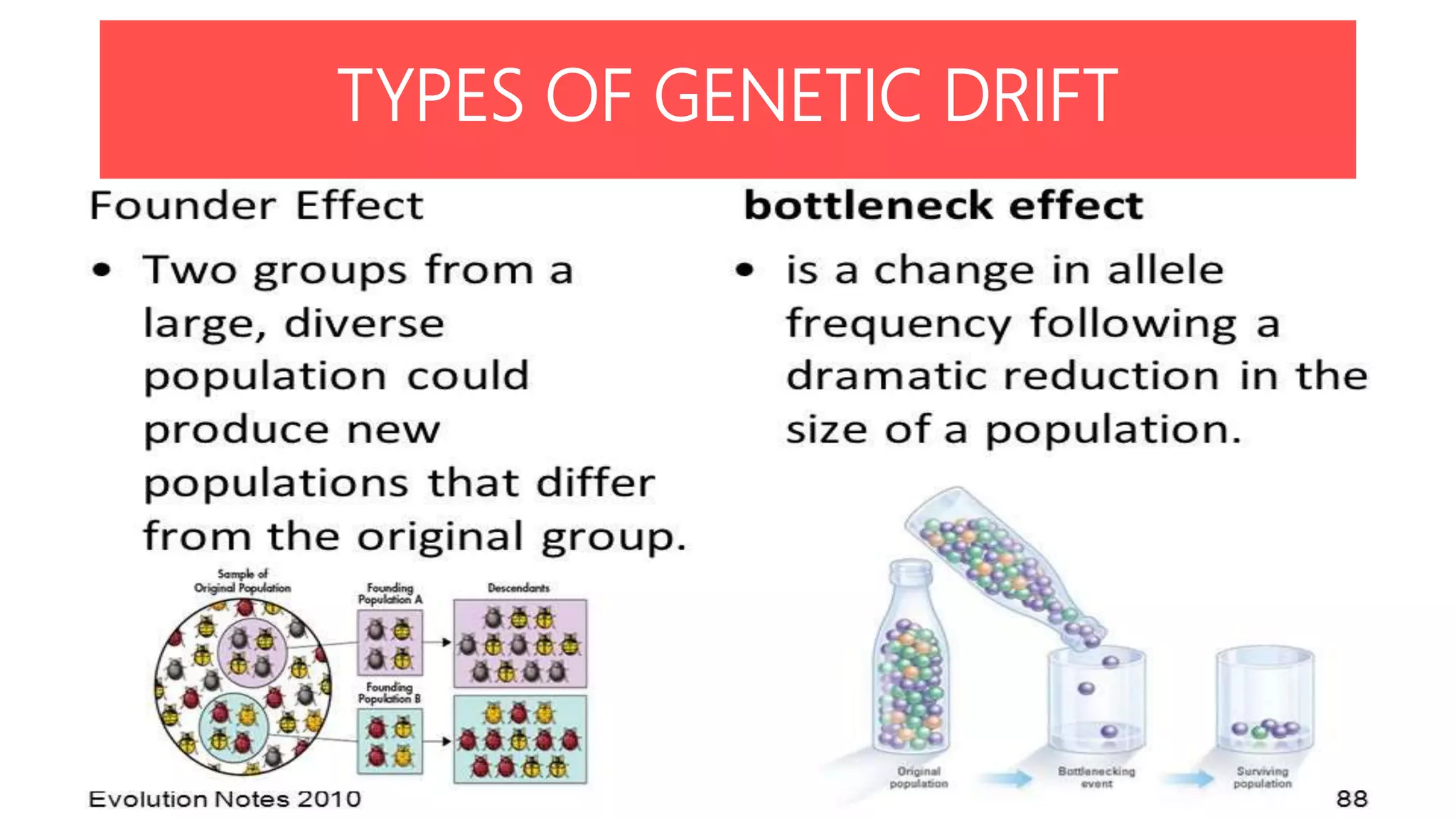
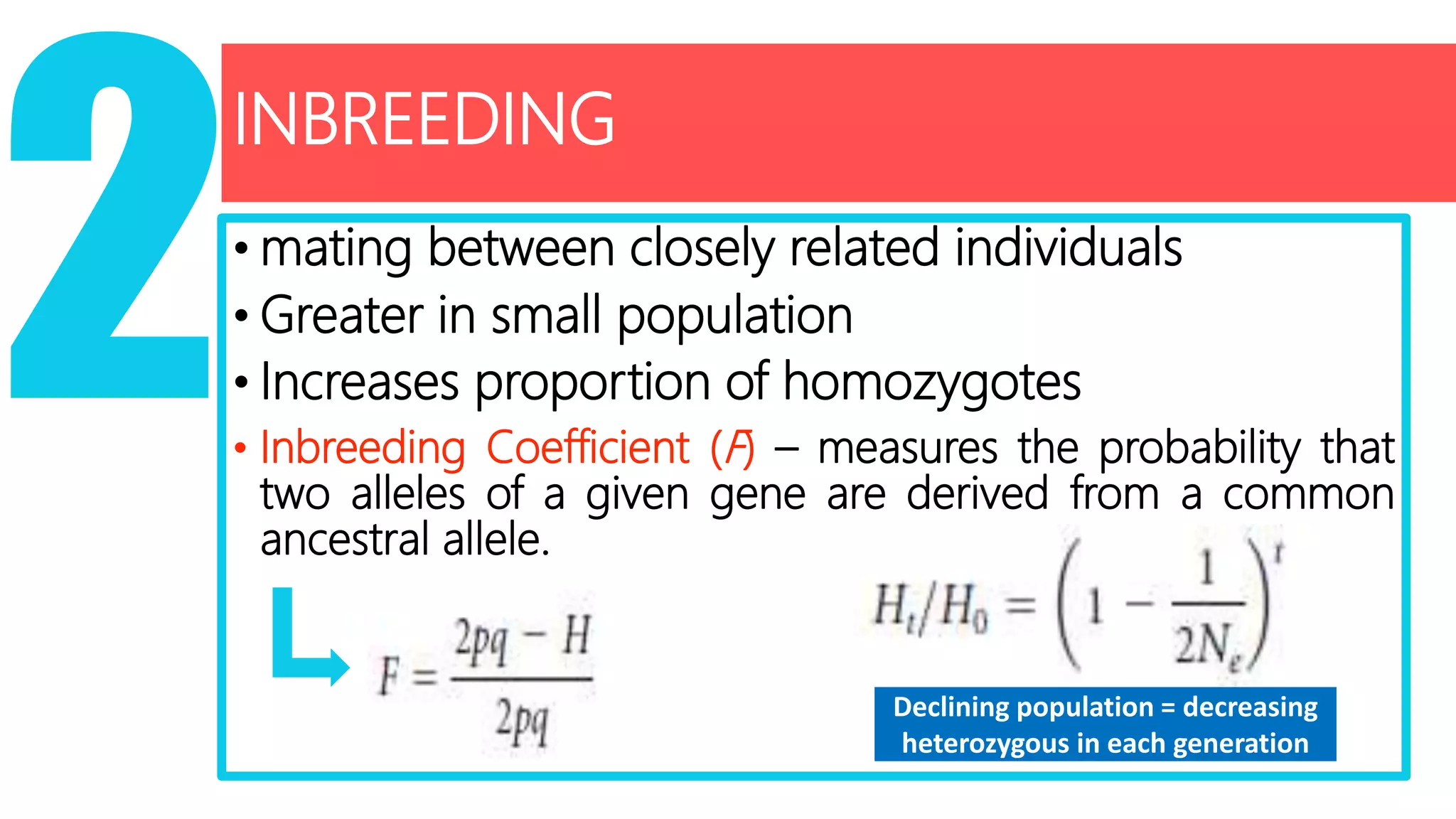
Conservation genetics applies genetic methods to preserve biodiversity and avoid species extinction. It studies levels of genetic diversity within and among populations and species. Small, isolated populations are vulnerable to loss of diversity through genetic drift, inbreeding, and reduced gene flow. Ex situ conservation involves captive breeding programs and gene banks, while in situ conservation preserves species in their natural habitats through parks and reserves. Population augmentation also aims to boost small populations but risks outbreeding depression if not done carefully. Conservation genetics uses an interdisciplinary approach to understand and preserve genetic diversity in threatened species.