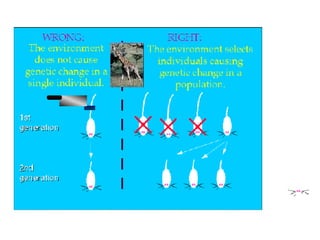
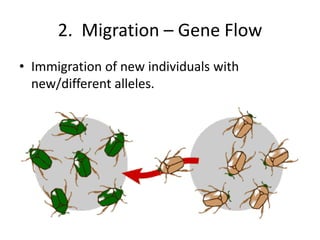
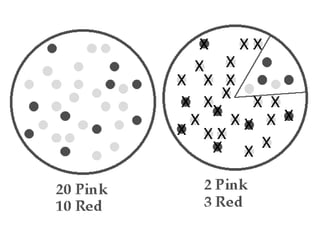
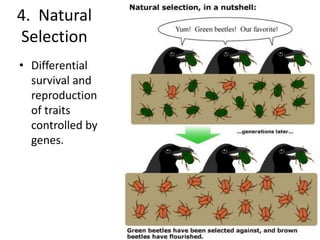
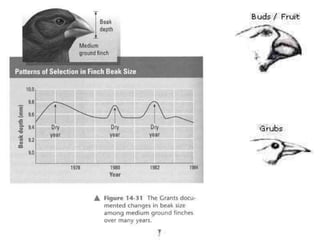
This document discusses key concepts relating to genes, variation, and evolution. It defines evolution as any change in the relative frequency of alleles in a population's gene pool over time. Allele frequencies can change due to mutations, migration, genetic drift, and natural selection. For a population to maintain genetic equilibrium without evolving, it must meet five conditions of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium: random mating, large population size, no gene flow, no mutations, and no natural selection. Isolation through geographic or behavioral means can lead to the formation of new species through speciation over long periods of time.

![In the 1930’s, evolutionary biologists began to connect Mendel’s work to Darwin’s theory.With the discovery of DNA’s structure in 1953 by Watson and Crick, the gene became the focus of evolution. [Scientists began speaking about evolution in genetic terms.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genesandvariation-100504125710-phpapp02/85/Genes-And-Variation-2-320.jpg)