This document discusses several key concepts related to the occurrence and mechanisms of evolution:
1. It outlines Jean Baptiste de Lamarck and Charles Darwin's influential theories of evolution, including Lamarck's theories of need, use and disuse, and acquired characteristics as well as Darwin's theory of natural selection.
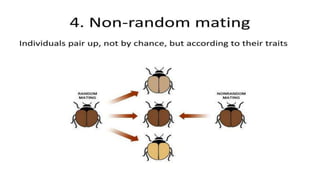
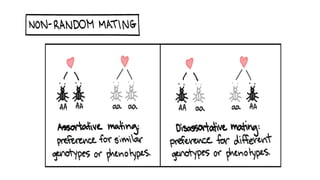
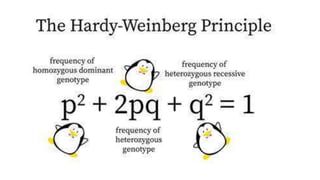
2. It explores the genetic basis of evolution through concepts like population genetics, gene flow, allele frequencies, non-random mating, and the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
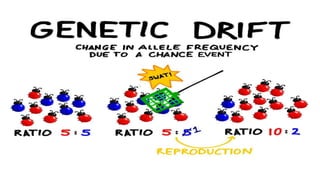
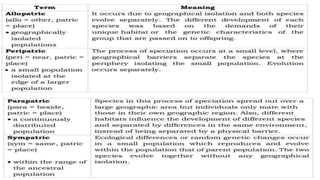
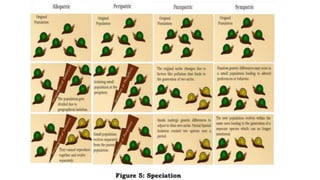
3. It examines various evolutionary patterns such as natural selection, genetic drift, speciation, punctuated equilibrium, microevolution, coevolution, convergent evolution, and adaptive radiation.