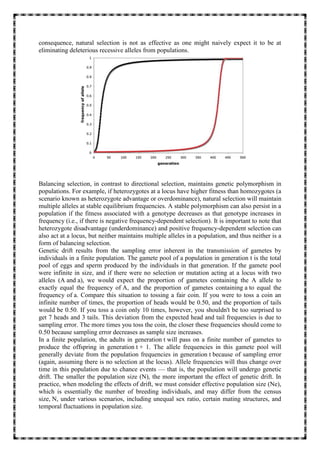
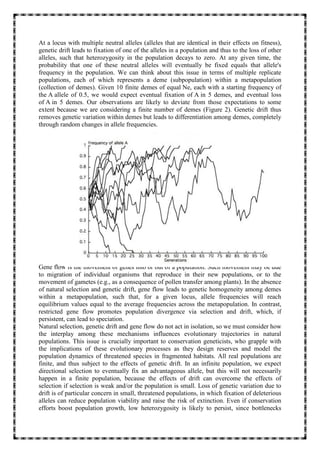
1. The document discusses five key evolutionary mechanisms: mutation, genetic drift, gene flow, non-random mating, and natural selection. Each mechanism affects traits and genetic diversity in a population differently.
2. Mutation introduces new genetic variation, while genetic drift causes random changes in allele frequencies regardless of fitness. Gene flow makes populations more similar by exchanging migrants. Non-random mating results from mate choice.
3. Natural selection occurs when some genotypes are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on alleles to the next generation. It can drive directional evolution of traits or maintain genetic diversity through balancing selection.