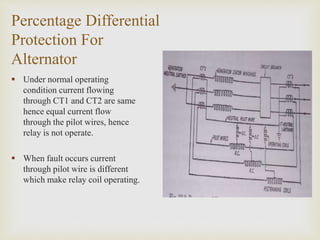
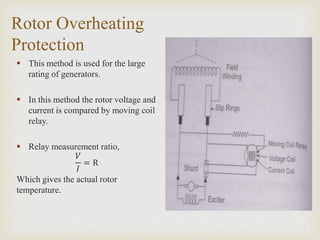
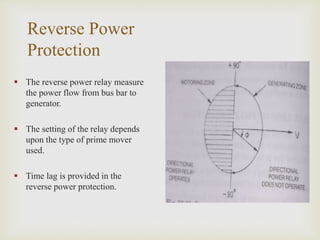
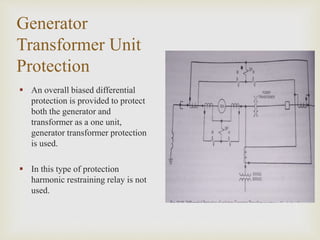
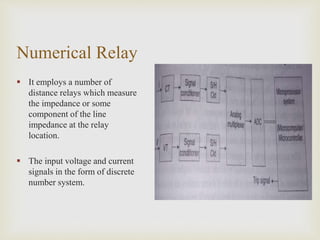
The presentation by Mr. Chetan Patil discusses various generator protection methods, including percentage differential protection, restricted earth fault relay, rotor overheating protection, and several others designed to ensure generator safety. It outlines the functions of each protective relay and their operational principles under different fault conditions. The document emphasizes the importance of protection schemes to prevent equipment damage and ensure system reliability.