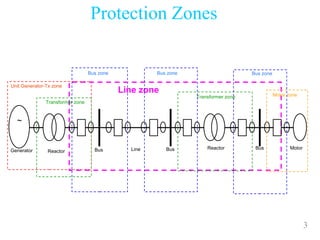
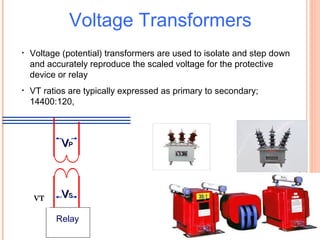
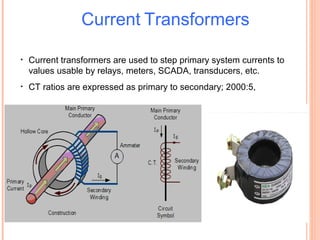
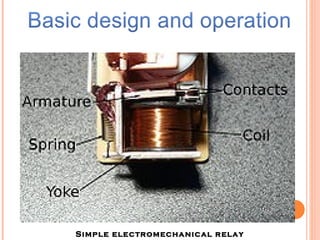
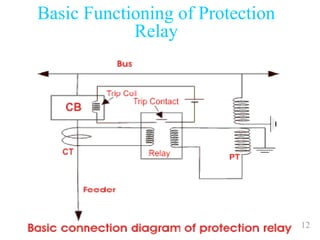
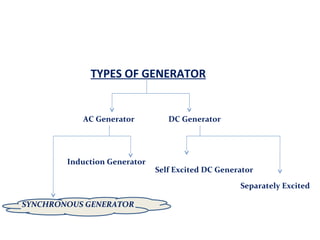
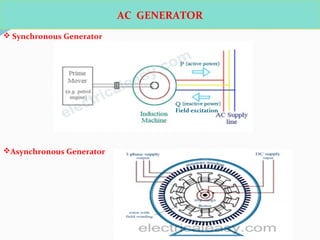
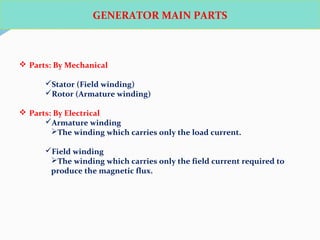
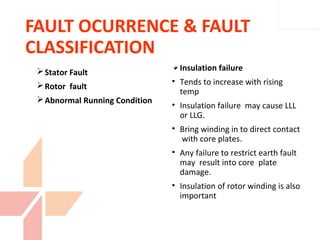
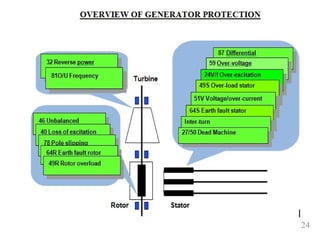
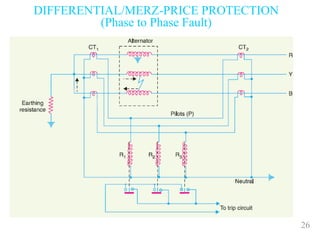
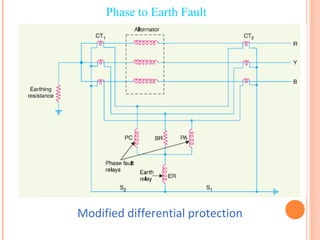
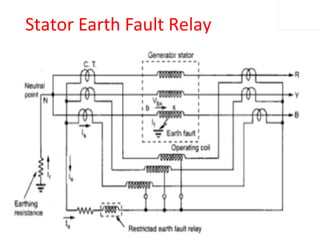
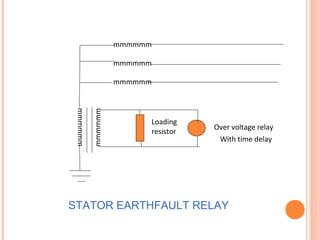
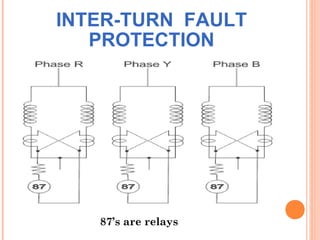
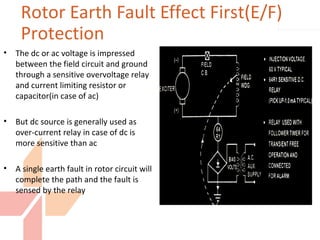
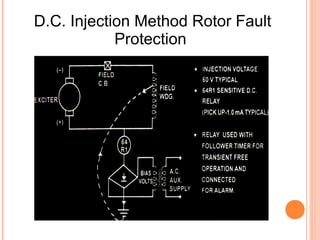
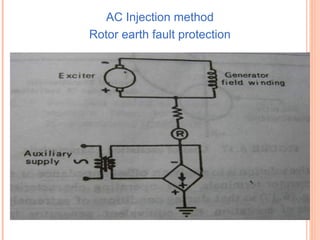
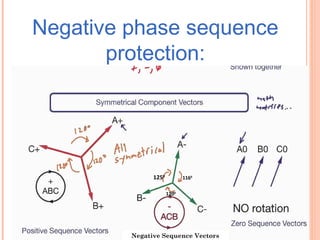
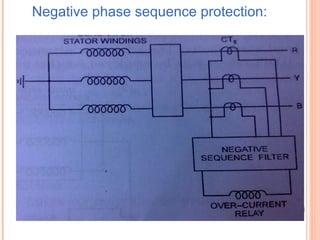
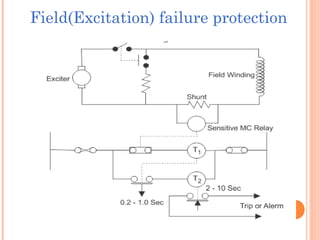
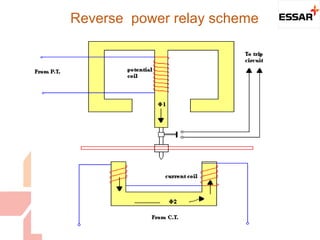
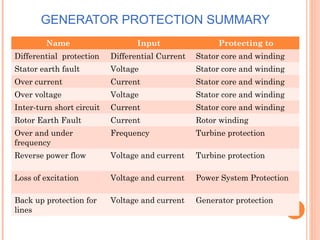
The document discusses various protection schemes for generators. It describes (1) differential protection that protects the stator winding from internal faults, (2) rotor earth fault protection that protects the rotor winding, and (3) loss of excitation protection that protects the power system from instability if the generator loses its field excitation. Various other protections discussed include overcurrent, overvoltage, temperature, and reverse power protections. The document provides details on the operating principles and components of these various generator protection schemes.