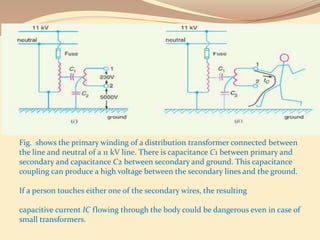
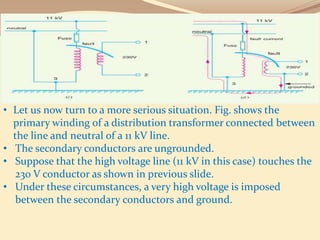
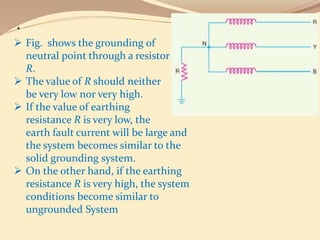
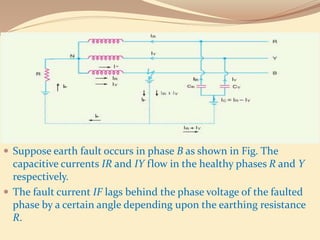
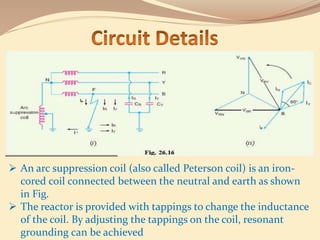
This document discusses different methods of grounding electrical systems, including solid grounding, resistance grounding, reactance grounding, and resonant groundings using a Peterson coil. Solid grounding directly connects the neutral point to earth, holding it at earth potential but allowing high fault currents. Resistance grounding limits fault current by connecting through a resistor. Reactance grounding uses an inductor instead of resistor. Resonant grounding with a Peterson coil adjusts the inductance to balance capacitive currents and prevent arcing faults.