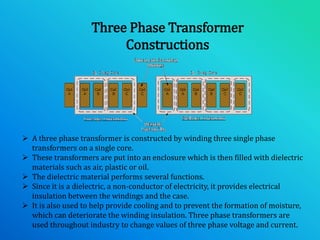
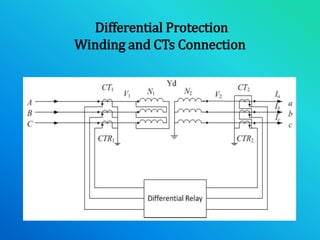
This document discusses 3-phase transformer protection. It begins with an overview and introduction to 3-phase transformer construction and connections. It then discusses differential protection, restricted earth fault protection, overcurrent protection, and protection against overheating, fire, and lightning. Differential protection and restricted earth fault protection are described in more detail. Protection methods like Buchholz relays and pressure relief valves that protect against incipient faults are also explained. The document emphasizes that transformers are critical and expensive components that require proper protection methods to ensure uninterrupted and efficient operation.