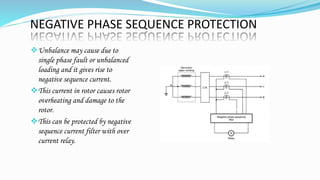
Generators require protective systems to quickly clear faults and ensure continuous power supply. This document discusses different generator faults like stator and rotor winding faults. It describes protection schemes for generators like differential protection, biased circulating current protection, and rotor earth fault protection. Differential protection uses two sets of current transformers to detect differences between currents at each end of a protected section during a fault. Rotor earth fault protection uses a sensitive relay connected across the rotor circuit through a high resistance or injection method to detect earth faults. Loss of excitation protection and negative sequence protection are also discussed to prevent overheating during unbalanced faults or loss of excitation. Protective devices are important to detect faults, notify maintenance, and disconnect faulty elements to maintain safety and continuous operation