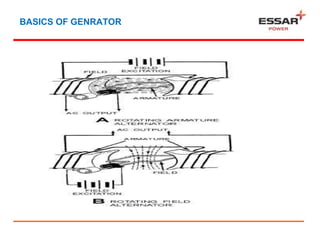
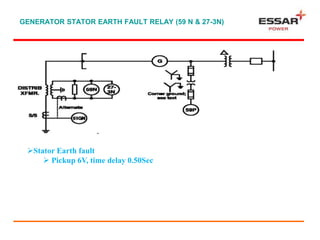
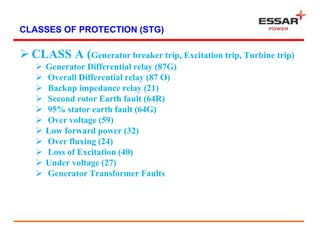
This document discusses the main components and construction of generators, how generators produce power, and generator protection systems. It describes the rotor, stator, and other main generator parts. It explains how generators work using the principle of electromagnetic induction. It then discusses various electrical, system, and mechanical faults that can occur in generators. Finally, it provides details on primary, backup, and different classes of protection systems for generators, including differential protection, earth fault protection, loss of excitation protection, and more.