This document provides an introduction to magnetic circuits, including key definitions:
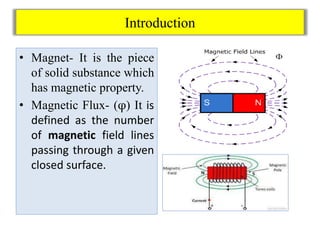
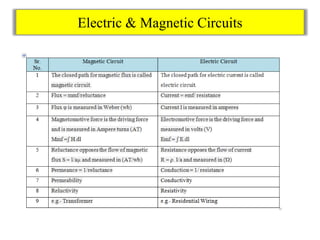
- Magnet provides magnetic property, magnetic flux is the number of field lines passing through a closed surface.
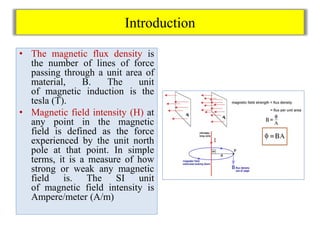
- Magnetic flux density B and field intensity H are defined, with units of tesla and ampere/meter respectively.
- Magneto motive force (MMF) is the force that causes flux to flow, measured in ampere-turns. Reluctance is the opposition to flux flow, measured in ampere-turns/weber.
- Permeance is the reciprocal of reluctance. Permeability is the ability of a material to allow flux flow.
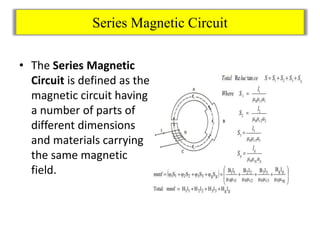
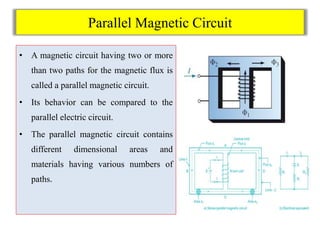
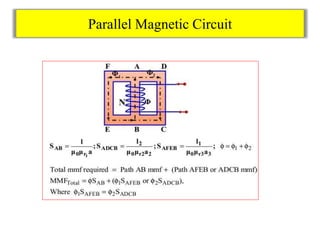
- Series and parallel magnetic circuits are discussed, behaving similarly to electric