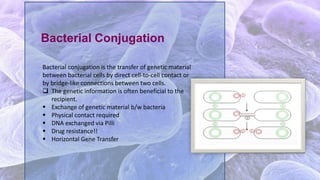
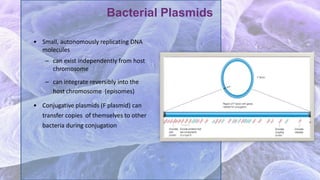
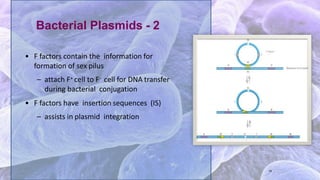
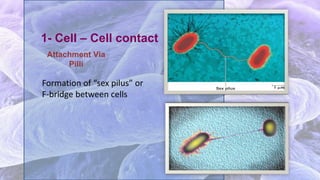
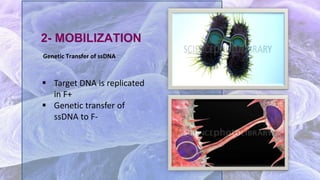
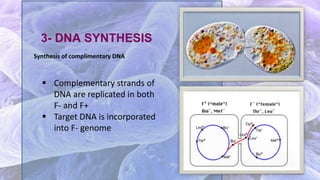
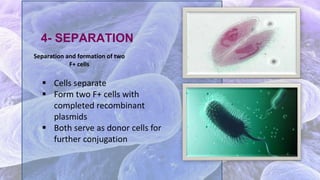
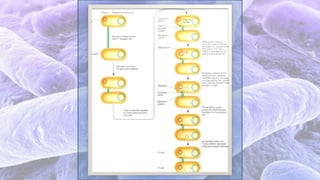
The document discusses bacterial conjugation, a process of genetic material transfer between bacteria via direct contact, specifically through the formation of a sex pilus. It outlines the roles of donor (F+) and recipient (F-) cells, the mechanisms of conjugation, and includes details on Hfr and F' conjugation types. Key points also mention the implications for genetic exchange, such as drug resistance and the nature of plasmids.