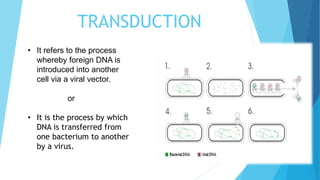
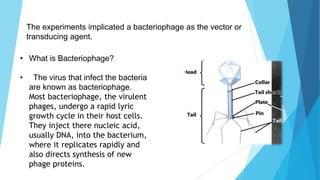
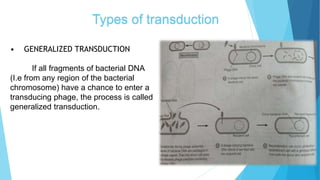
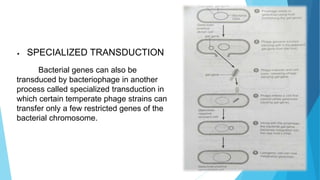
Transduction refers to the process by which DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another by a bacteriophage virus. There are two types of transduction: generalized transduction, where fragments of bacterial DNA from any region of the chromosome can enter the transducing phage, and specialized transduction, where certain temperate phage strains can transfer only restricted bacterial genes. Transduction occurs during the lytic or lysogenic cycles of bacteriophage infection and can introduce antibiotic resistance or be used by molecular biologists to introduce foreign genes into host cells.