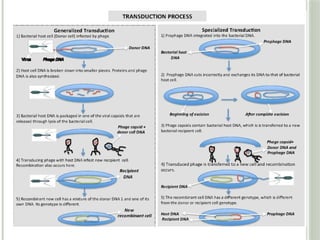
Transduction is the process by which DNA is transferred between bacteria through bacteriophages, leading to significant implications such as antibiotic resistance. There are two types of transduction: generalized, where random bacterial DNA is packaged into phages, and specialized, where specific DNA parts are transferred during lysogeny. Both mechanisms allow for genetic alterations in recipient bacteria, contributing to the evolution of bacterial traits.