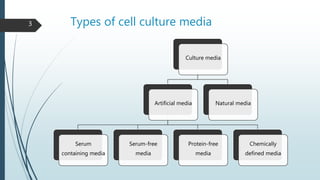
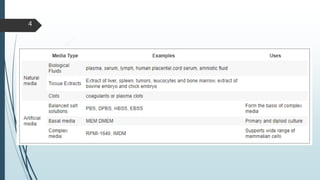
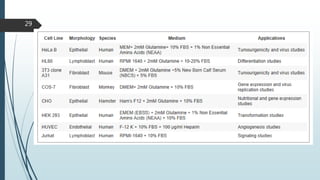
Cell culture media are designed to support the growth of cells outside their natural environment. They generally contain amino acids, salts, glucose, vitamins and other nutrients. Media can be natural (containing biological fluids) or artificial/synthetic. Artificial media are grouped into serum-containing, serum-free, chemically defined, and protein-free categories based on their ingredients. Key components of media include buffers, amino acids like glutamine, vitamins, inorganic salts, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, trace elements, and supplements specific to cell lines. Selection of the appropriate medium depends on the cell type and purpose of culture. Primary cells especially benefit from ready-to-use conditioned media.