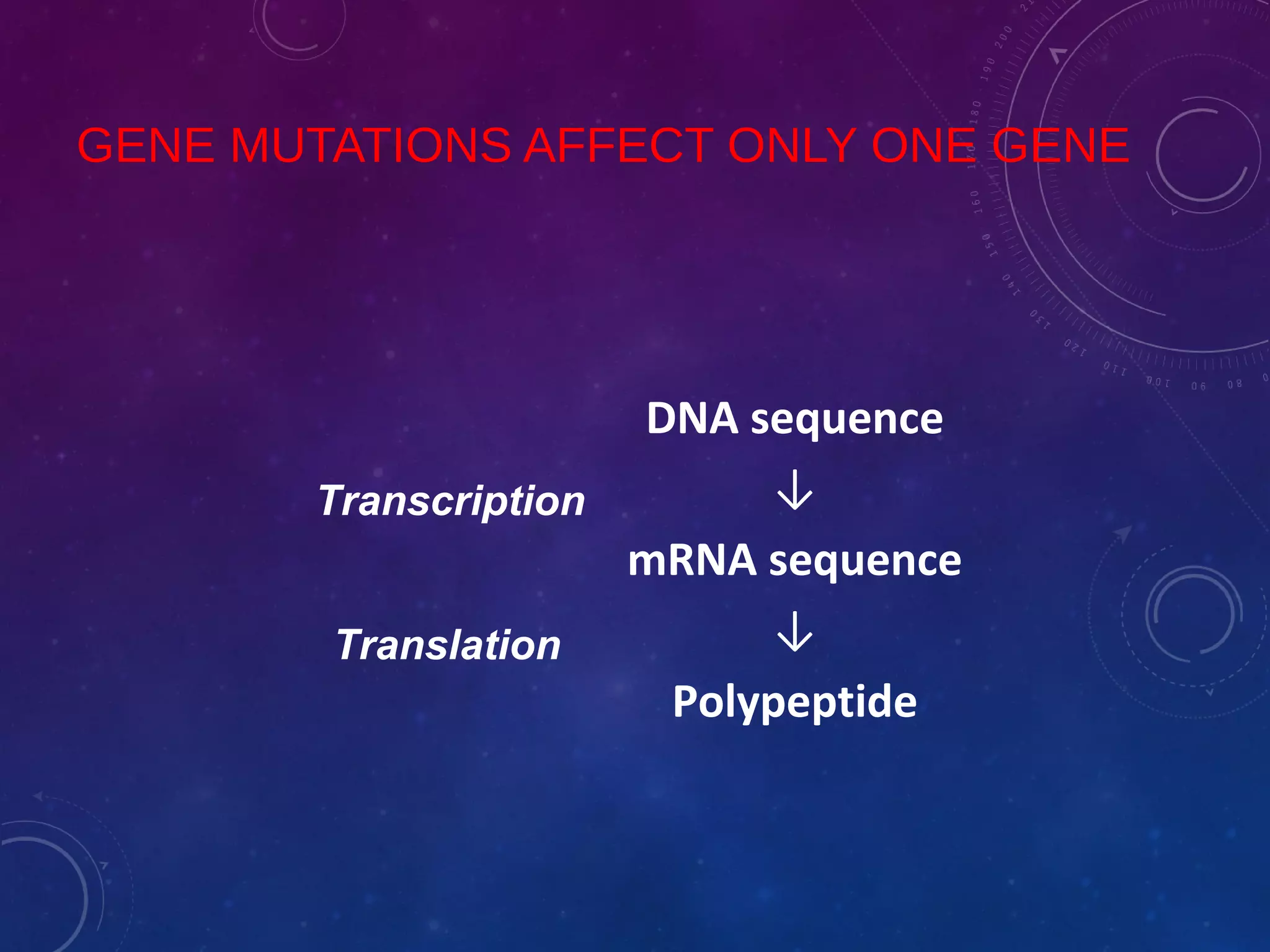
1. Gene mutations can affect a single gene by causing changes in a single codon through substitutions, inversions, additions or deletions.
2. Substitution mutations may not have serious effects unless they change an amino acid essential to the protein structure/function. For example, a single nucleotide change in the beta-globin gene causes sickle cell anemia.
3. The genetic code is degenerate, meaning a mutation in the third base may not affect the phenotype if it does not change the amino acid. Frameshift mutations from additions or deletions can have more significant effects.