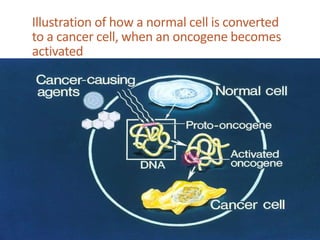
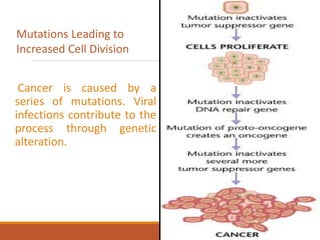
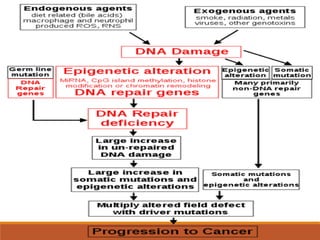
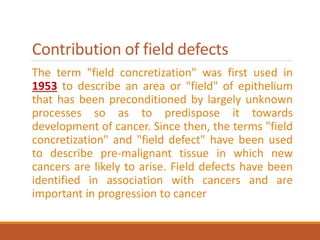
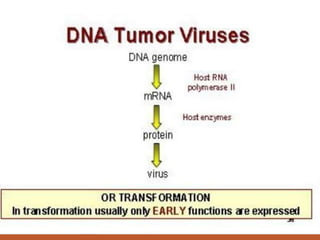
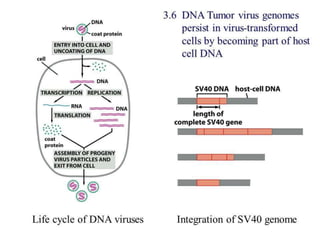
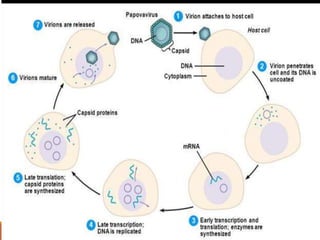
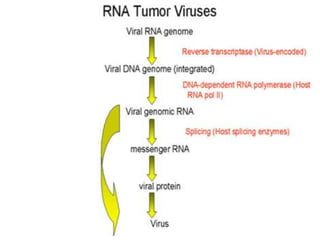
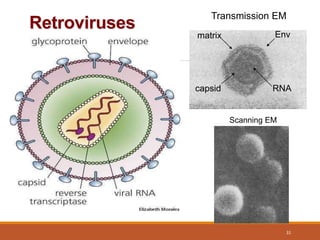
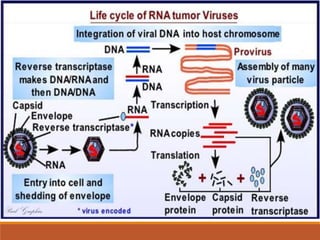
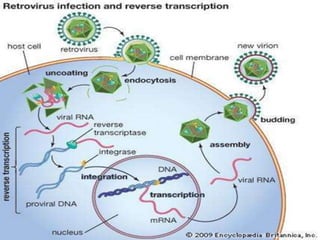
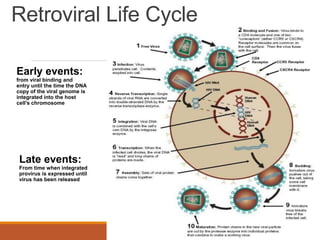
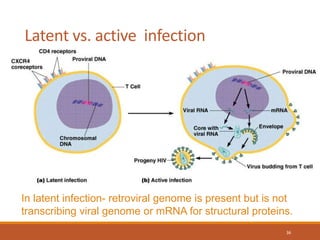
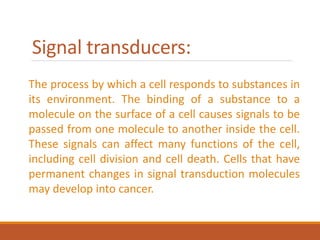
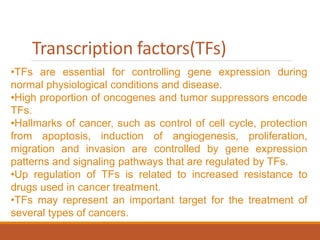
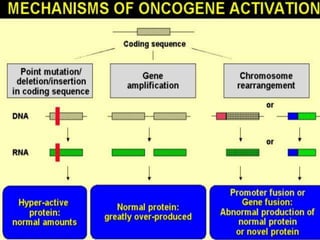
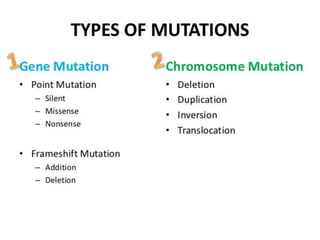
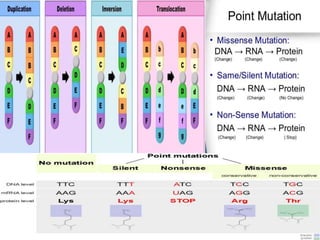
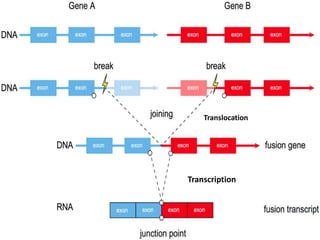
This document summarizes oncogenesis, the process by which normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. It discusses how proto-oncogenes can become activated oncogenes through mutations, increased expression, or chromosomal rearrangements. Oncogenes code for proteins involved in cell growth and division. The document also describes various causes of oncogenesis like genetic/epigenetic changes, DNA damage from endogenous or exogenous sources, field defects, and oncogenic viruses that activate proto-oncogenes or inactivate tumor suppressor genes. The mechanisms of viral oncogenesis and classification of viral oncogenes into growth factors, receptors, signal transducers and transcription factors are summarized as well.