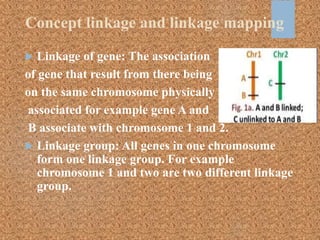
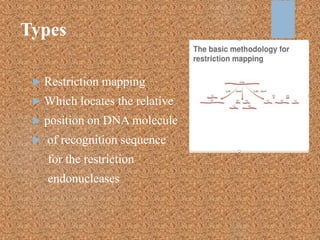
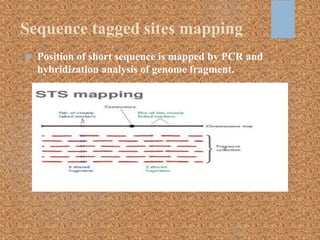
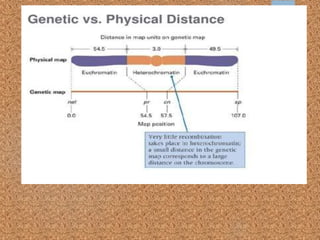
This document discusses gene mapping techniques used to locate genes on chromosomes. It describes linkage mapping, which provides a reference for a gene's location on a chromosome by looking at linked genetic markers, but does not give the exact position. Physical mapping identifies the precise location of a gene on a chromosome through methods like restriction mapping, which locates recognition sequences for restriction enzymes, and sequence tagged sites mapping, which identifies the position of short DNA sequences. Map-based sequencing then assembles sequenced genome fragments into a whole genome sequence using the known locations of genetic markers from physical and genetic maps.