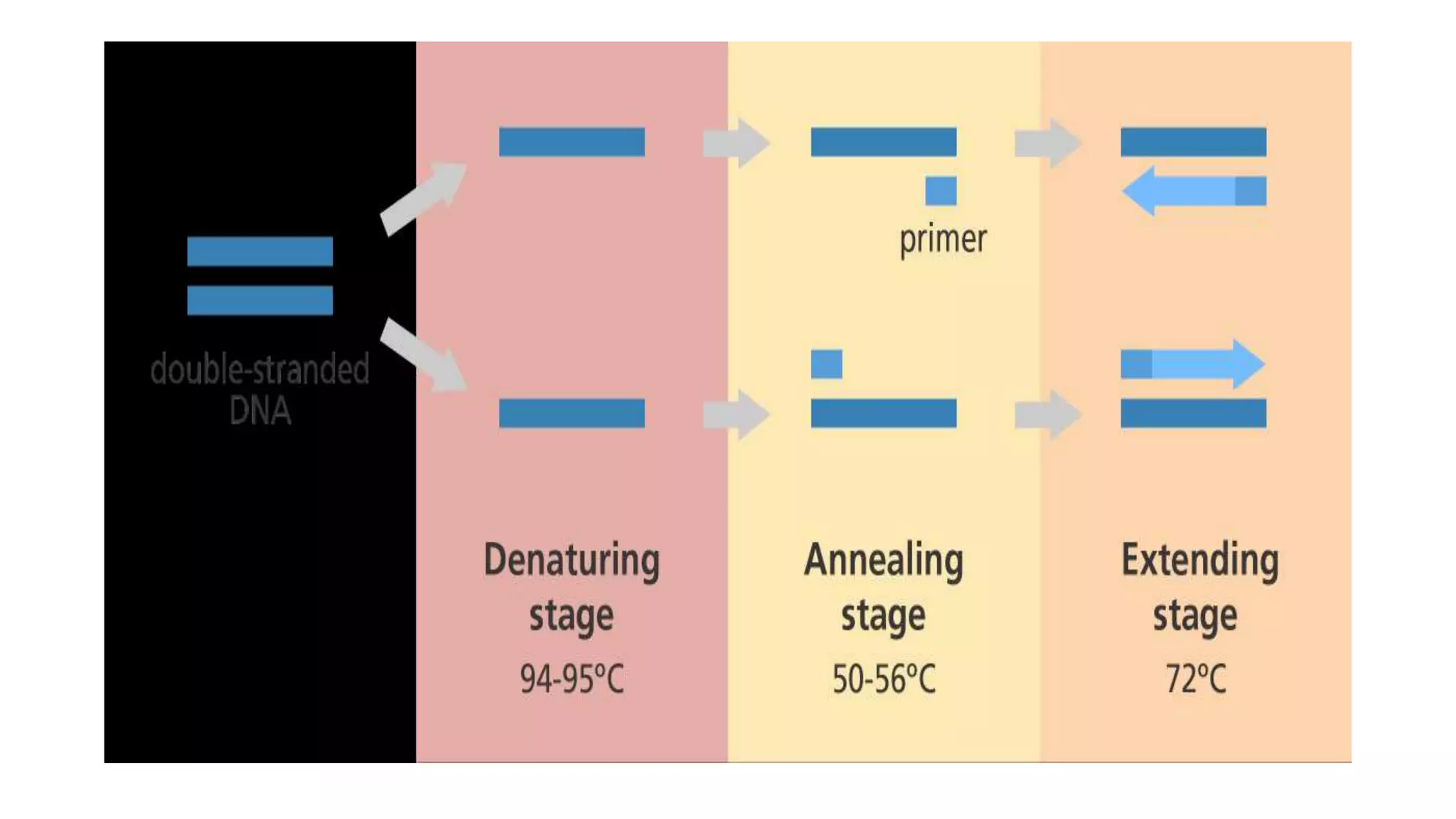
PCR involves copying a specific DNA segment through repeated cycles of heating and cooling. Each cycle consists of 3 stages - denaturation to separate DNA strands, annealing where primers attach to strands, and extension where new strands are synthesized. The process is carried out by a polymerase enzyme using primers, DNA bases, and thermal cycling to exponentially amplify the target DNA segment.