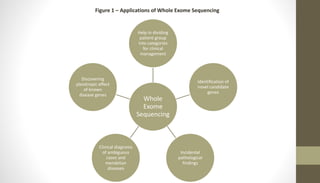
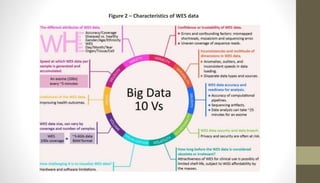
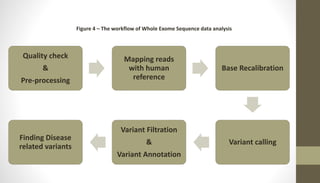
Whole exome sequencing is a technique that sequences the coding regions (exons) of the genome to identify genetic variants associated with diseases. It involves extracting DNA from samples, enriching the exome regions, sequencing the exome, and analyzing the data to identify variants linked to specific conditions. While more comprehensive than candidate gene analysis, exome sequencing is still limited compared to whole genome sequencing as it only covers the 2% of the genome that is protein-coding. However, it provides high coverage at a lower cost than whole genome sequencing.