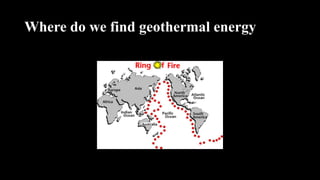
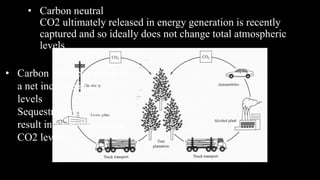
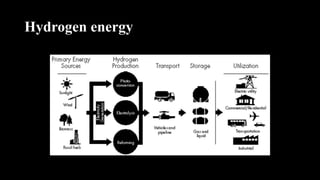
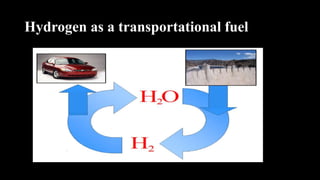
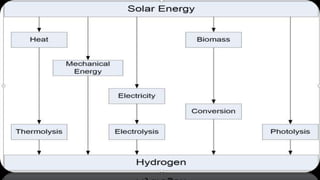
The document provides a comprehensive overview of renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass energy. It details the processes, advantages, and disadvantages of each energy type, emphasizing their potential and implications for sustainability. The information highlights how renewable resources can be harnessed effectively while addressing challenges such as energy storage, environmental impact, and operational costs.