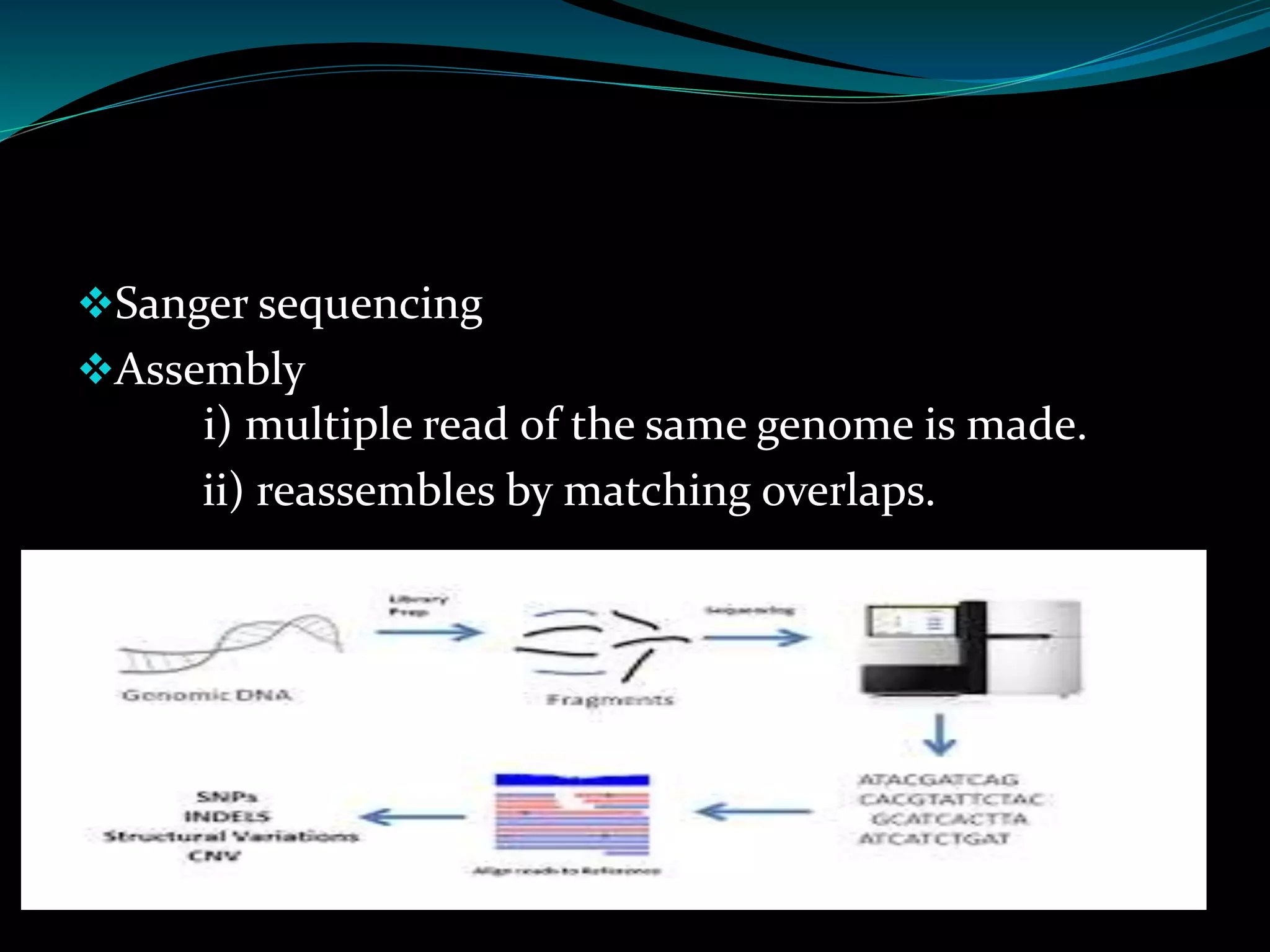
Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) is a process that determines the complete DNA sequence of an organism's genome and has evolved since its development in 1995. Various methods such as shotgun sequencing and nanopore sequencing are employed, involving steps like DNA fragmentation, amplification, and assembly of the sequence. WGS offers advantages like personalized medicine and evolutionary studies, but challenges include interpretation difficulties for physicians and potential unwanted information for patients.