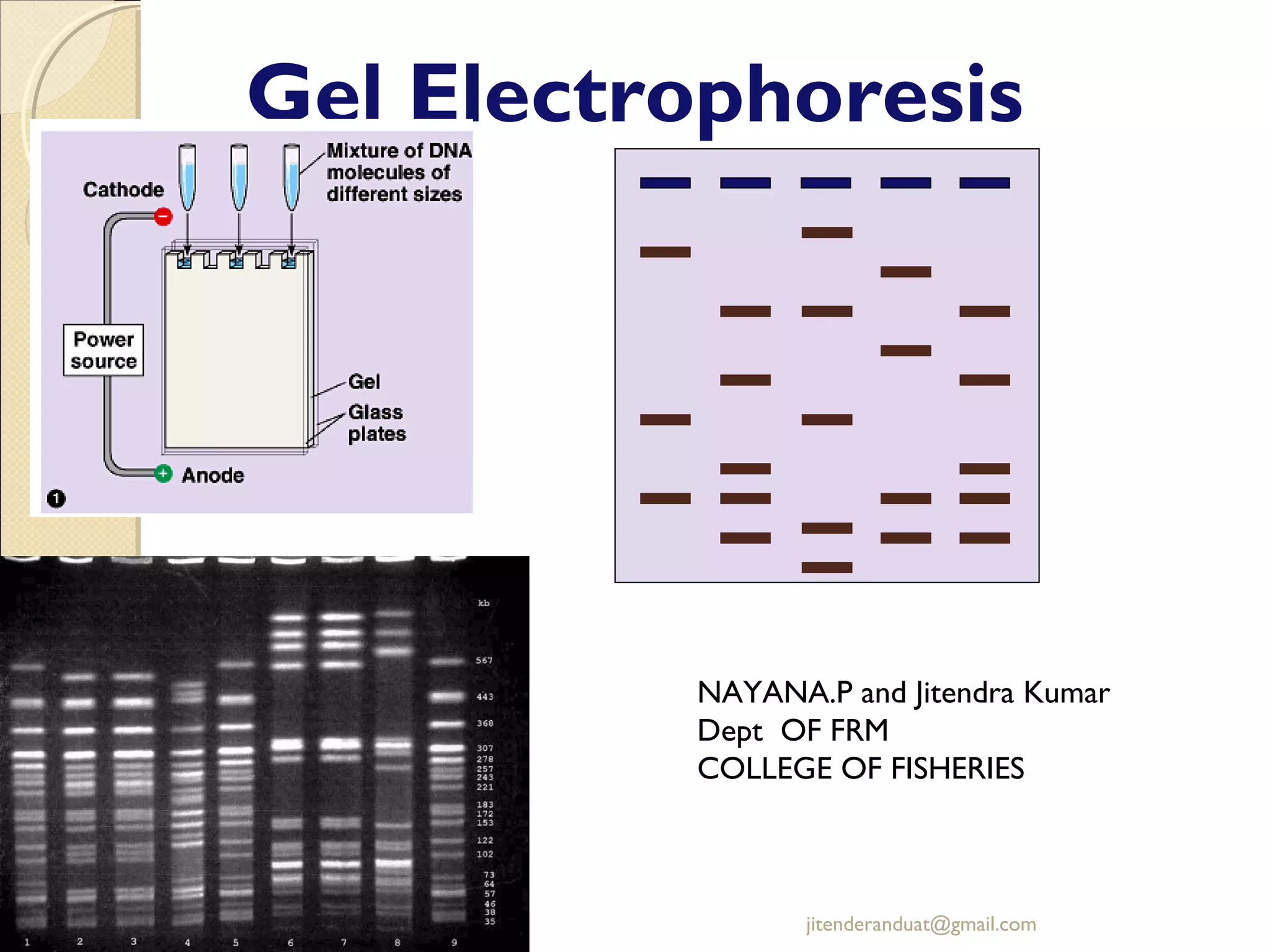
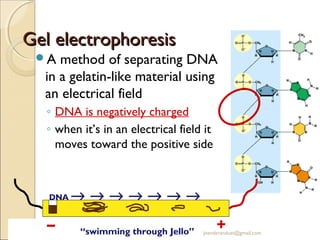
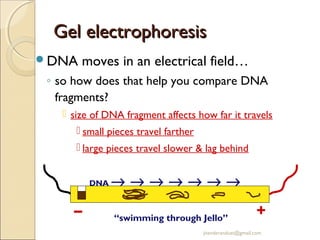
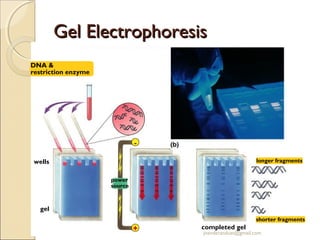
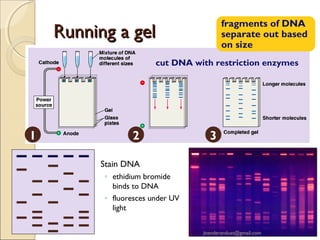
Gel electrophoresis is a method used to separate biomolecules like DNA, RNA, and proteins based on their size and charge. It works by applying an electric current to move the negatively charged molecules through a gel, with smaller molecules moving faster through the gel pores than larger ones. Common types of gels used include agarose for separating DNA, polyacrylamide for proteins, and starch for some protein analysis. The document provides details on how gel electrophoresis is performed and its applications in fields like forensics, molecular biology, and biochemistry.