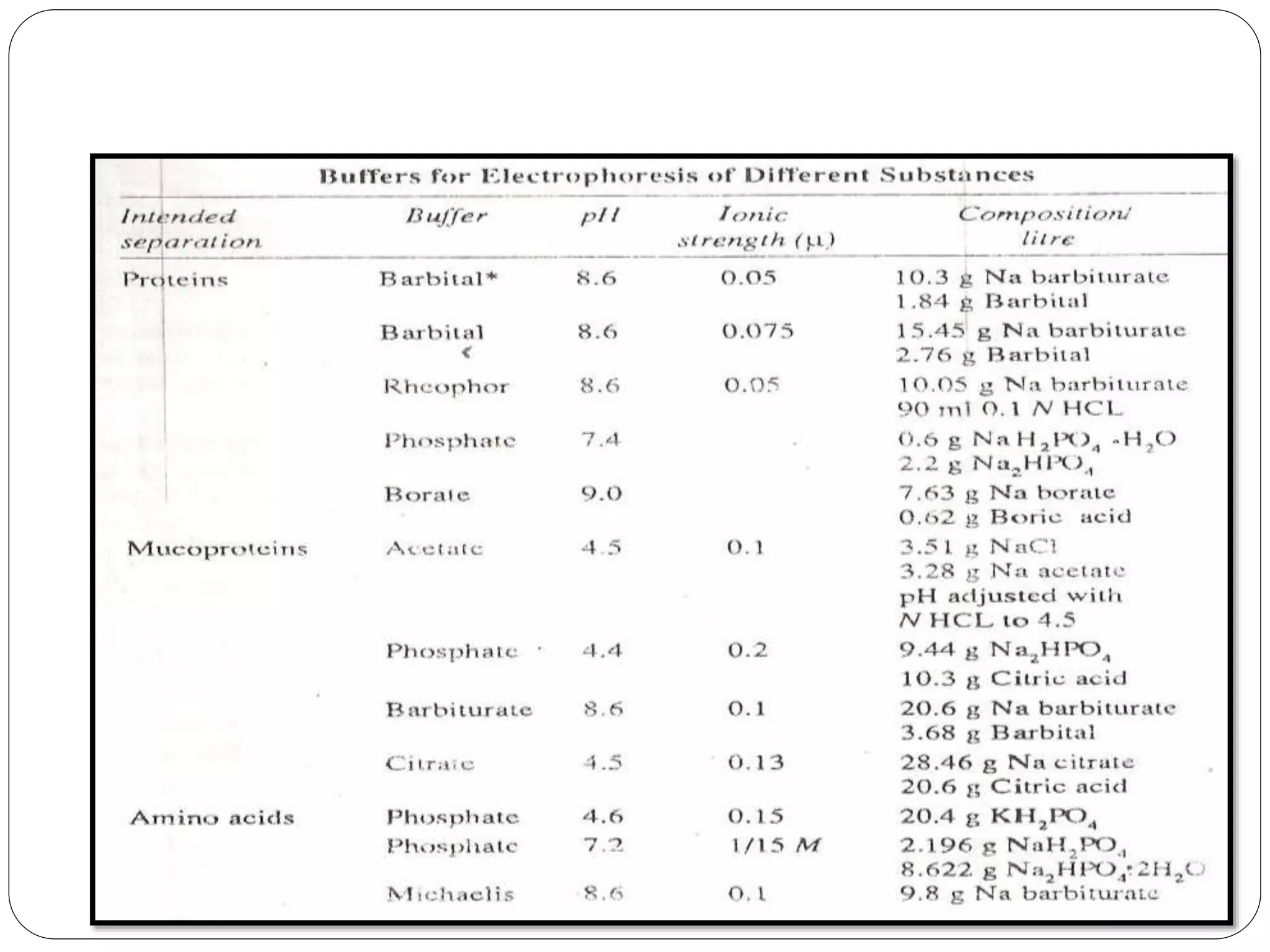
Electrophoresis is a technique used to separate charged particles based on their rates of movement in an electric field, with applications in biological analysis of proteins, peptides, and nucleic acids. Key factors affecting migration include net charge, particle mass, the medium's pH, and temperature. Various support media and buffers are employed in the process, which also includes steps of separation, staining, detection, and quantification for diverse applications in medical research, food industry, and biochemical analysis.