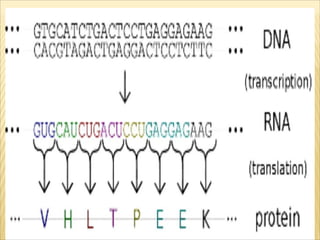
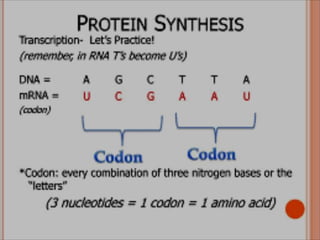
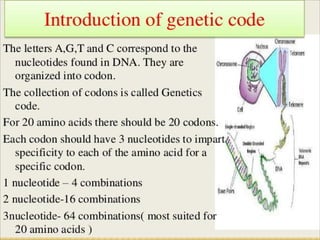
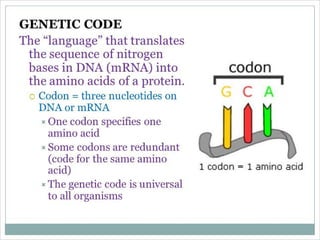
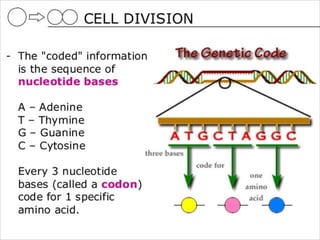
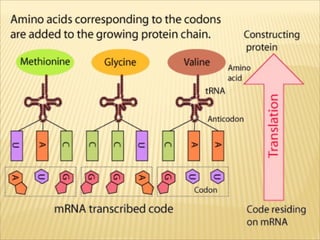
DNA contains the genetic code that directs protein synthesis. The genetic code is stored in the sequence of nitrogen bases (A, T, C, G) in DNA. It was discovered that the genetic code uses triplets of these bases, called codons, to specify the 20 different amino acids used to build proteins. Experiments by Nirenberg and Khorana helped decipher the genetic code by artificially synthesizing RNA sequences and determining which amino acids they coded for. The genetic code was found to be nearly universal across all life, using 64 codons to specify amino acids or termination of protein synthesis.