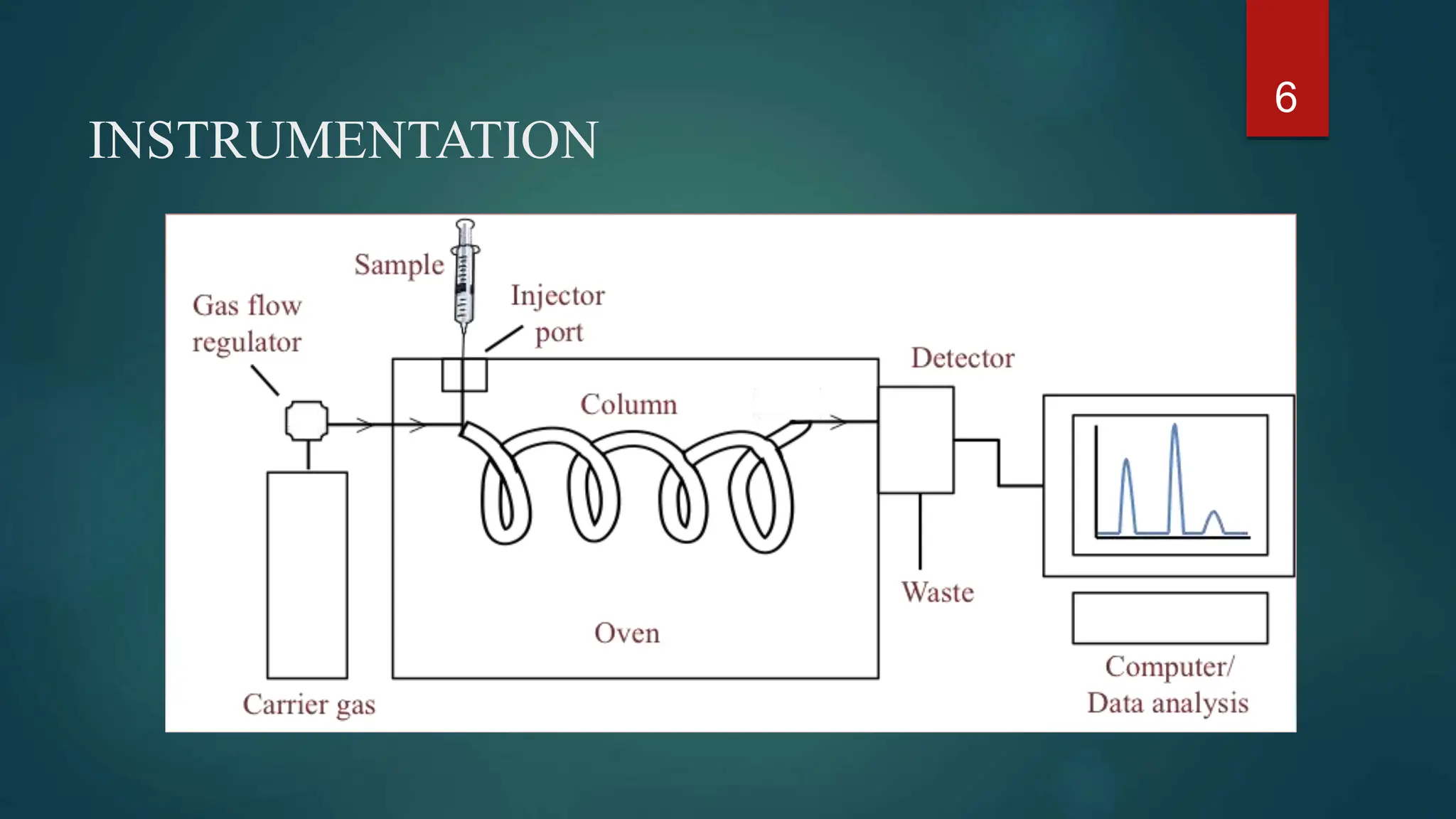
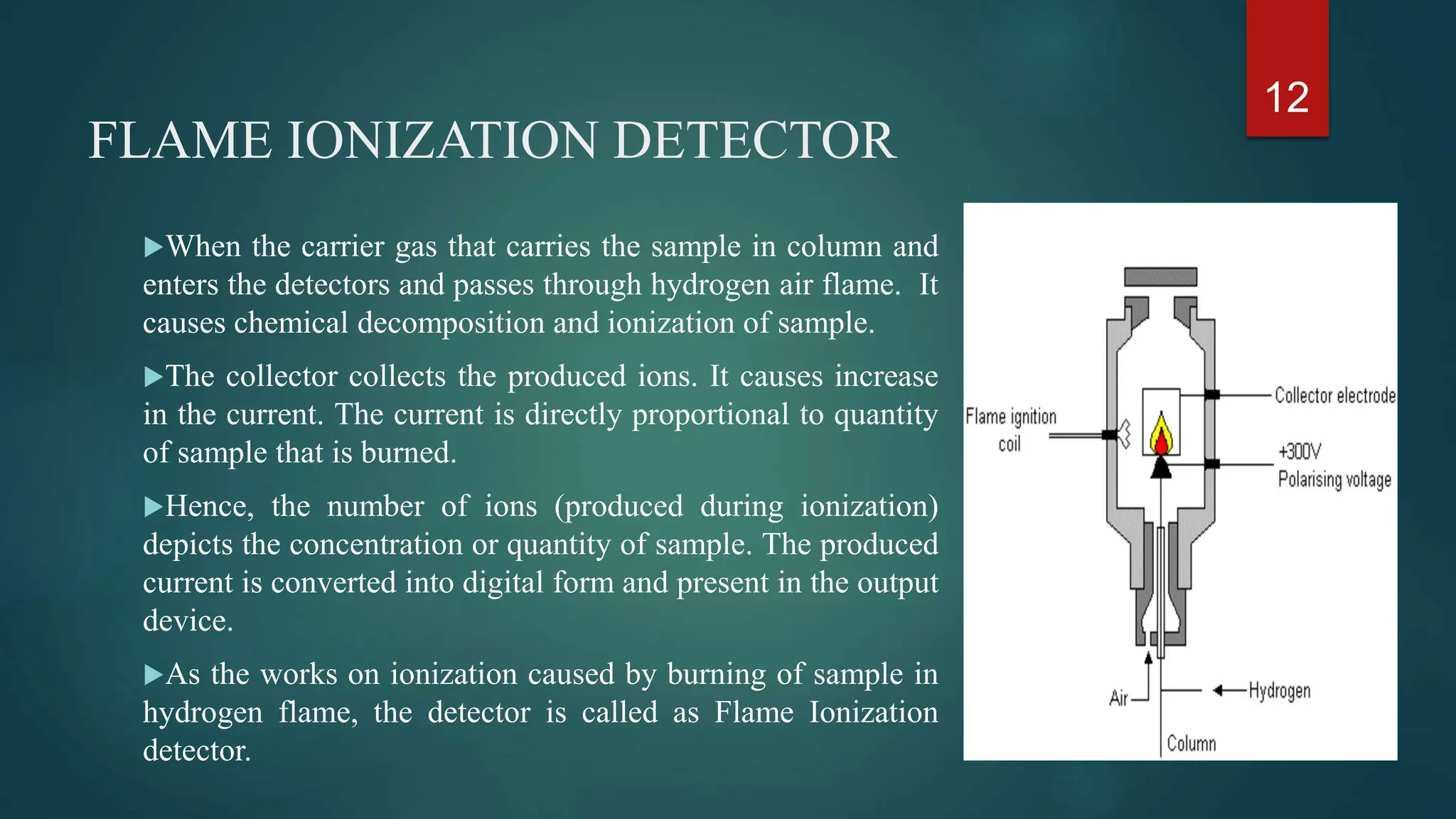
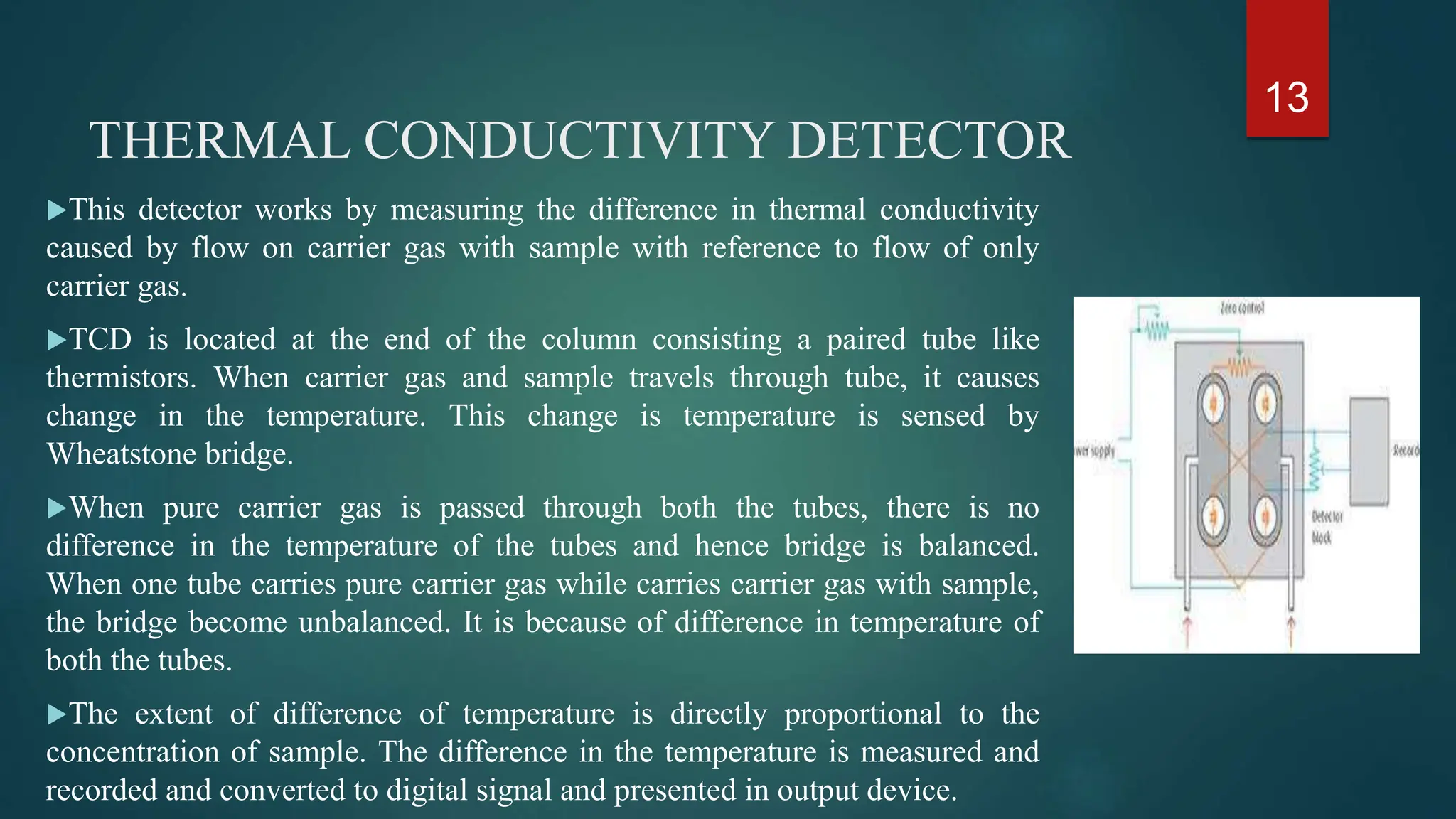
This document provides an overview of gas chromatography including its principles, instrumentation, applications, and conclusions. Gas chromatography is an analytical technique used to separate chemical components of a sample mixture. It works by vaporizing the sample and carrying it through a column with an inert gas, which separates the components based on how they interact with the stationary phase in the column. Common instrumentation includes the carrier gas, injector, column, and detectors like the flame ionization detector or thermal conductivity detector. Applications of gas chromatography include qualitative and quantitative analysis in pharmaceuticals, food, forensics, and environmental testing.