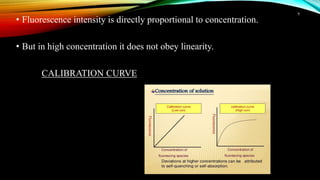
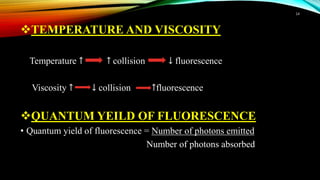
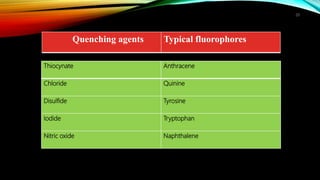
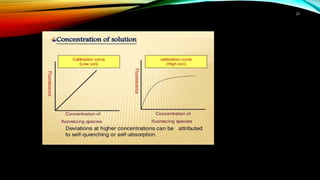
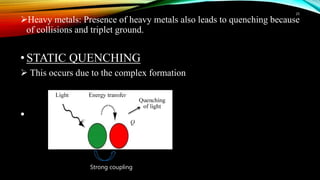
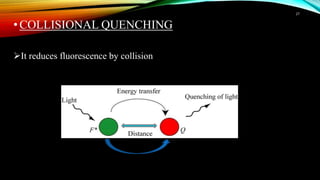
This document discusses factors that affect fluorimetry and quenching. It lists several factors that can influence fluorescence, including the nature of molecules, substituents, concentration, adsorption, light, oxygen, pH, temperature, and viscosity. It also describes different types of quenching such as self-quenching, chemical quenching, static quenching, and collisional quenching. Chemical quenching can occur due to changes in pH, presence of oxygen, or heavy metals. Static quenching involves complex formation between the fluorophore and quencher. Collisional quenching occurs through interactions between an excited fluorophore and quencher molecule.