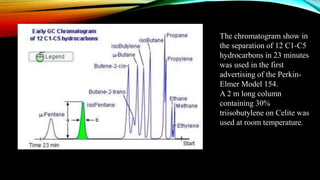
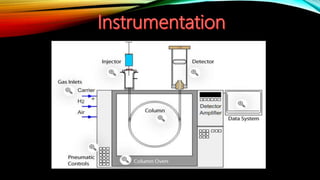
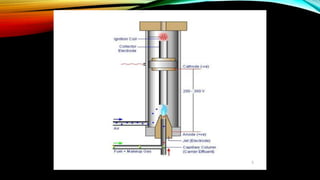
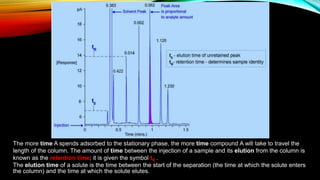
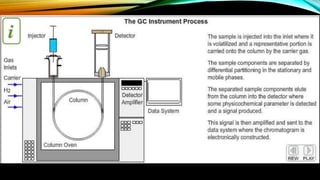
Gas chromatography (GC) is an analytical technique used for separating and analyzing vaporized compounds, offering advantages such as fast analysis, high efficiency, and sensitive detection. Developed in the 1940s and 1950s, it utilizes a stationary liquid phase and a mobile gas phase to separate mixtures, with applications in various fields including pharmaceuticals, food quality testing, and environmental monitoring. However, GC is limited to volatile samples and can be destructive, necessitating specific detectors for accurate analysis.