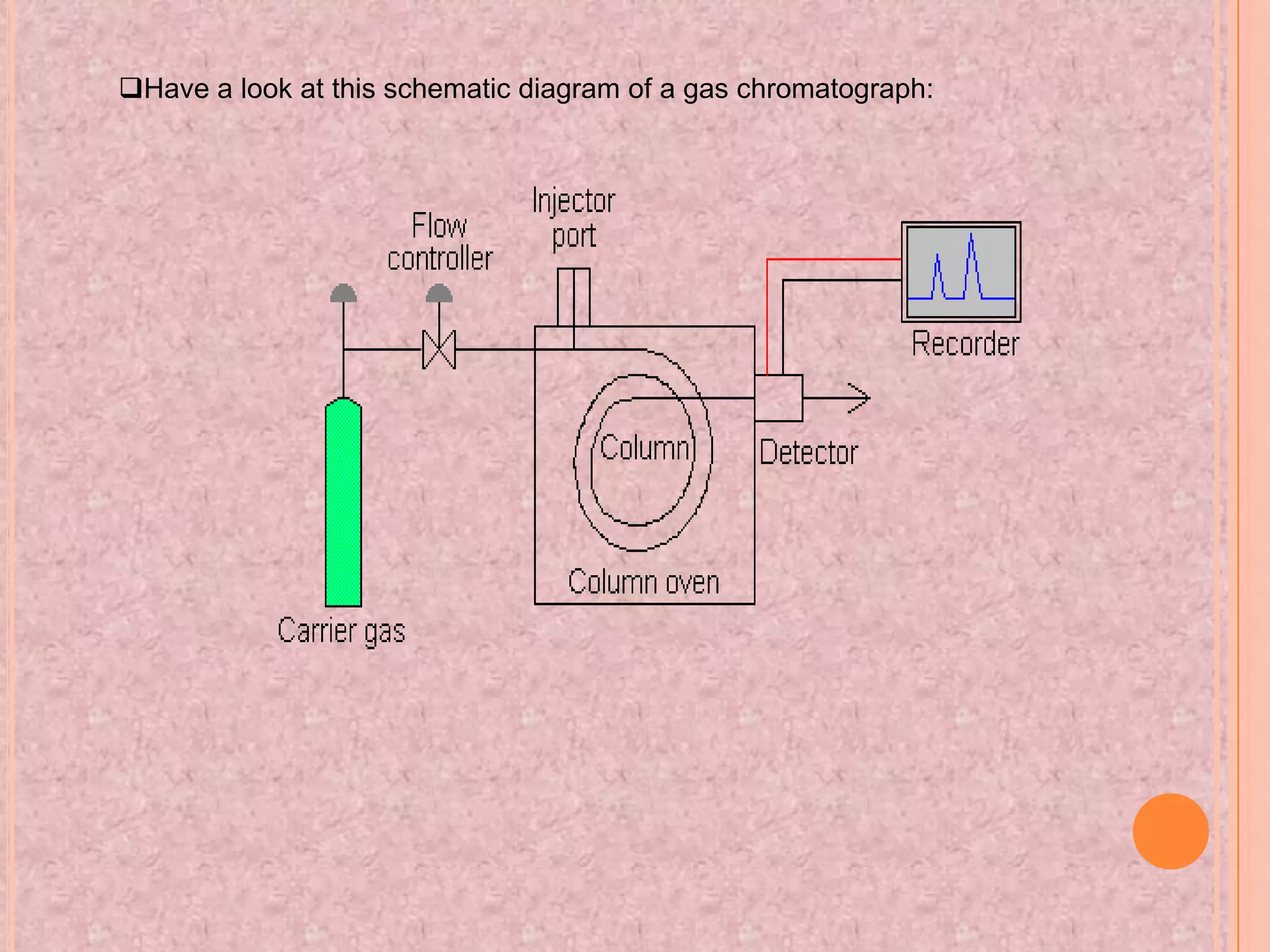
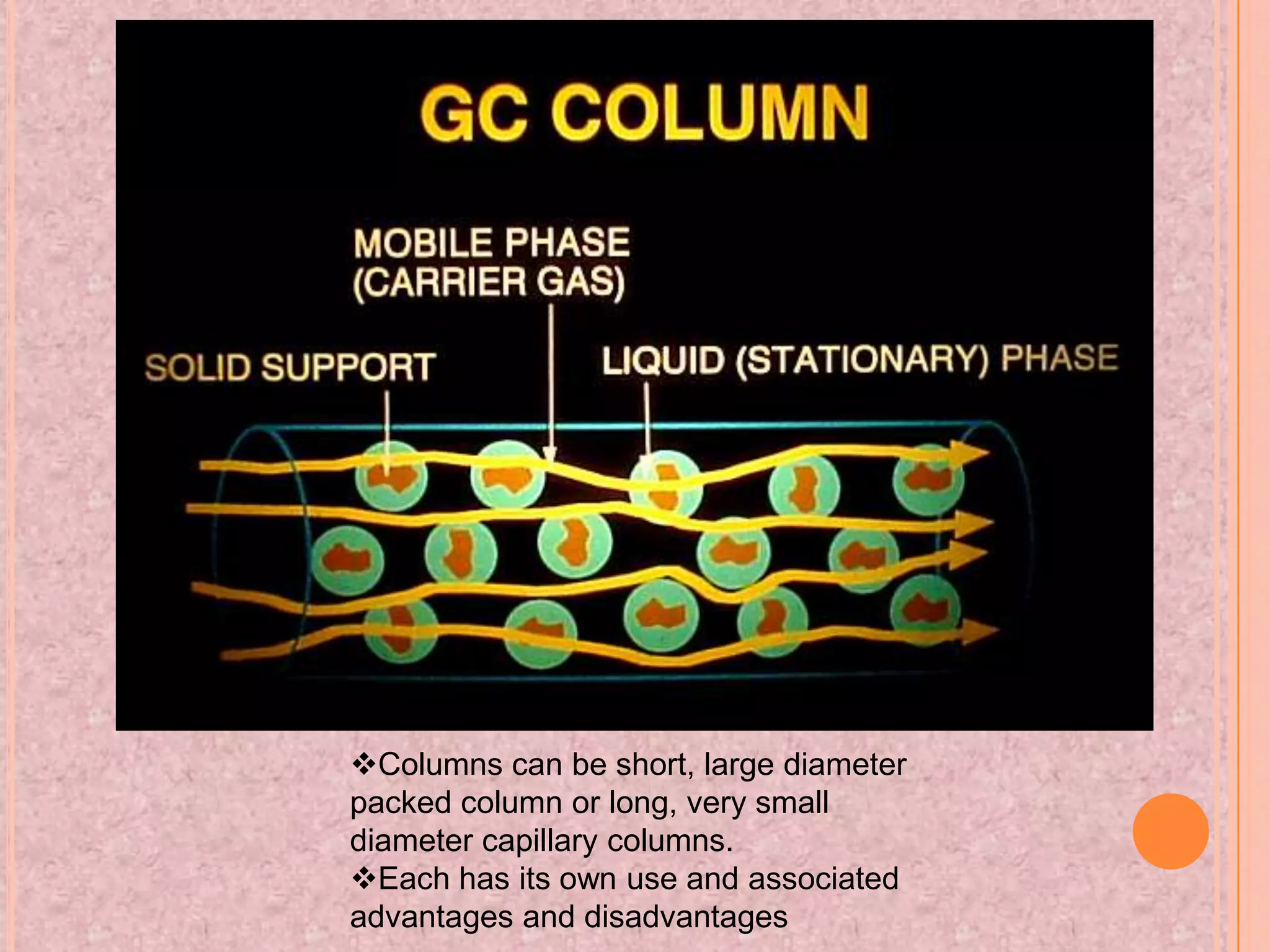
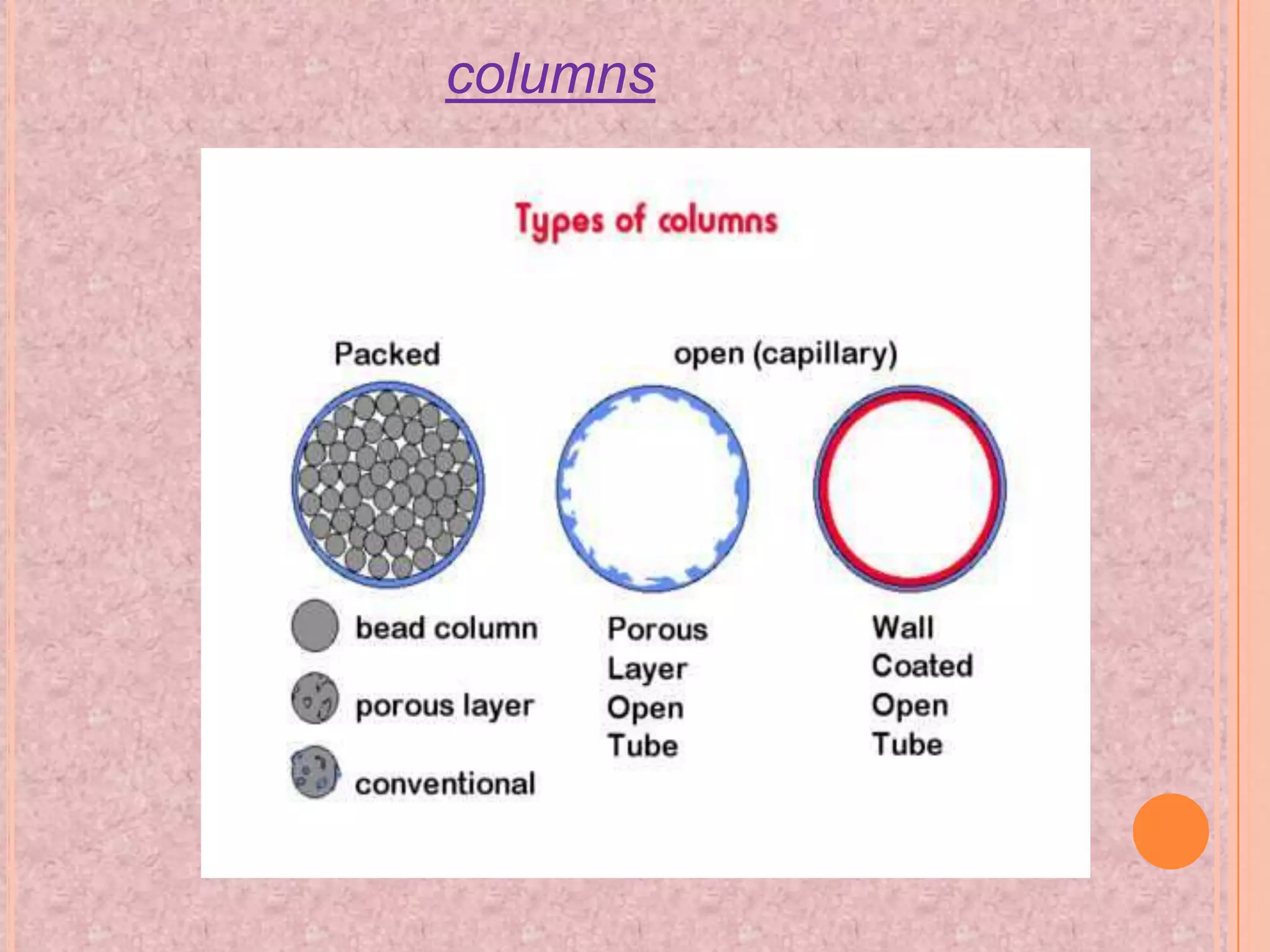
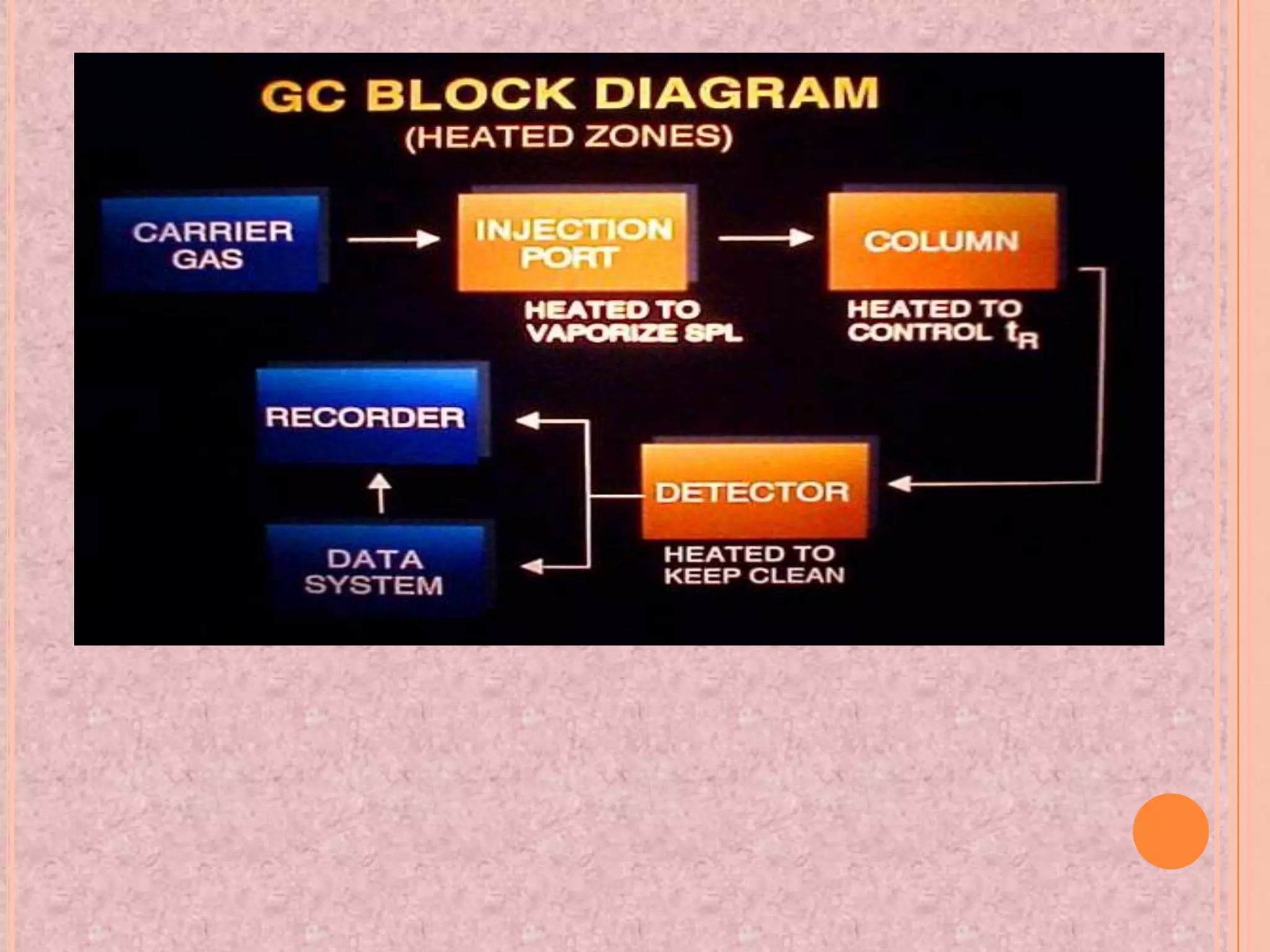
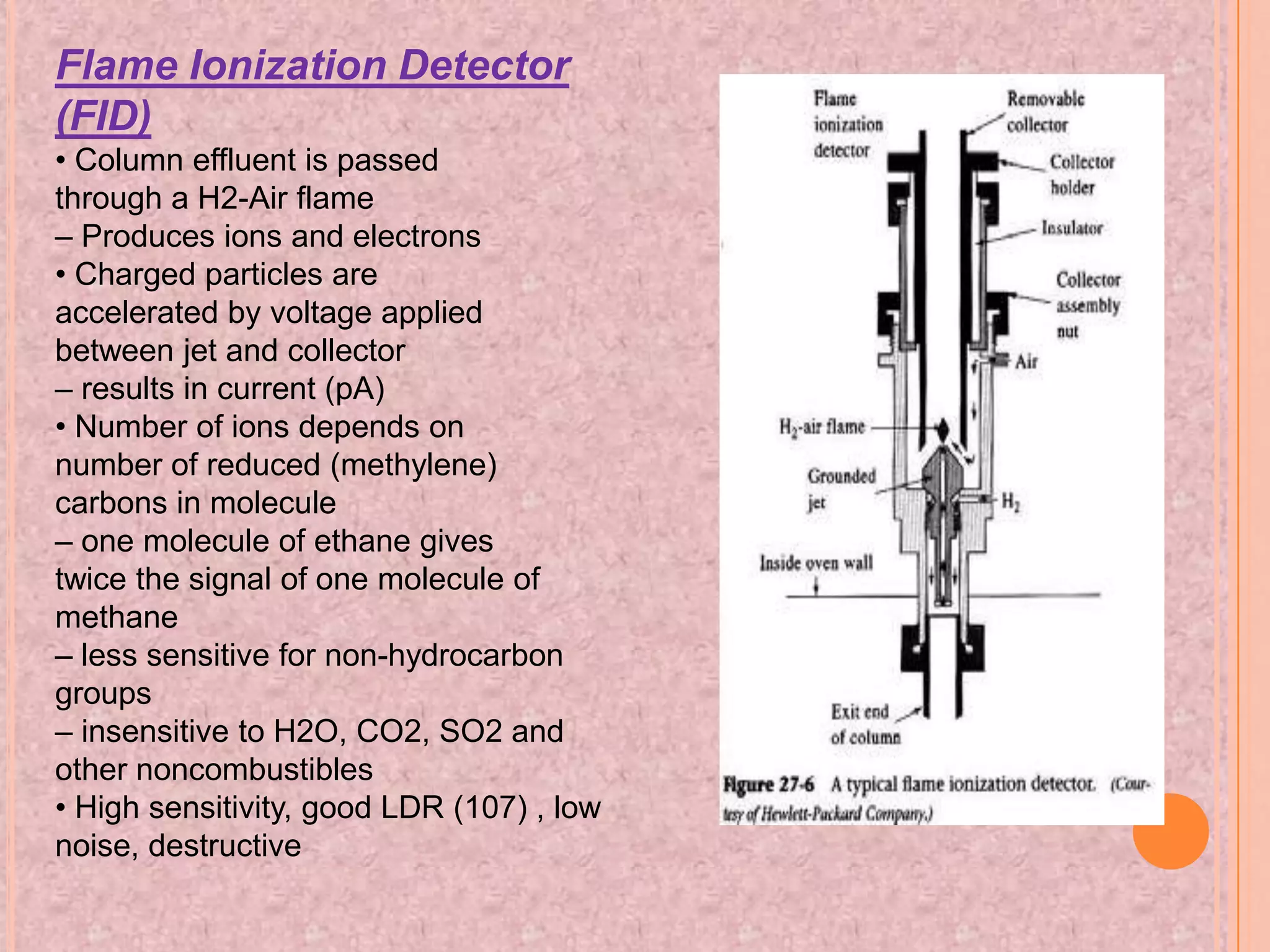
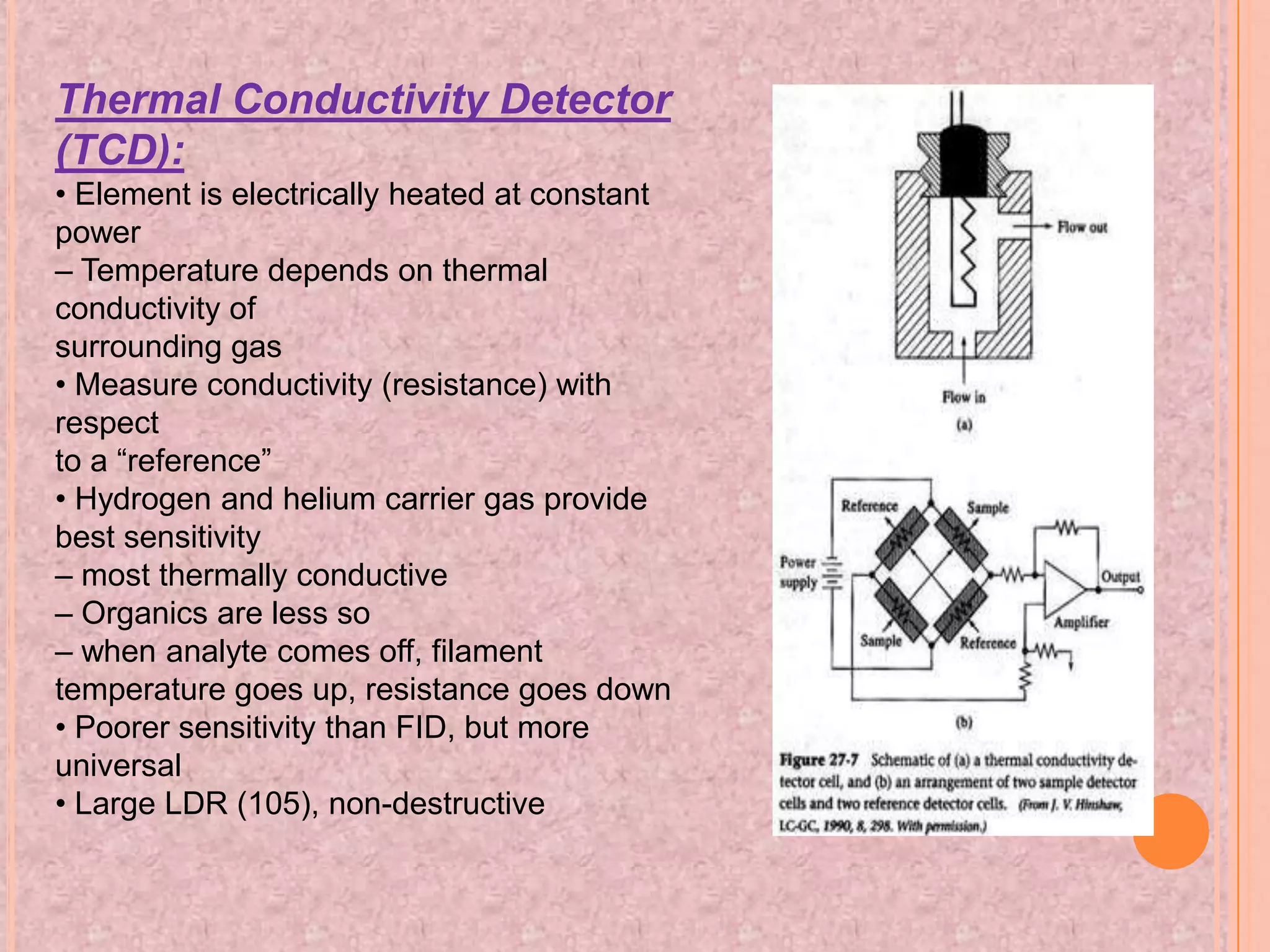
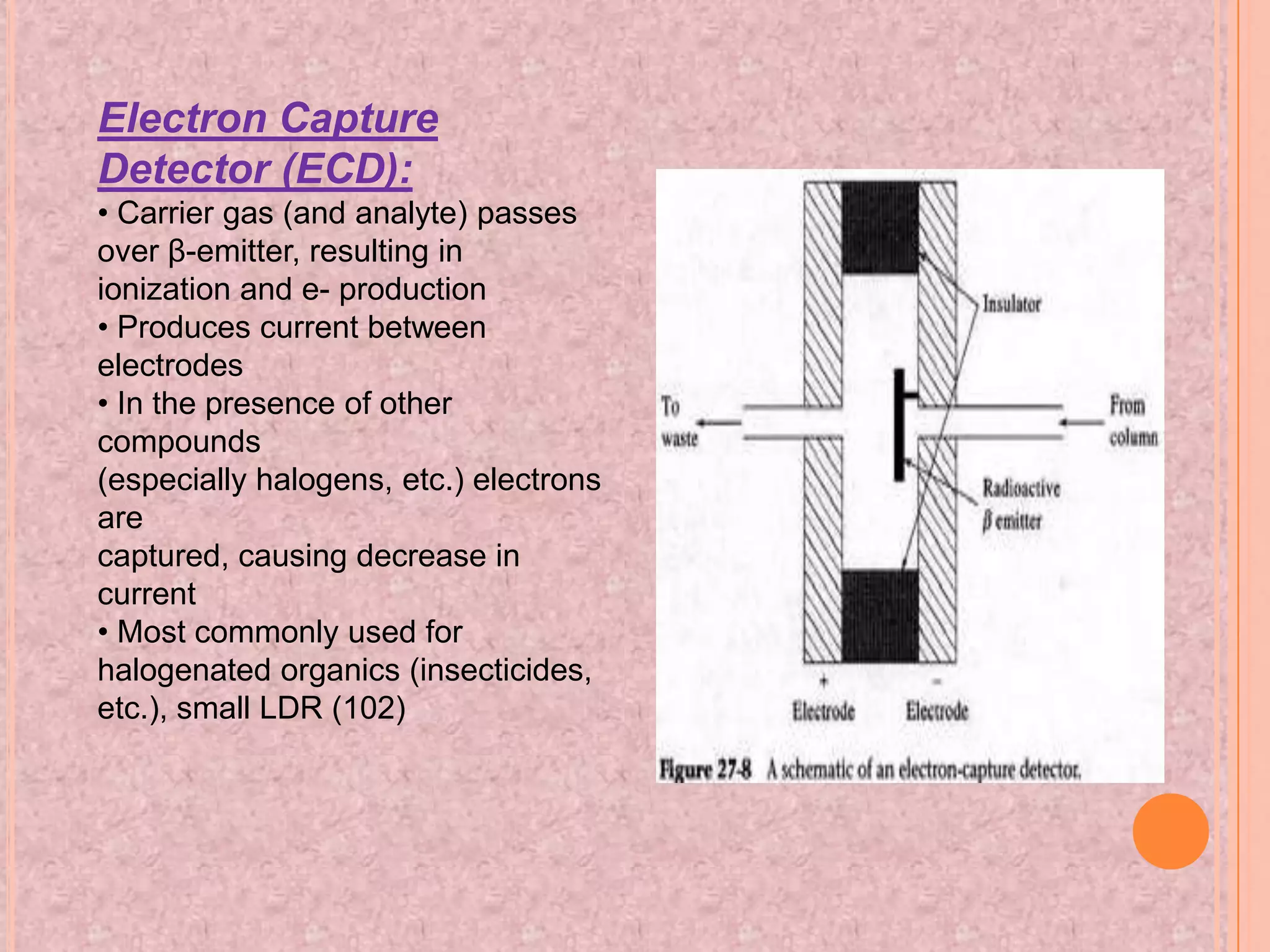
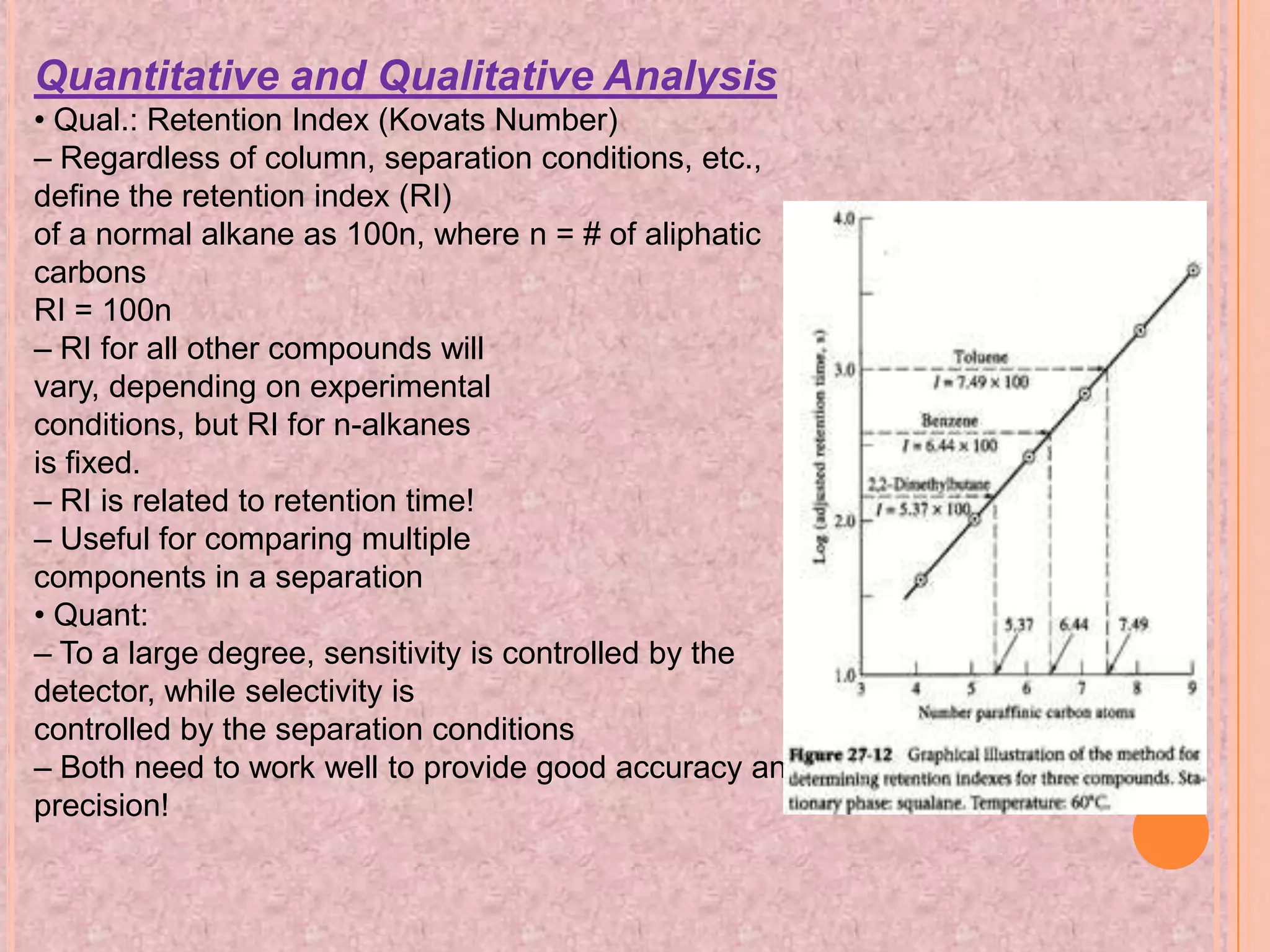
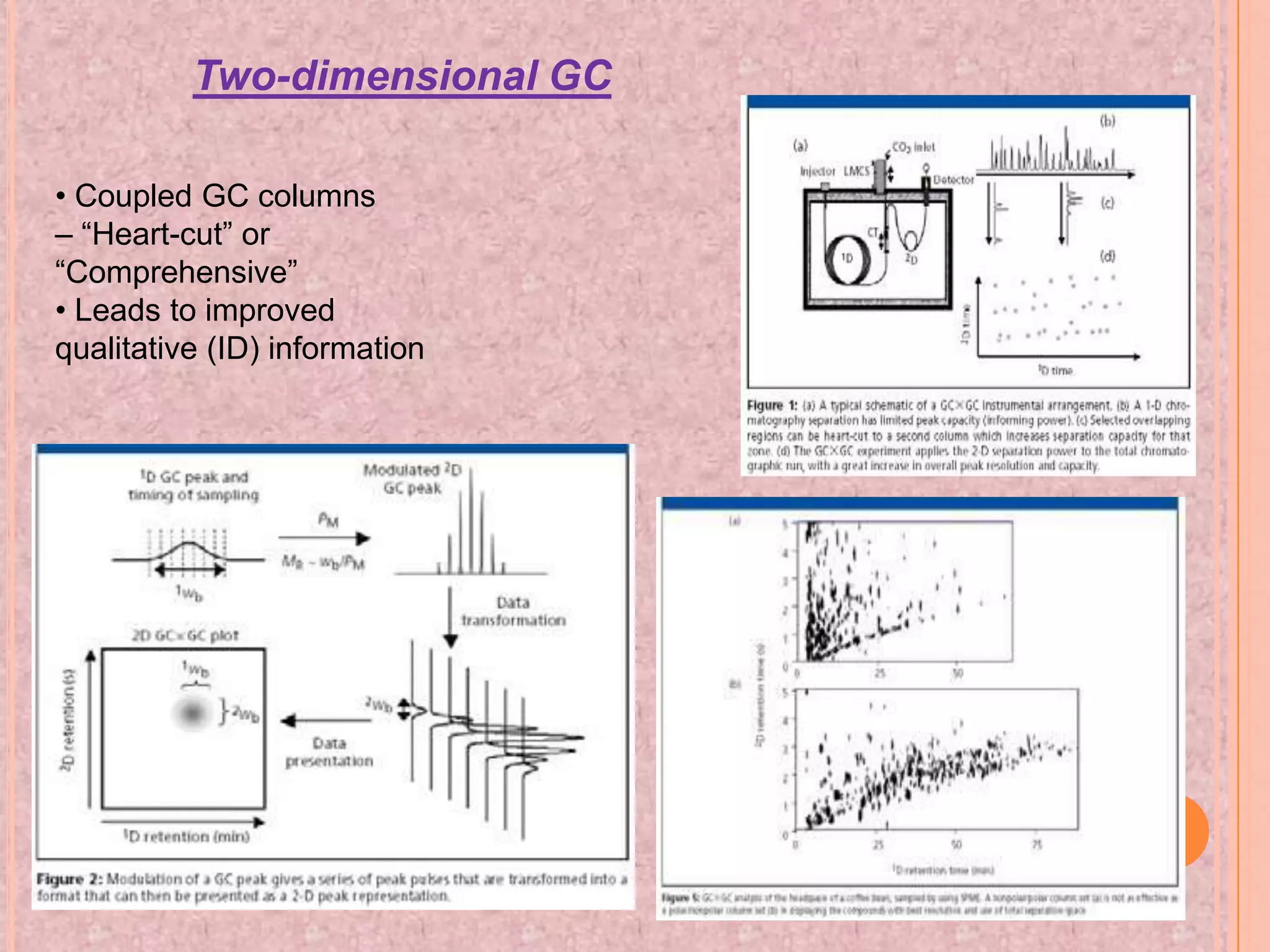
Gas chromatography is an analytical technique used to separate and analyze chemical compounds. It involves vaporizing a sample and injecting it into a column with a gaseous mobile phase. Components are separated based on how they partition between the mobile and stationary phases. The separated components exit the column and are detected, producing a chromatogram. Key advantages are its speed, sensitivity, and ability to analyze volatile organic and inorganic compounds. Common detectors include the flame ionization detector and thermal conductivity detector. Gas chromatography has many applications in fields like drug analysis, food testing, and environmental analysis.