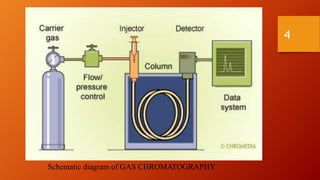
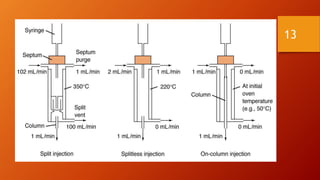
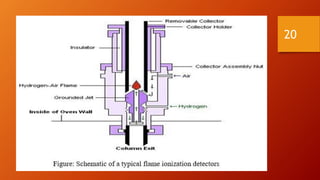
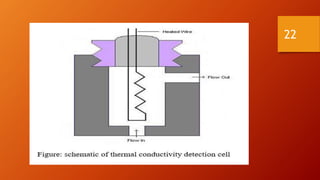
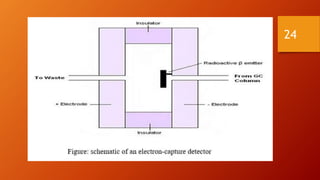
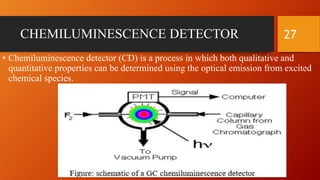
Gas chromatography is an analytical technique used to separate and analyze volatile compounds. It works by distributing the sample between a stationary phase and a mobile gas phase. Key components of a gas chromatography system include the carrier gas, injector, column, and detector. The column allows separation of compounds based on differences in partitioning between the stationary and mobile phases. Detectors then provide a quantitative measurement of separated components. Common applications of gas chromatography include analysis of pharmaceuticals, foods, flavors, fragrances, and petrochemicals.