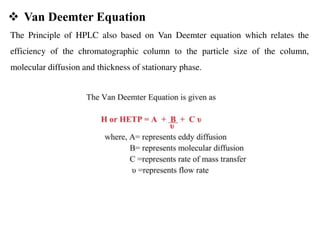
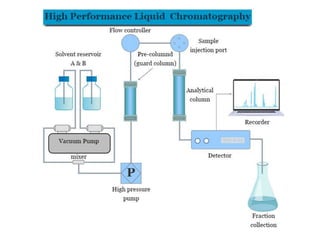
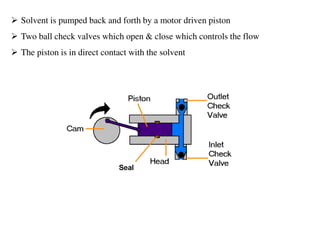
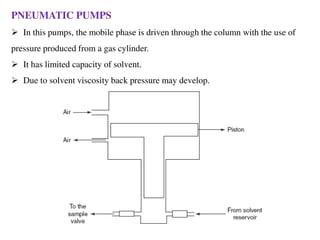
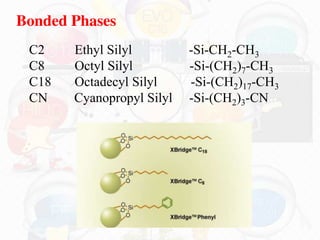
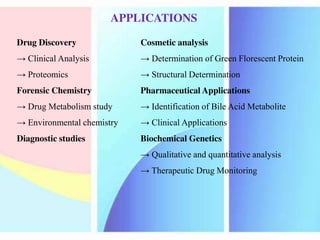
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a liquid chromatography technique used to separate both volatile and non-volatile compounds through high pressure, involving various modes and applications. It requires specific instrumentation including pumps, columns, detectors, and sample injection systems, and operates based on principles of adsorption and partition chromatography. HPLC is essential in fields like drug discovery, environmental chemistry, and clinical analysis, providing high resolution and efficiency in separating complex mixtures.