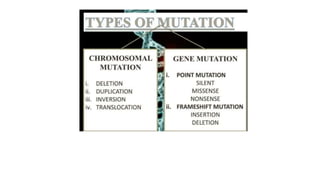
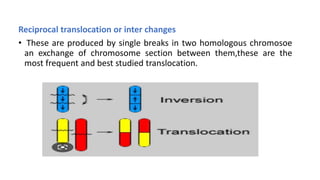
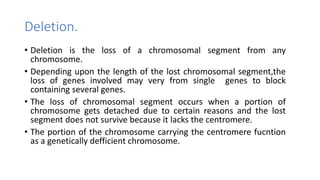
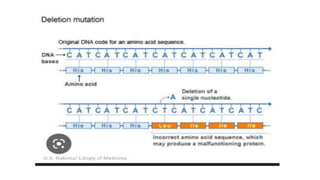
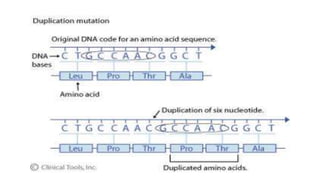
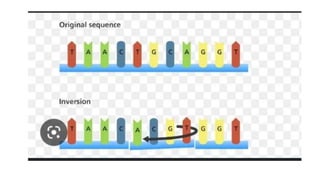
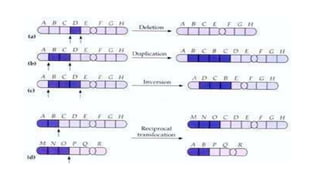
Frameshift mutations are caused by the addition or deletion of DNA bases, shifting the reading frame of codons from the mutation site onward. There are two types: deletions caused by losing bases, and insertions caused by adding extra bases. These mutations can originate from errors in DNA replication or damage from mutagens like acridine dyes. Chromosomal aberrations like translocations, deletions, duplications, and inversions are also a type of mutation and result from breaks in chromosomes that cause structural changes. Translocations transfer parts of one chromosome to another, while deletions, duplications, and inversions involve the loss, repetition, or reversal of chromosomal segments.