Embed presentation
Download to read offline





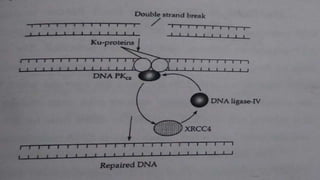

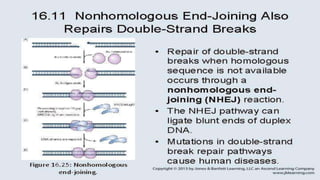

The document discusses non-homologous end joining (NHEJ), a critical DNA repair mechanism for double-stranded breaks caused by ionizing radiation or chemical agents. It details the role of a multi-component protein complex, including the ku protein and dna-pk kinase, in binding broken DNA ends and facilitating repair via mammalian dna ligase-IV. This process ensures genomic integrity by directly repairing double-stranded breaks without the need for homologous sequences.








