Embed presentation
Download to read offline




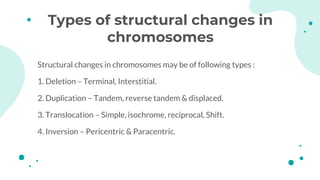

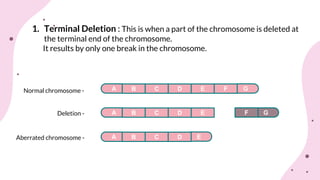
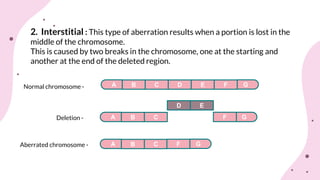
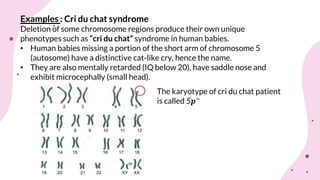

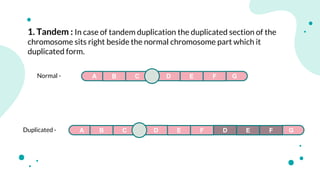
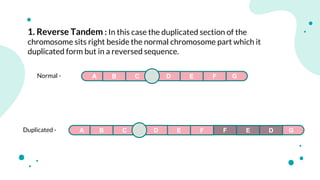
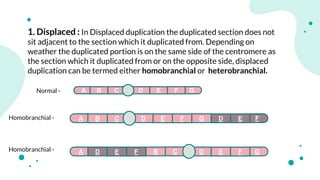


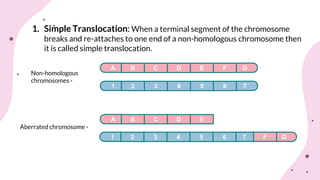
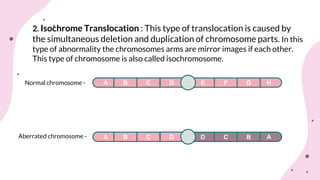
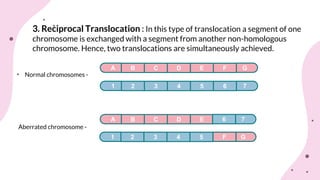
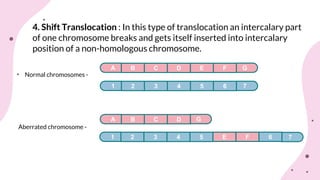

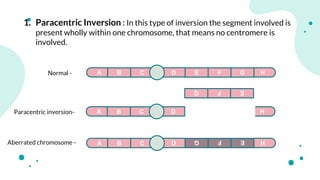
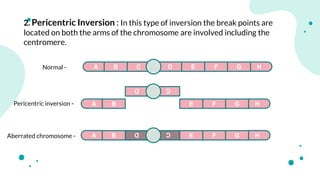



The document discusses chromosomal aberrations, which are structural changes in chromosomes that can affect their morphology and number, often occurring during cell division or fertilization. It categorizes these aberrations into deletions, duplications, translocations, and inversions, explaining their mechanisms and providing examples of their phenotypic effects, such as cri du chat syndrome and bar-eyed Drosophila. Additionally, it details specific types and subtypes of each aberration, emphasizing their implications for genetics and inheritance.
























