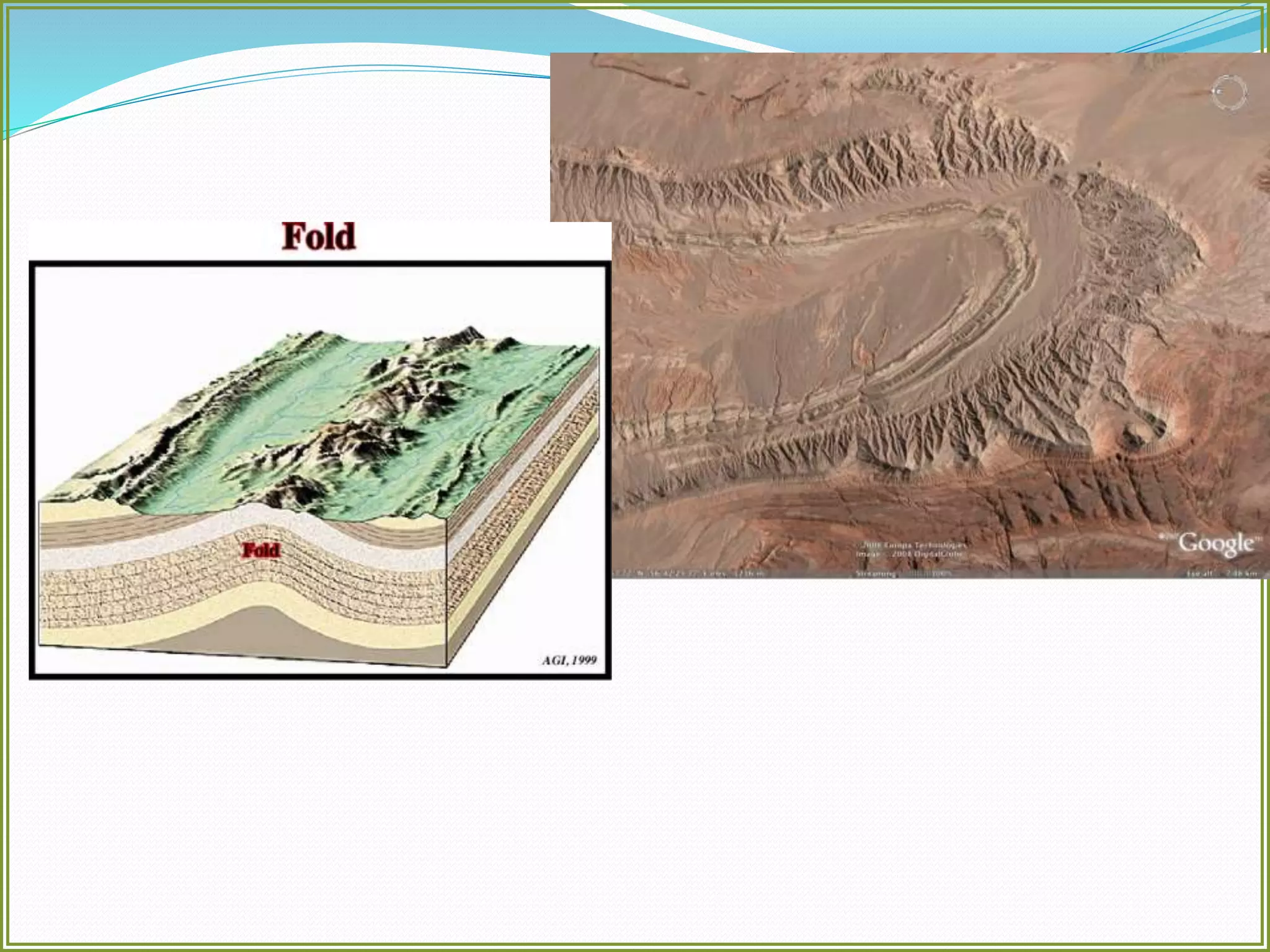
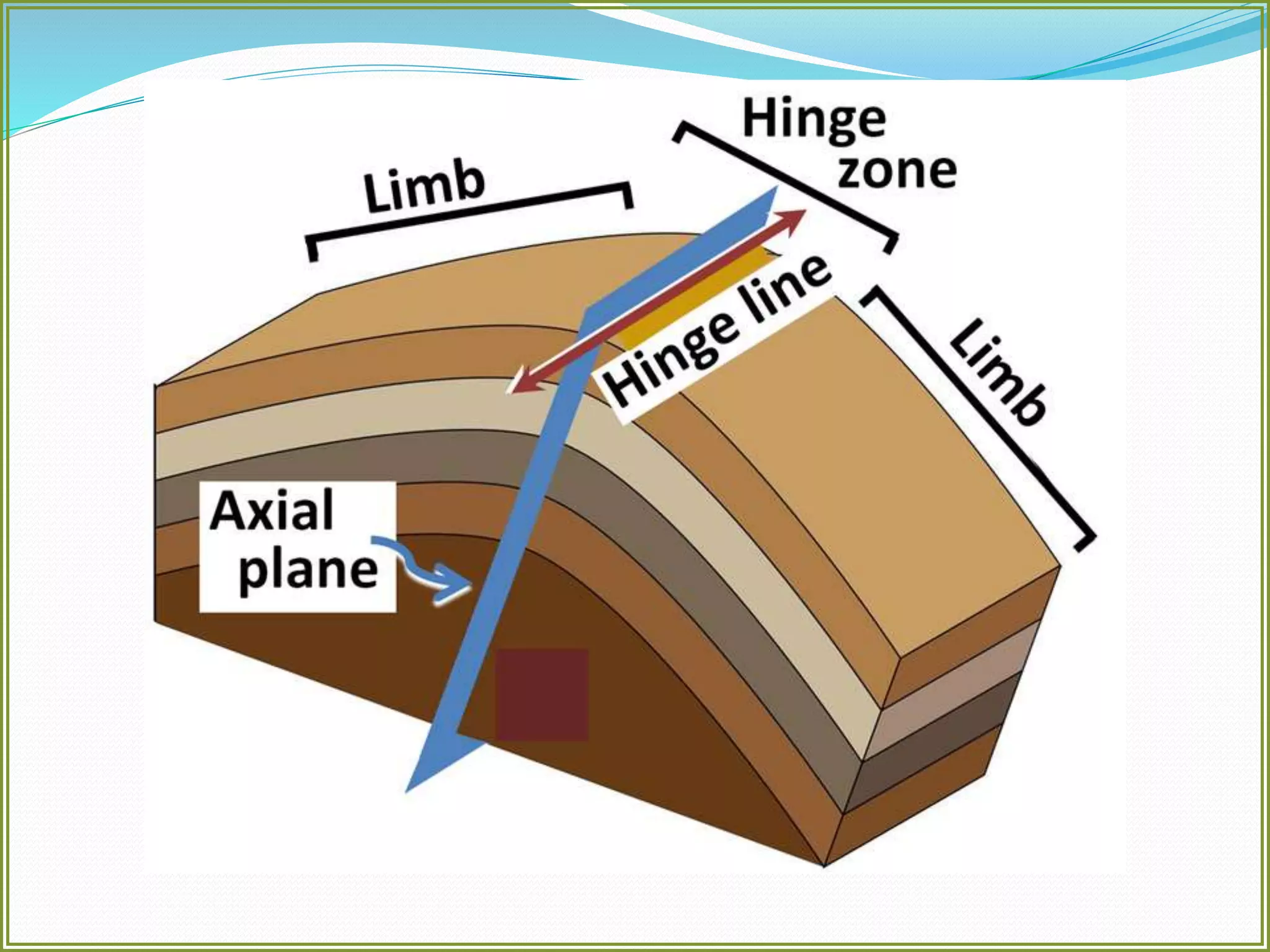
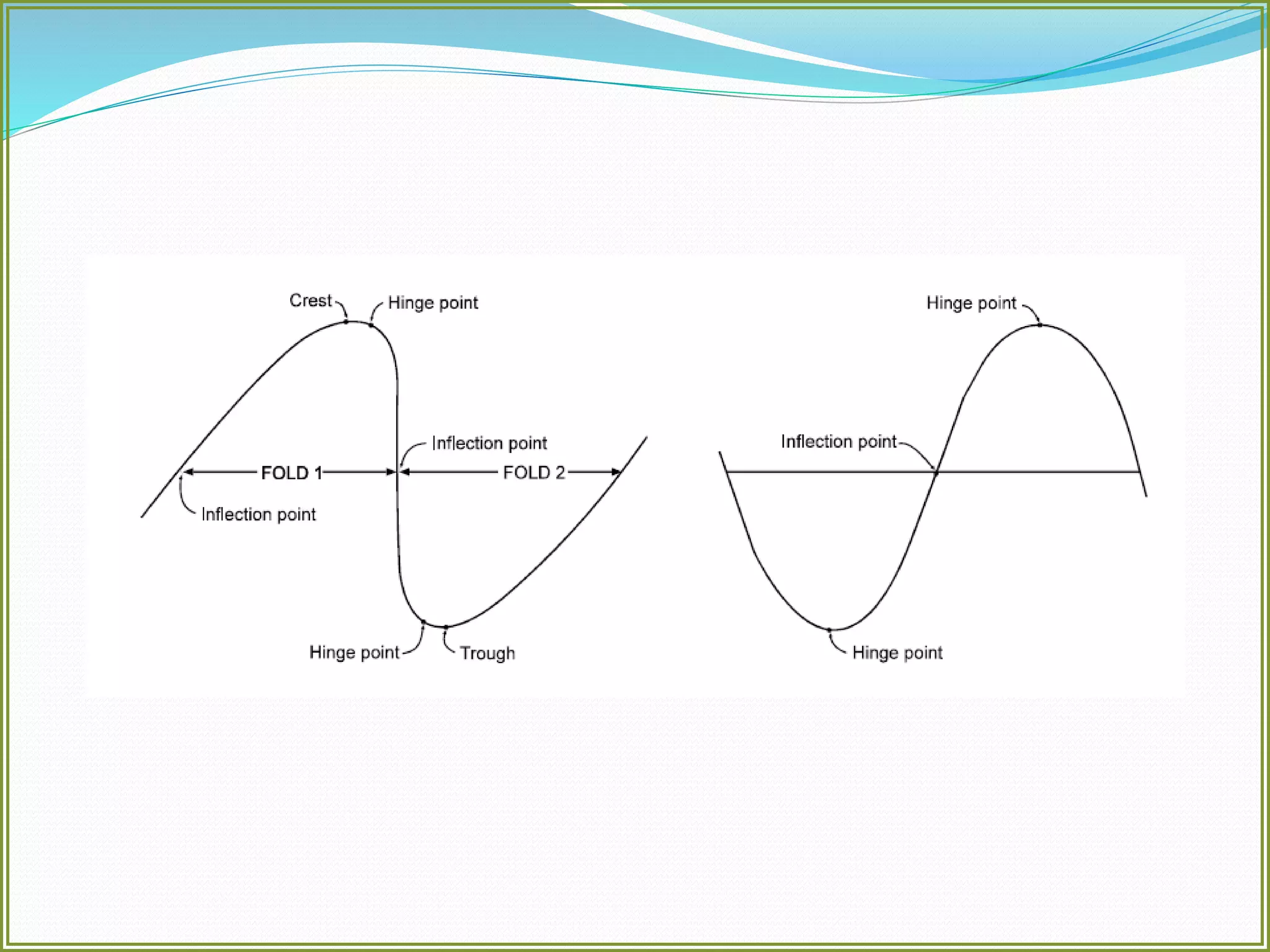
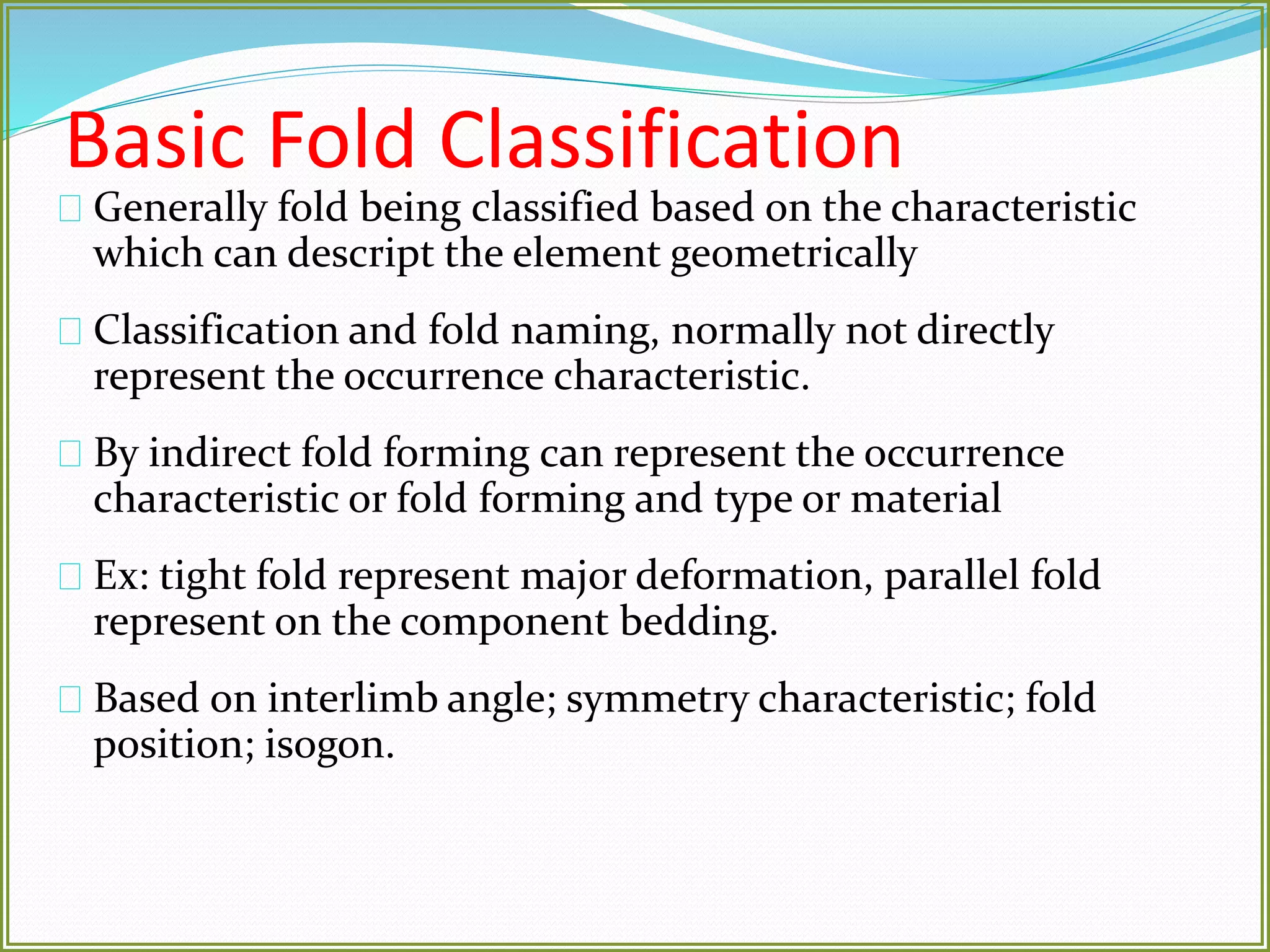
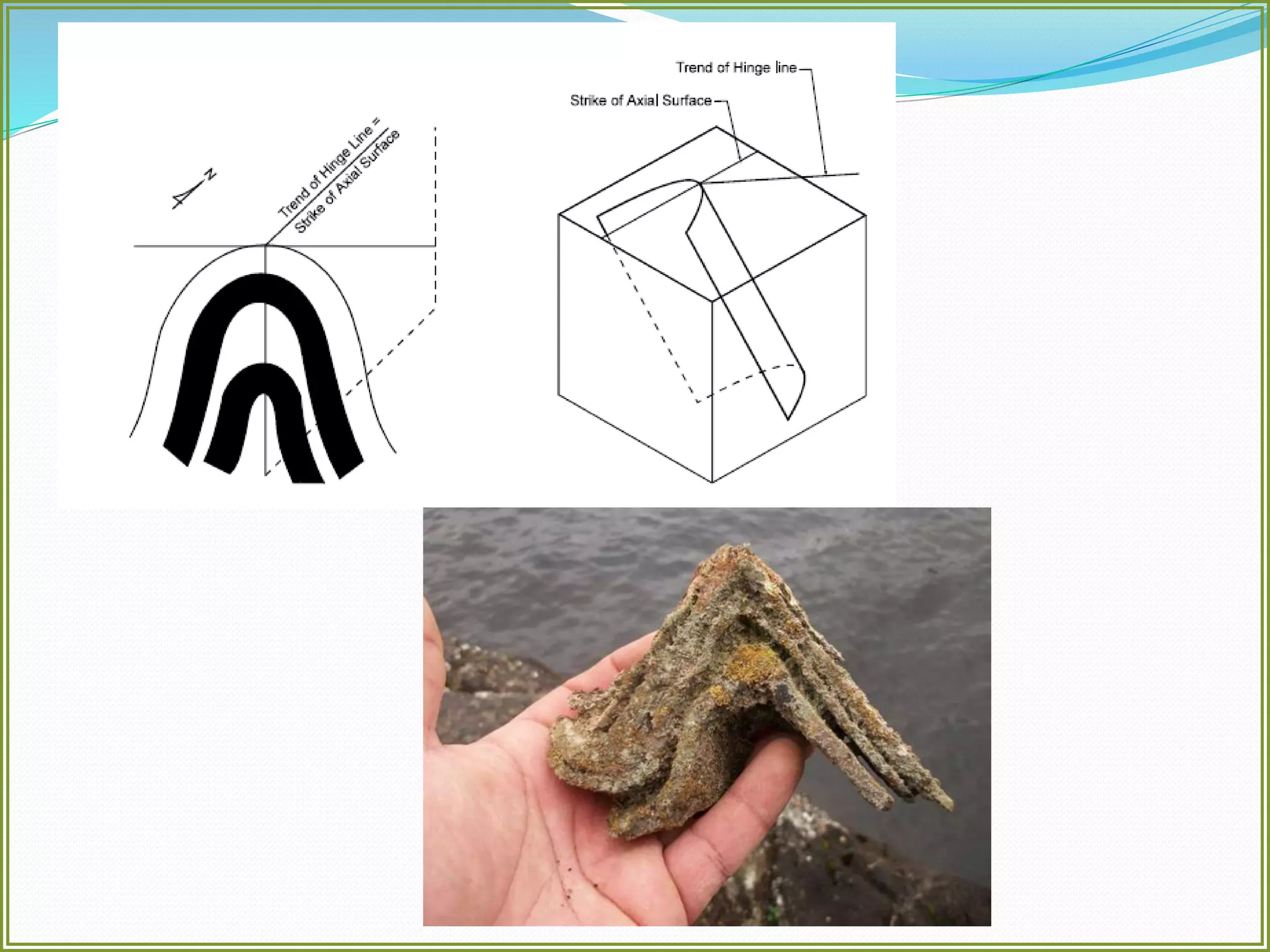
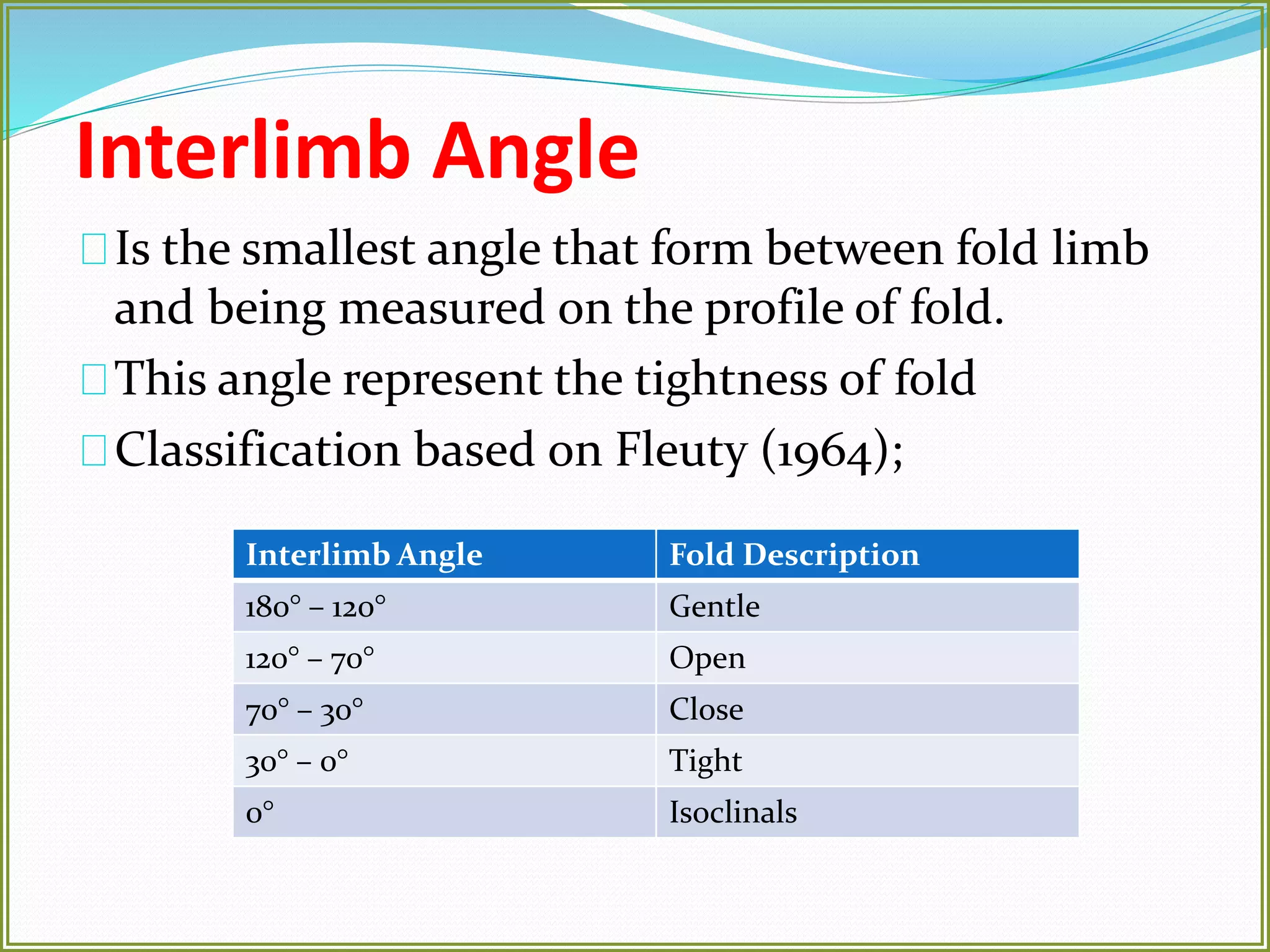
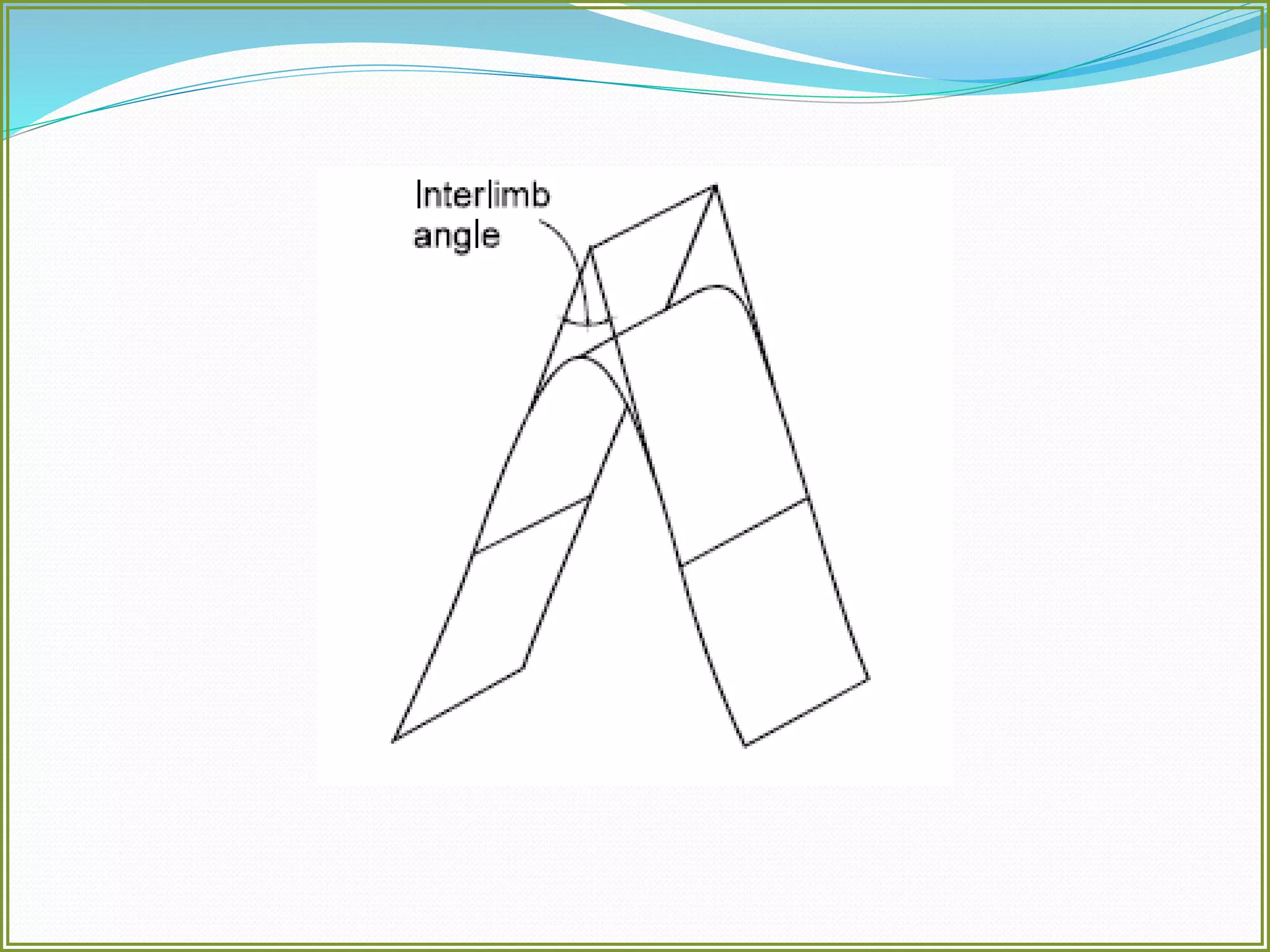
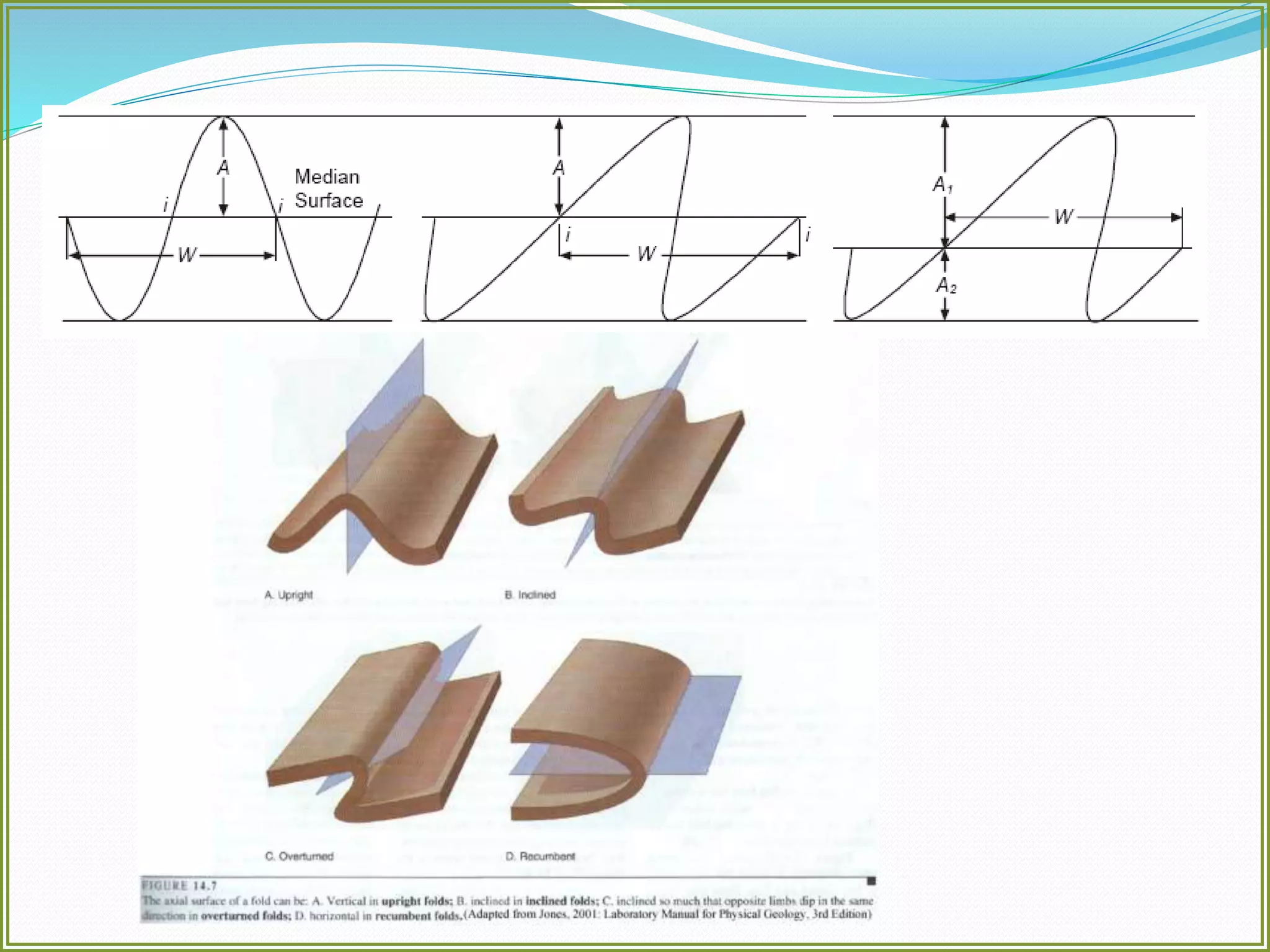
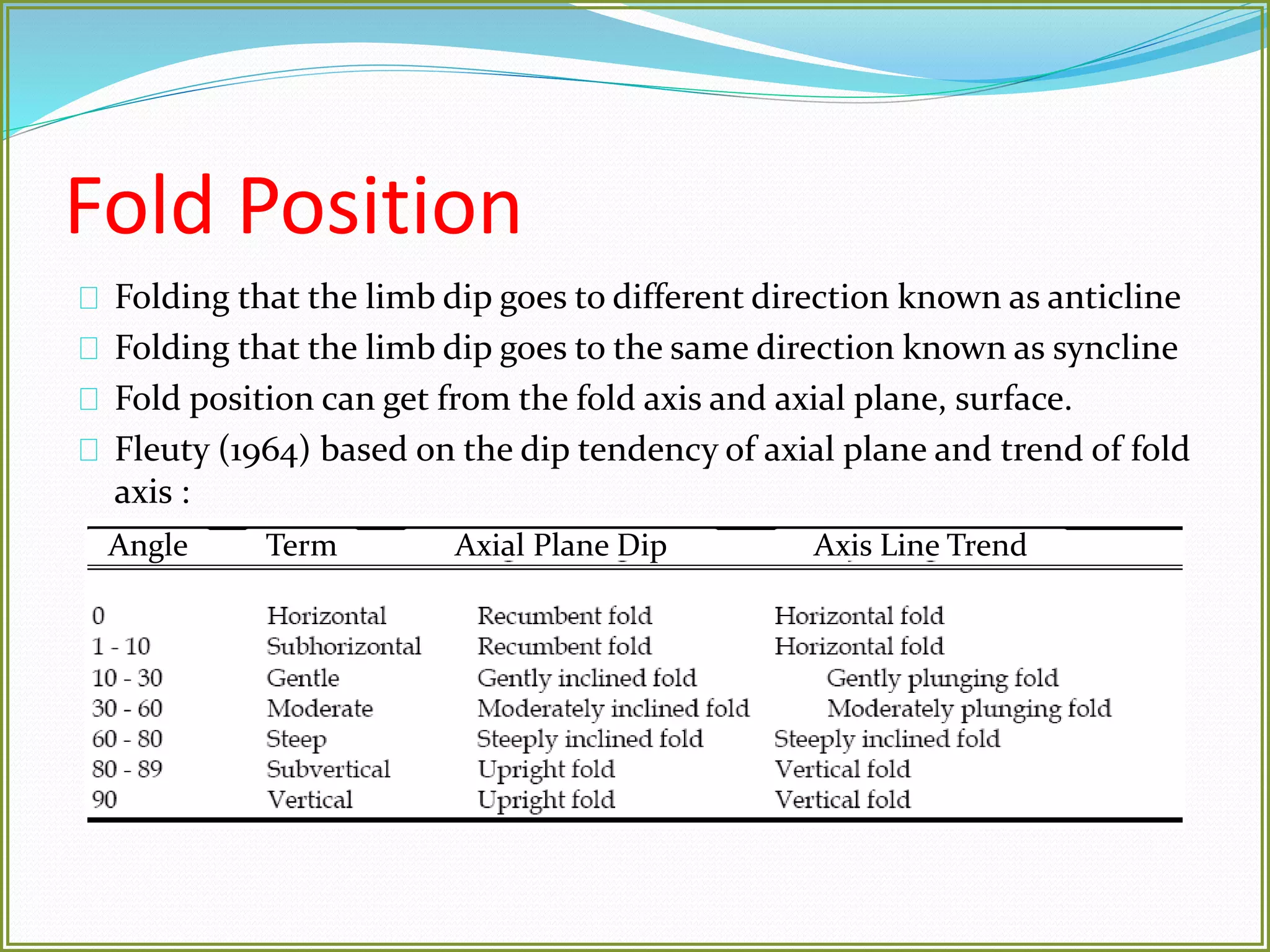
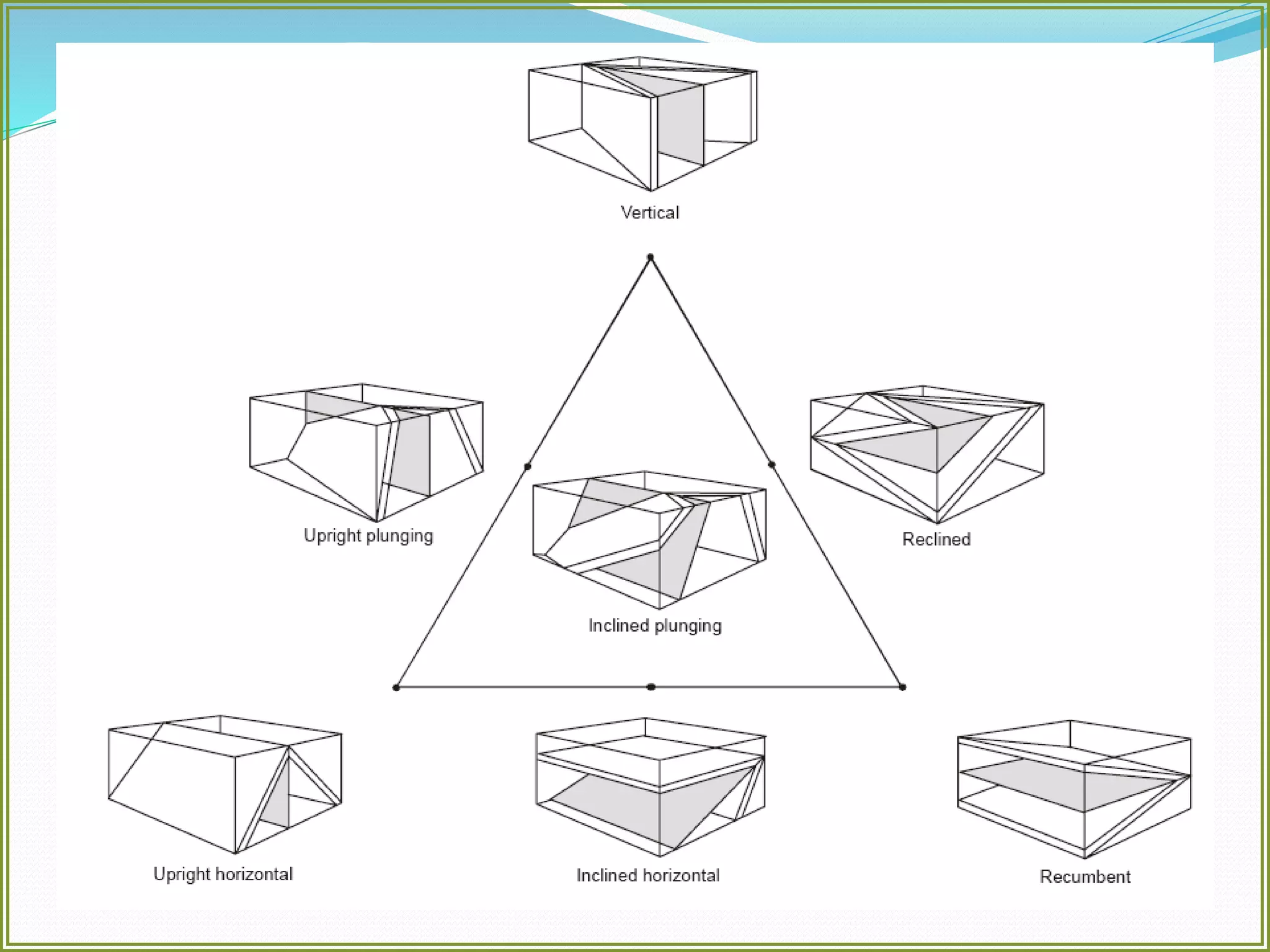
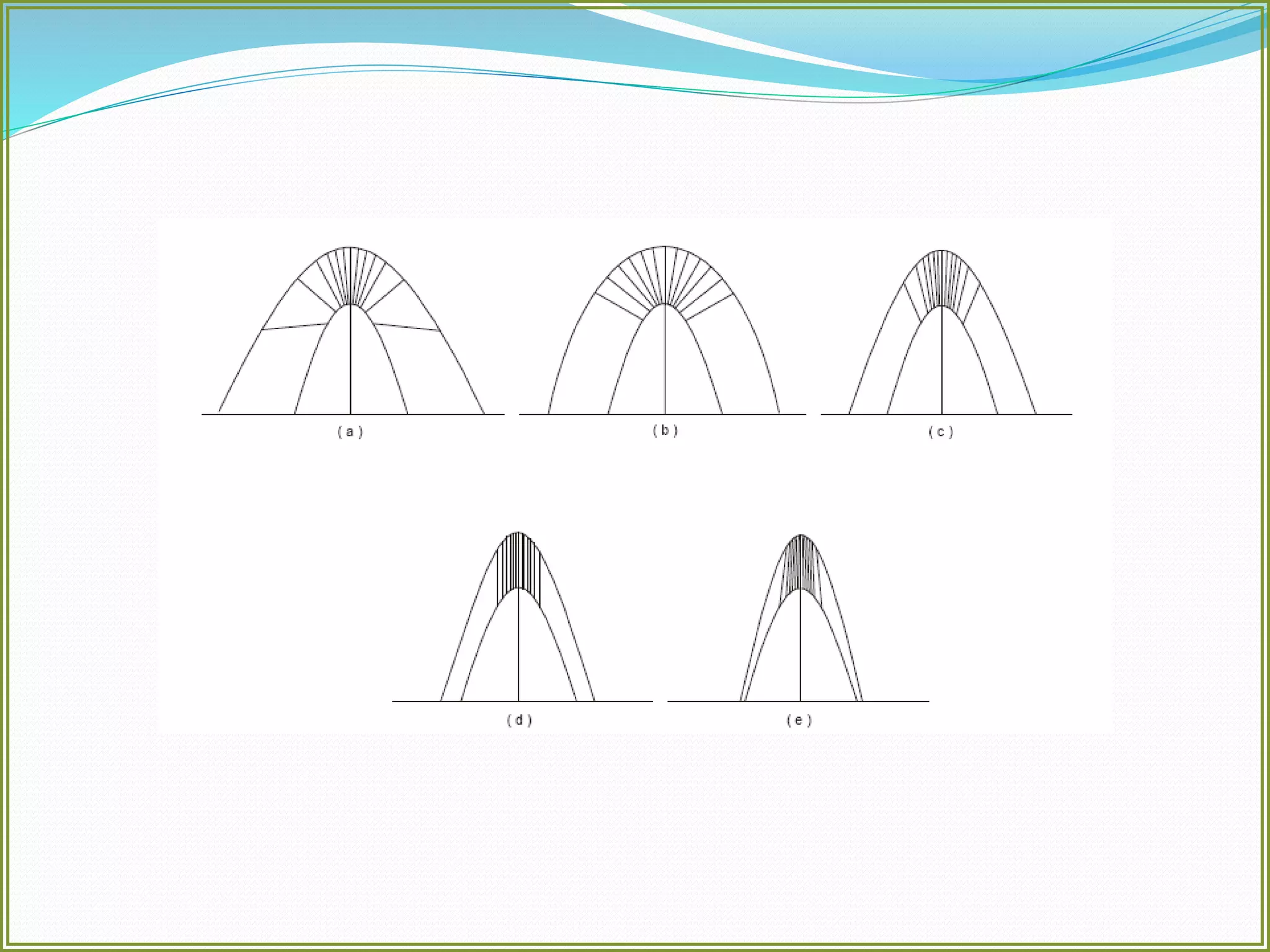
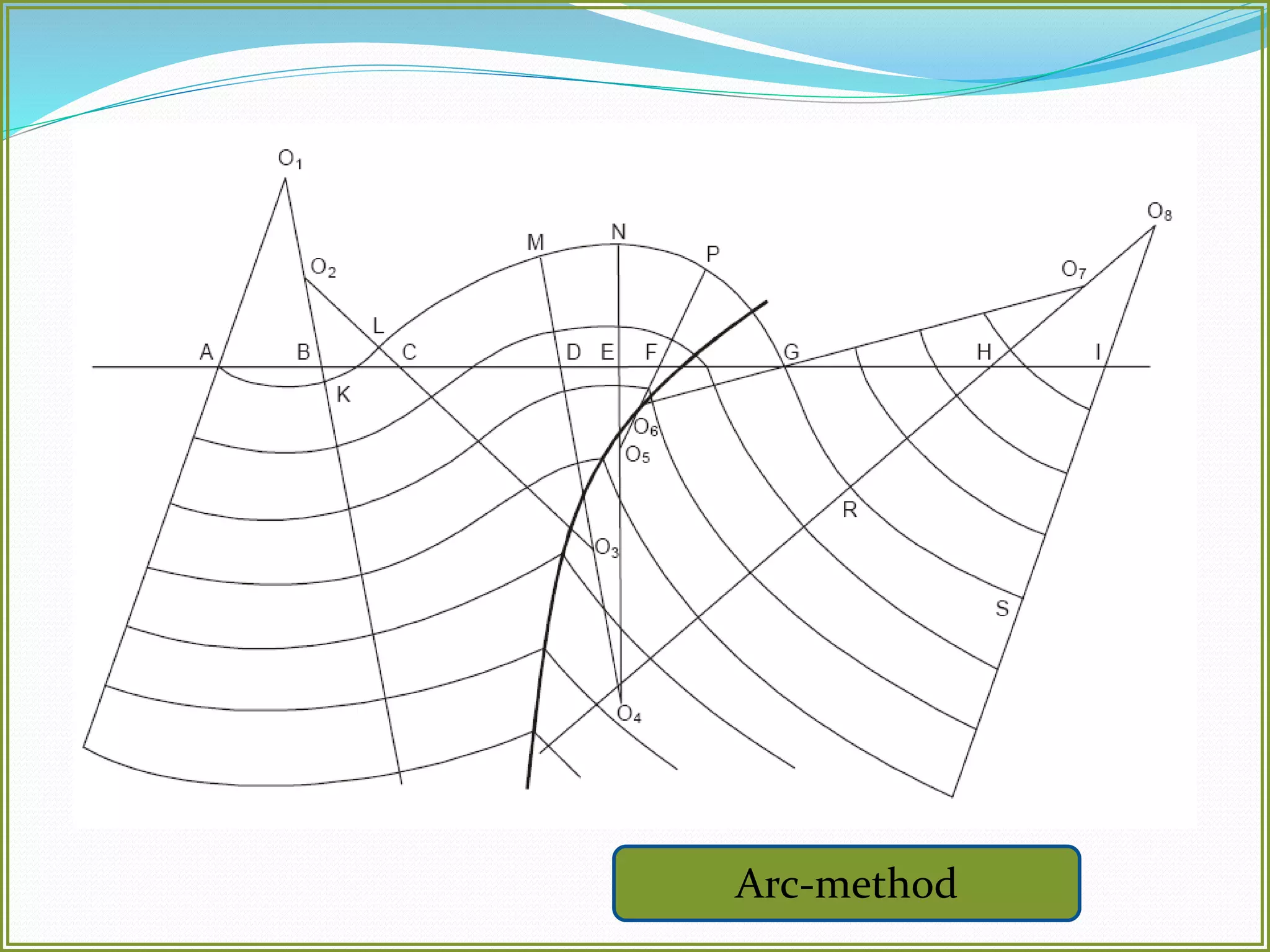
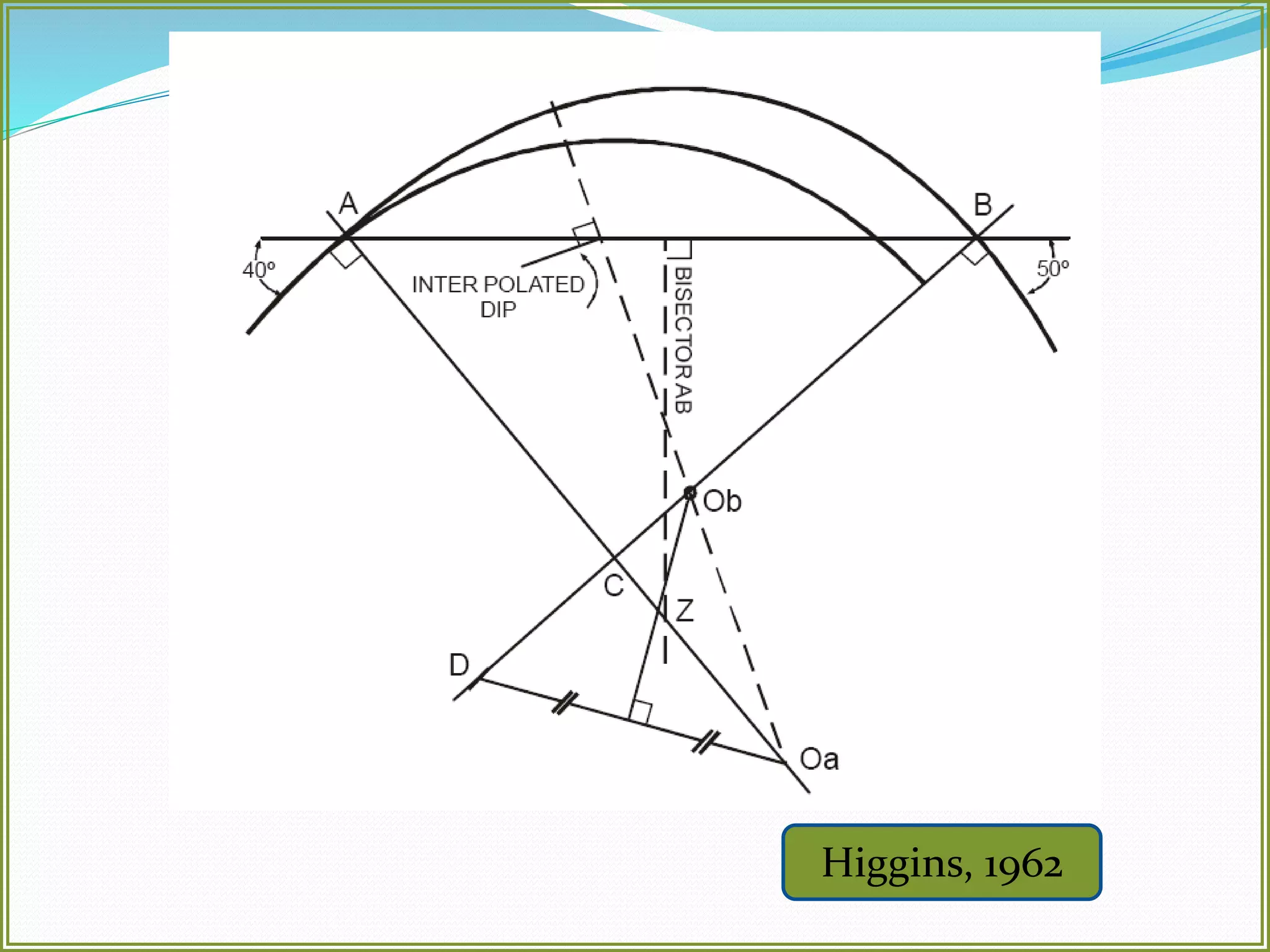
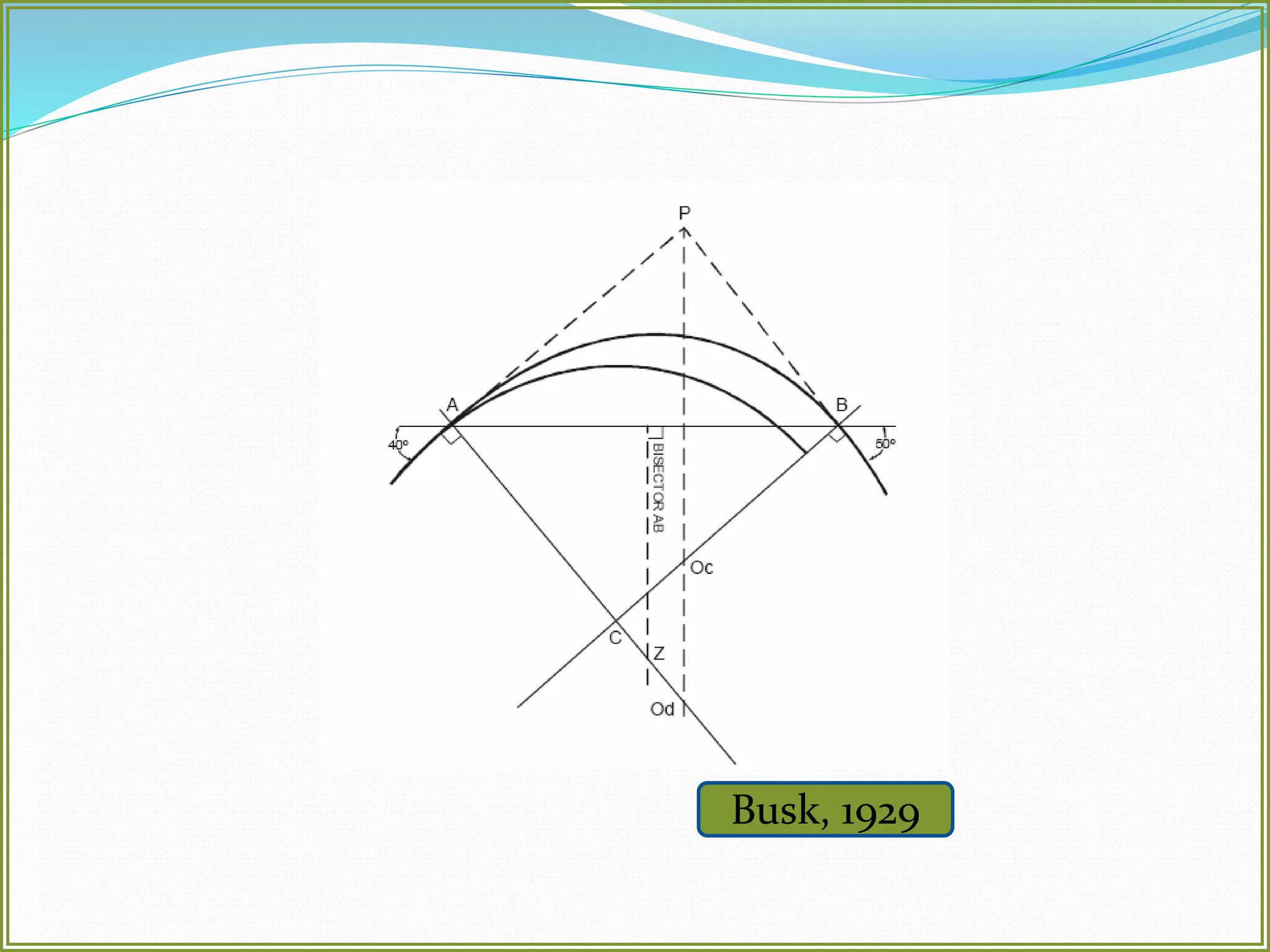
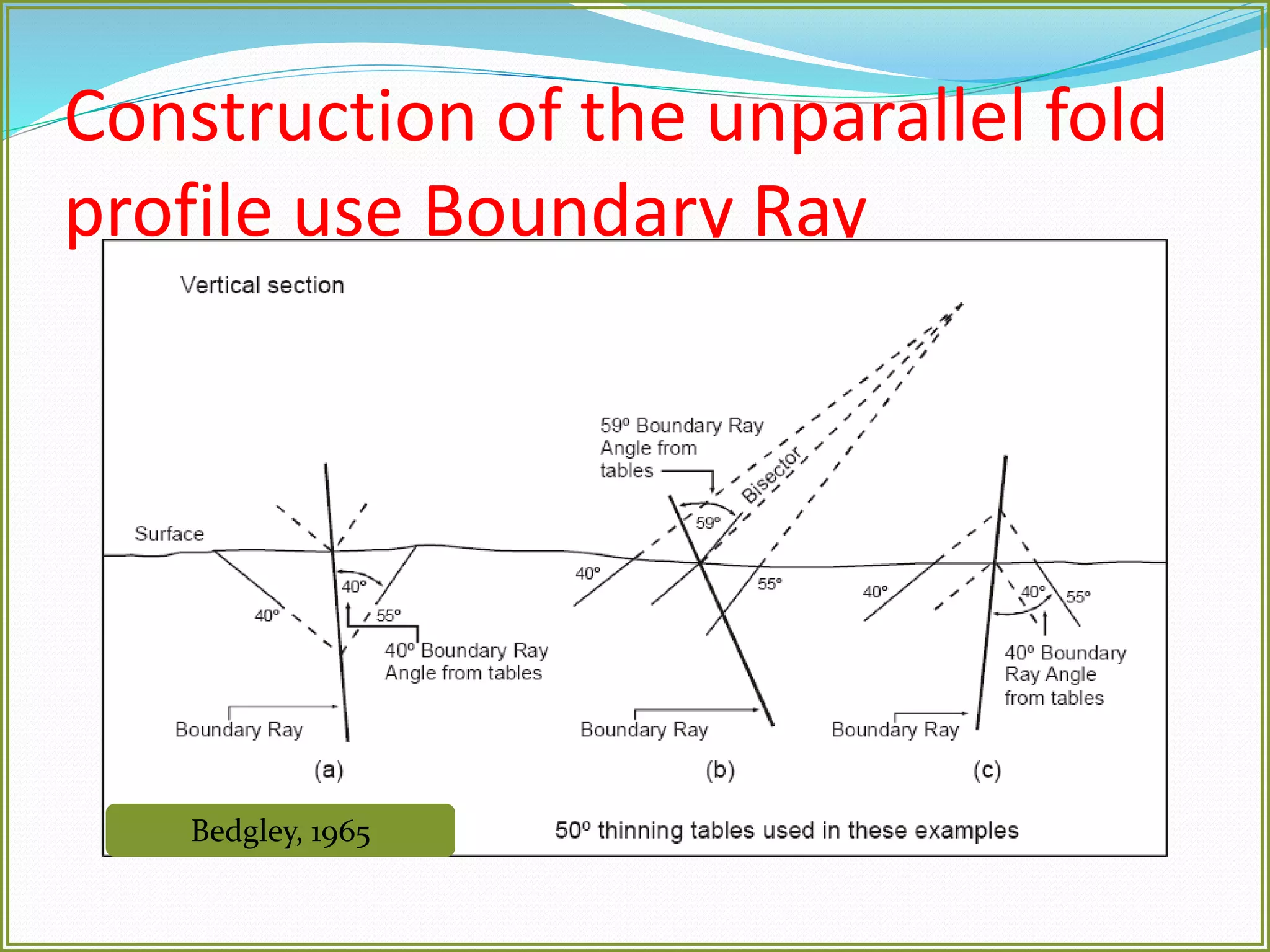
This document defines folds and describes their key elements and classification. Folds are shapes or volume changes in rock layers caused by deformation. They indicate stress and can be described geometrically. Folds are classified based on attributes like their interlimb angle, symmetry, position, and isogon characteristics. Gentle folds have interlimb angles from 180 to 120 degrees, while tight folds are from 30 to 0 degrees. Symmetric folds have symmetry planes, while asymmetric folds are monoclinal. Anticlines fold upwards and synclines fold downwards. The document also discusses methods for constructing fold profiles.