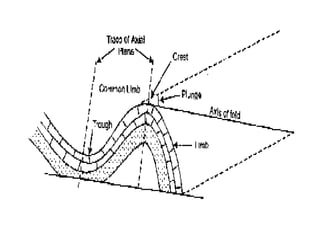
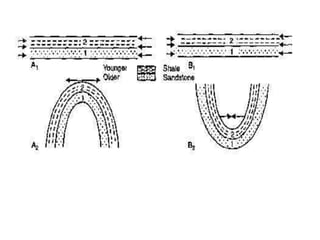
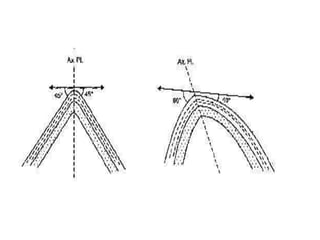
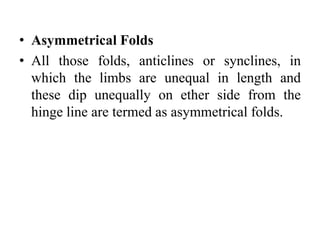
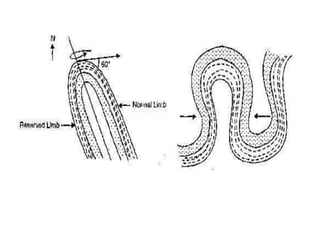
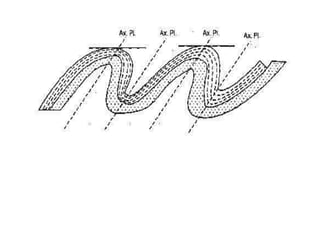
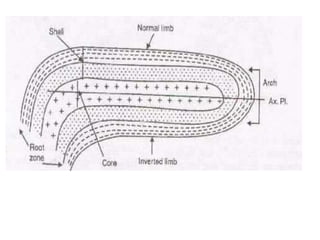
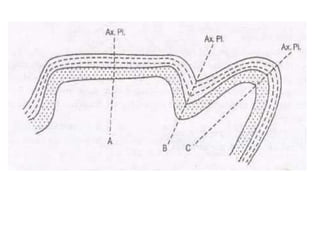
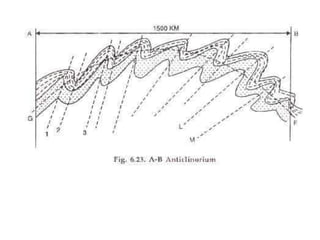
Folds are bends or curvatures that develop in rocks due to stresses. They can take many shapes depending on factors like force magnitude and direction. Folds develop slowly over geological time as rocks adjust to changing stress fields. They are classified based on whether the strata bend up (anticlines) or down (synclines). Additional classifications consider the position of the axial plane and relative dipping of the limbs. Complex fold types include overturned, recumbent, and box folds. Folds form over a range of scales from small individual structures to large regional folding.