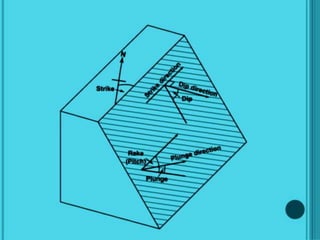
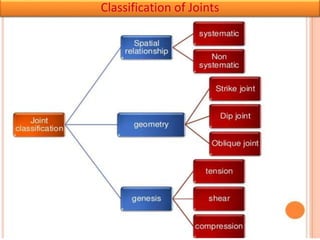
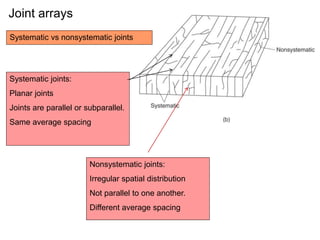
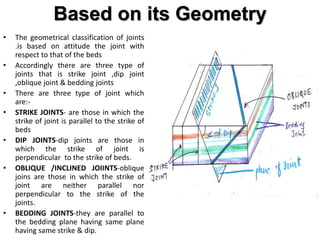
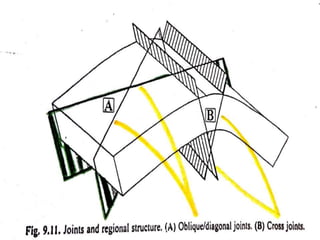
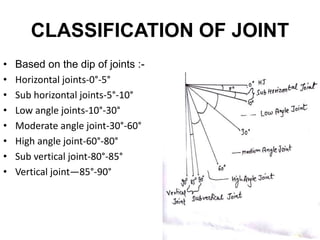
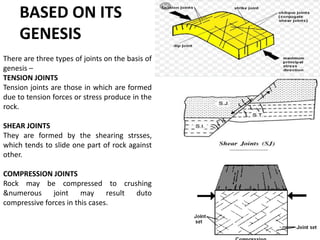
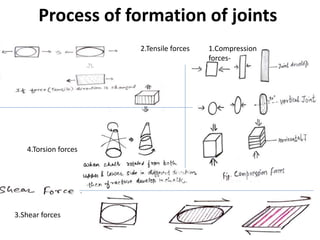
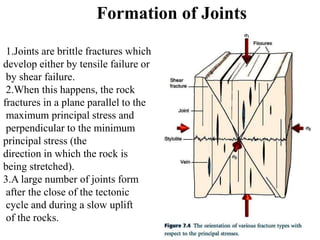
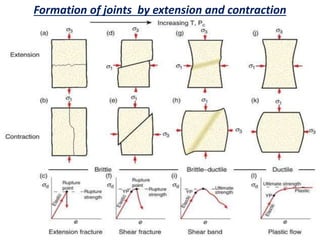
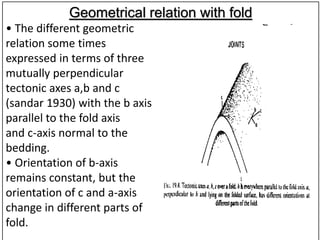
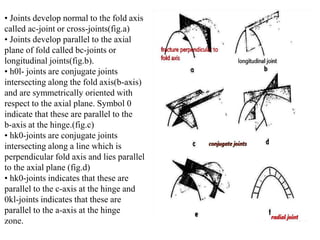
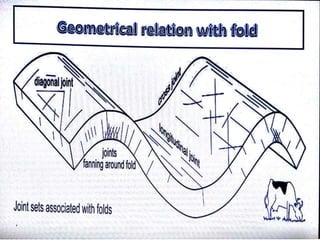
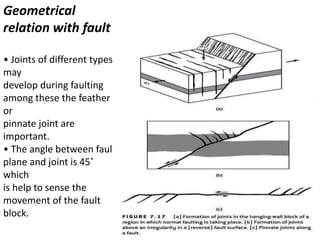
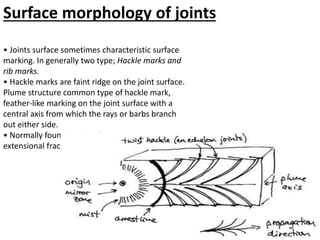
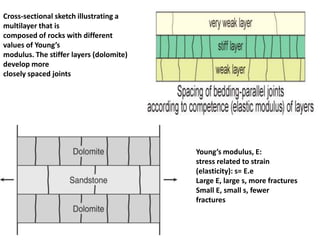
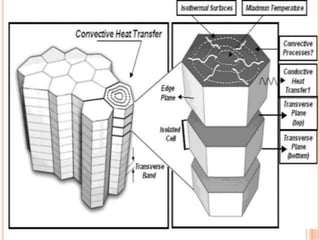
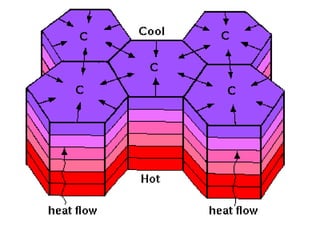
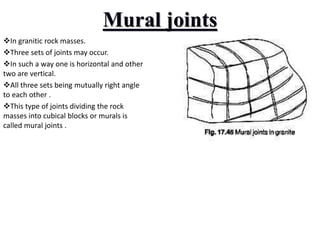
Joints are fractures in rock without displacement. They form due to tension, shear, or compressive stresses. Joints can be classified based on their orientation relative to bedding, their geometry, genesis, and dip. Systematic joints are parallel while nonsystematic joints have irregular distributions. Joints influence groundwater flow, construction, and are important in mining and resource exploration. They provide pathways for fluid migration and impact slope stability.
![A SEMINARON
JOINTS AND ITS CLASSIFICATION&
RECOGNITION OF JOINTS
DEPARTMENT OF APPLIED GEOLOGY
DR.HARISINGH GOUR VISWAVIDYALAYA,SAGAR [M.P.]
SUBMITTED TO –PROF.A.K. SHANDILYA SUBMITTED BY –SHIVAM JAIN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shivamjain-181209070235/75/joints-and-its-classification-and-its-recognition-1-2048.jpg)