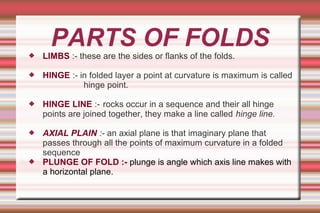
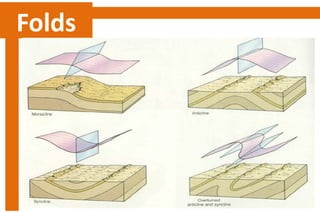
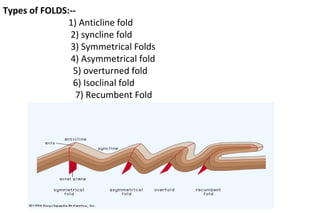
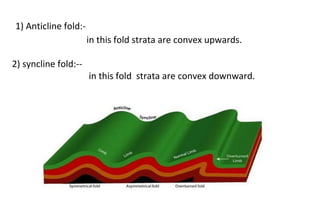
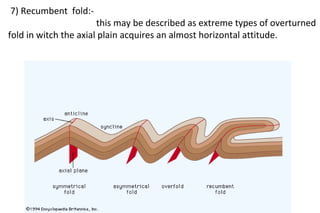
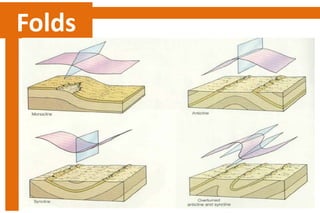
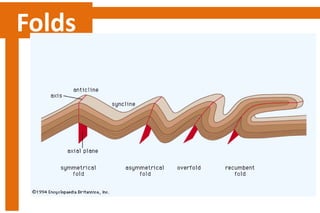
Folds are bends or curvatures in rock layers caused by stresses in the Earth's history. The shape of a fold depends on factors like the nature, magnitude, and direction of forces, and the type of rock. Folds have key parts like limbs, the sides of the fold, a hinge where curvature is greatest, and a hinge line or axial plane connecting all hinge points. Folds also have a crest at the top of an upfold or a trough at the bottom of a downfold. There are several types of folds including anticlines that bend upward, synclines that bend downward, symmetrical folds with equal limbs, and asymmetrical folds with unequal limbs.