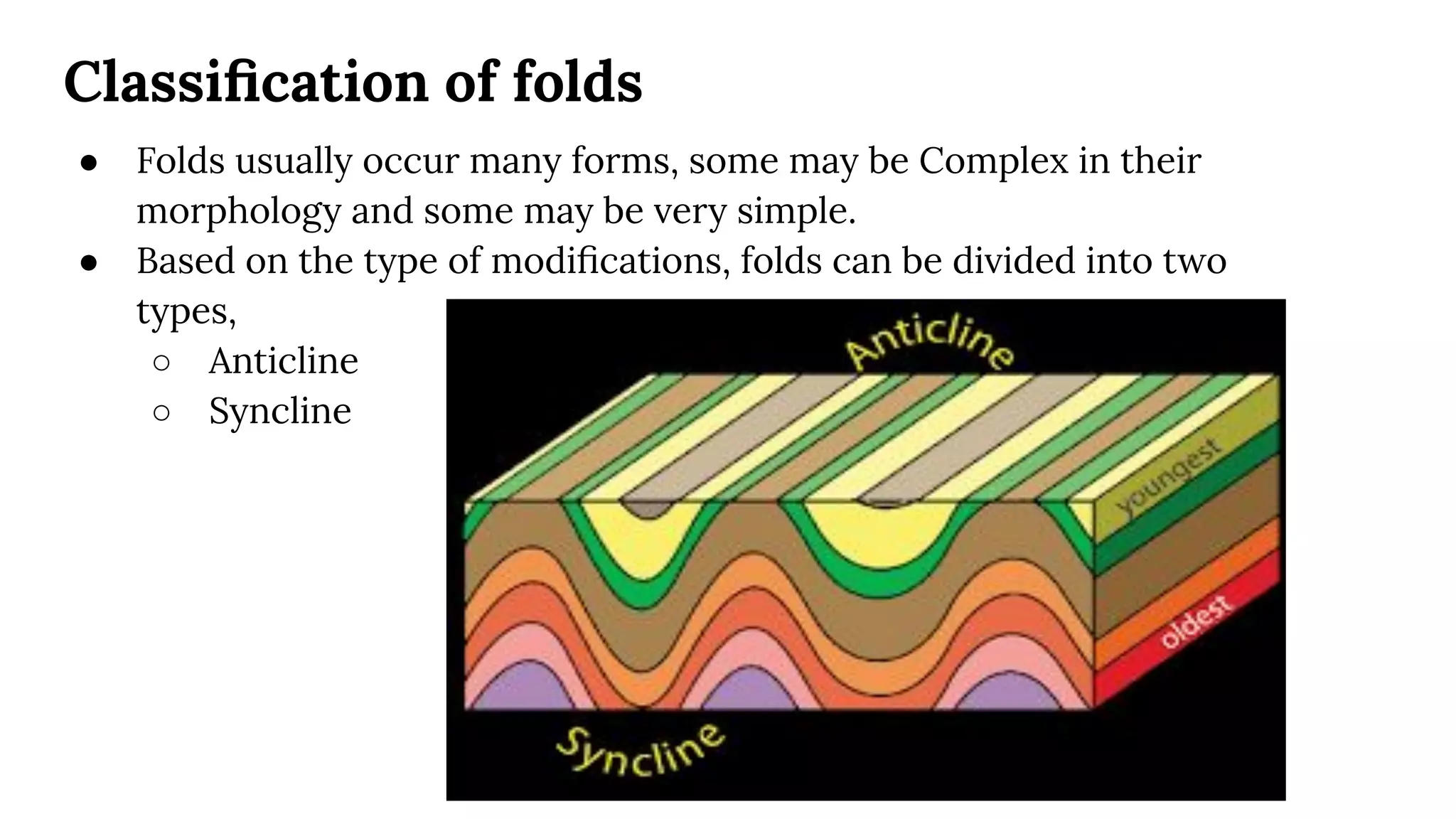
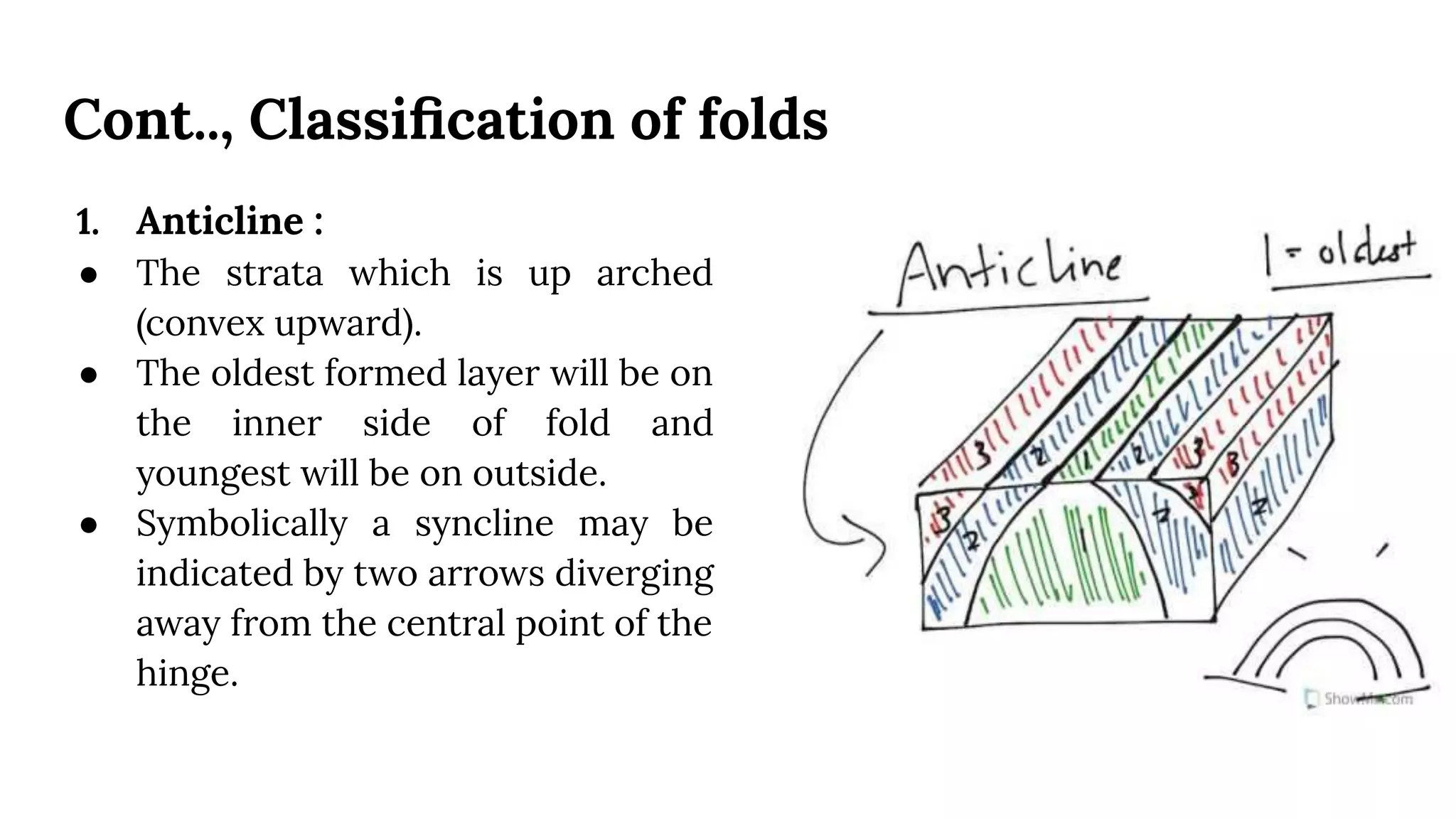
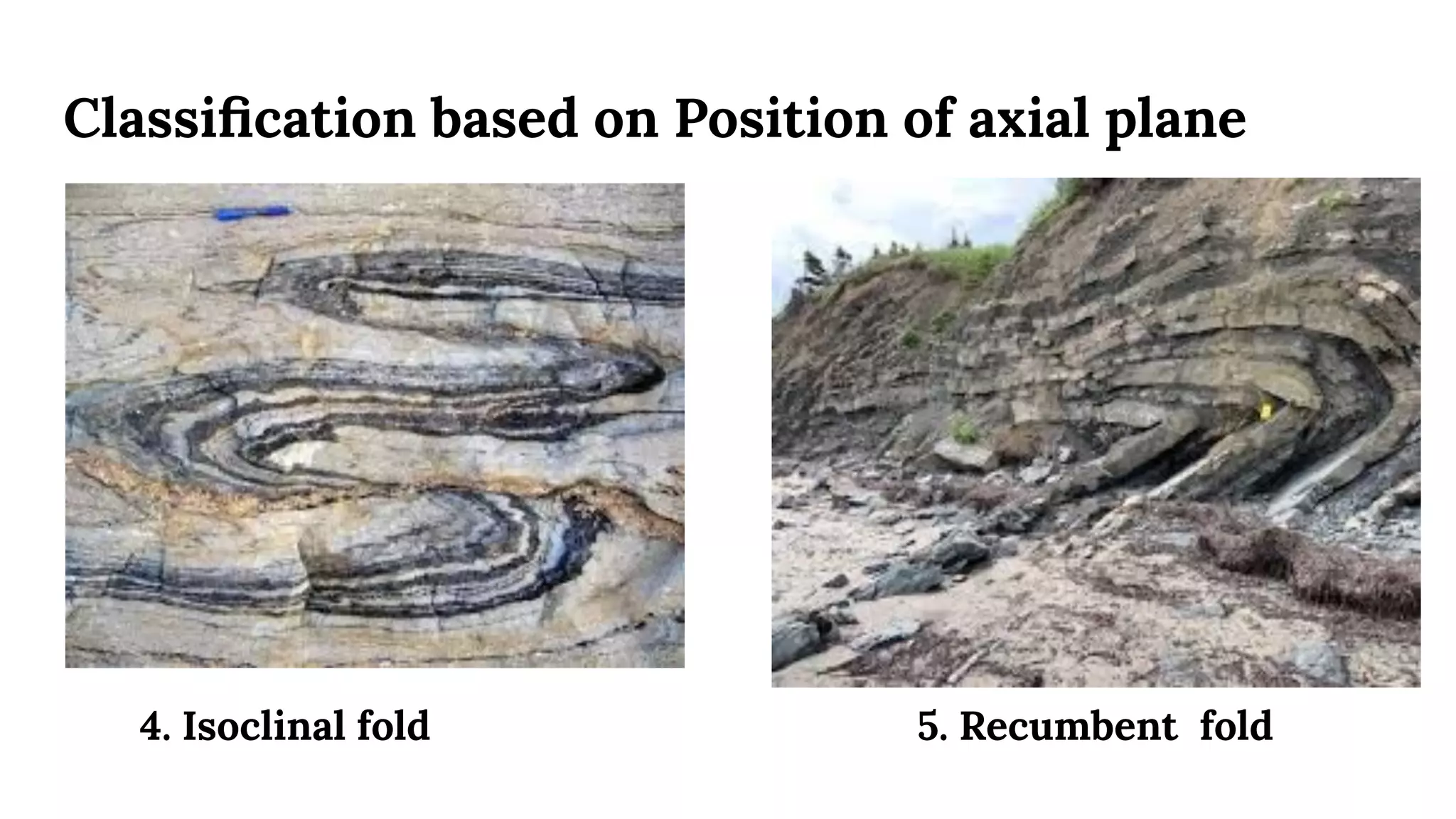
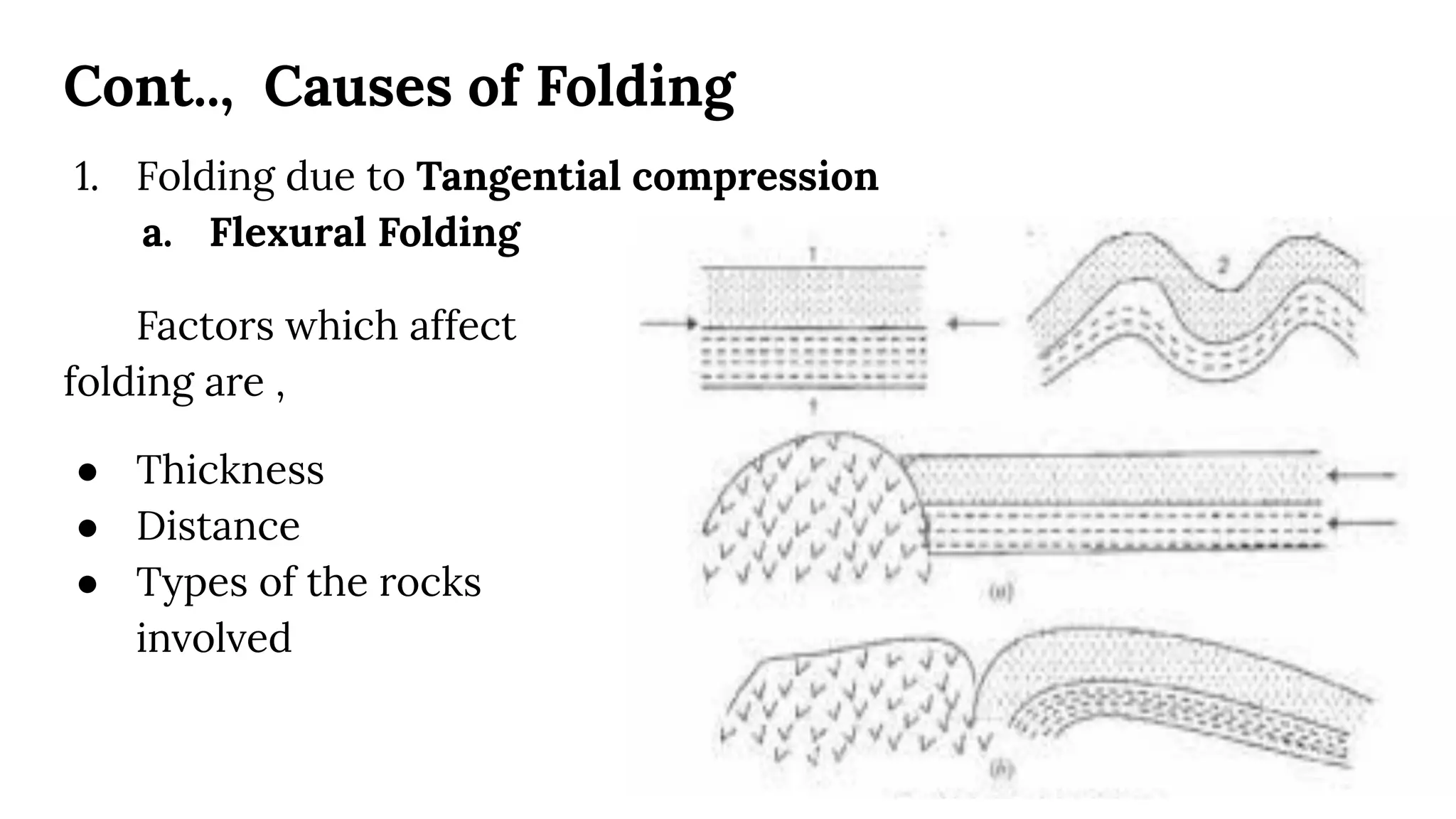
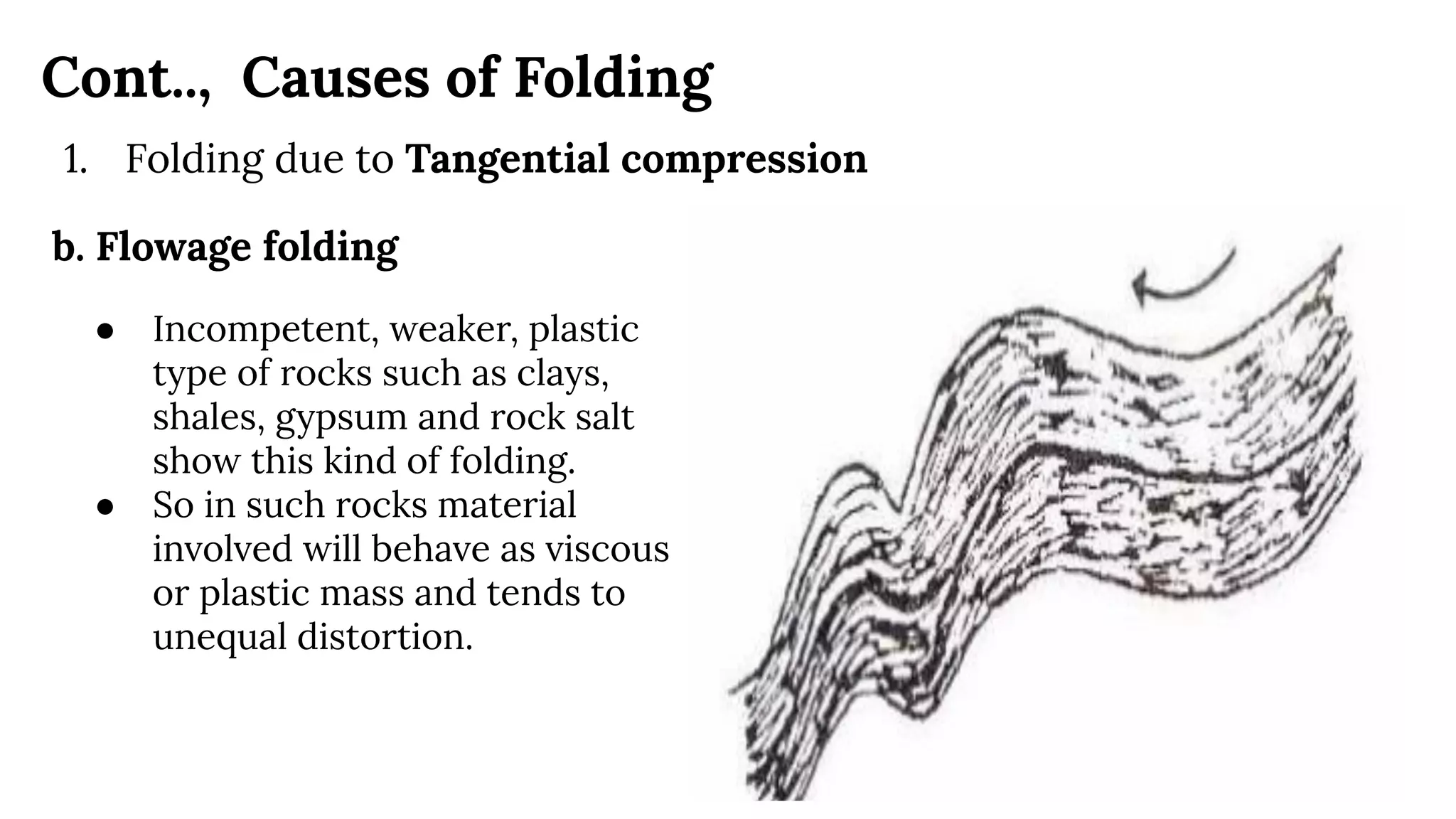
This document discusses structural geography and stratigraphy, specifically focusing on folds and folding. It defines folds as bends or curvatures in rock surfaces developed due to stress during formation. It describes the key parts of folds, including limbs, hinges, axial surfaces, and plunge. Folds are classified as anticlines, which are upfolded, or synclines, which are downfolded. Additional classifications are based on parameters like axial plane position, curvature, and plunge. Causes of folding include tangential compression, intrusions, and differential compression. Field observations and engineering considerations of folds are also discussed.