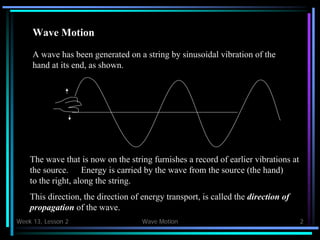
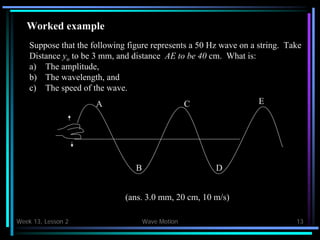
This document provides an overview of wave motion concepts including wave propagation, types of waves, wave terminology, speed of transverse waves, standing waves, and resonance. Key points covered include:
- Transverse waves have vibration perpendicular to propagation direction, while longitudinal waves have parallel vibration.
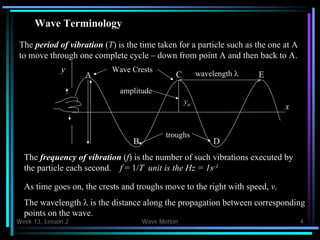
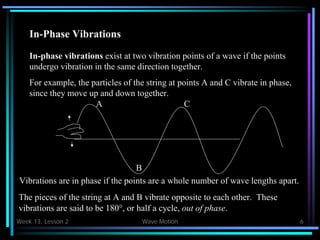
- Period, frequency, wavelength, speed, and phase are defined for waves.
- The speed of a transverse wave depends on the tension and linear mass density of the string.
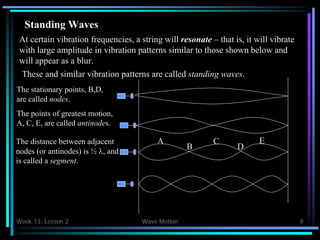
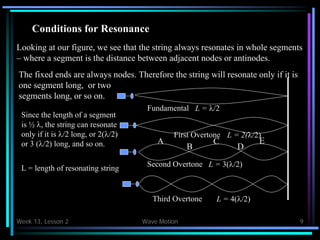
- Standing waves occur at resonant frequencies when the string length is an integer multiple of half wavelengths.