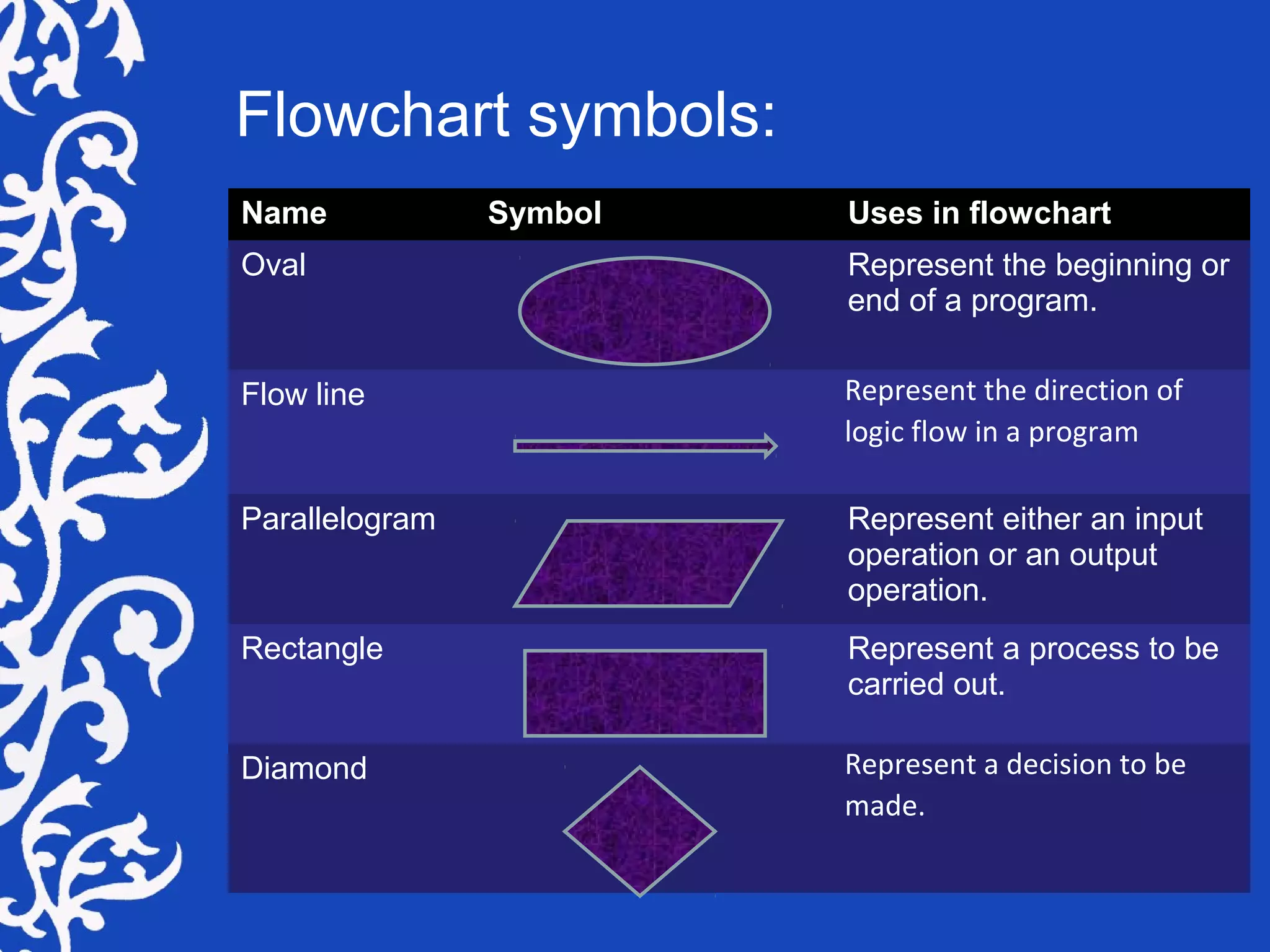
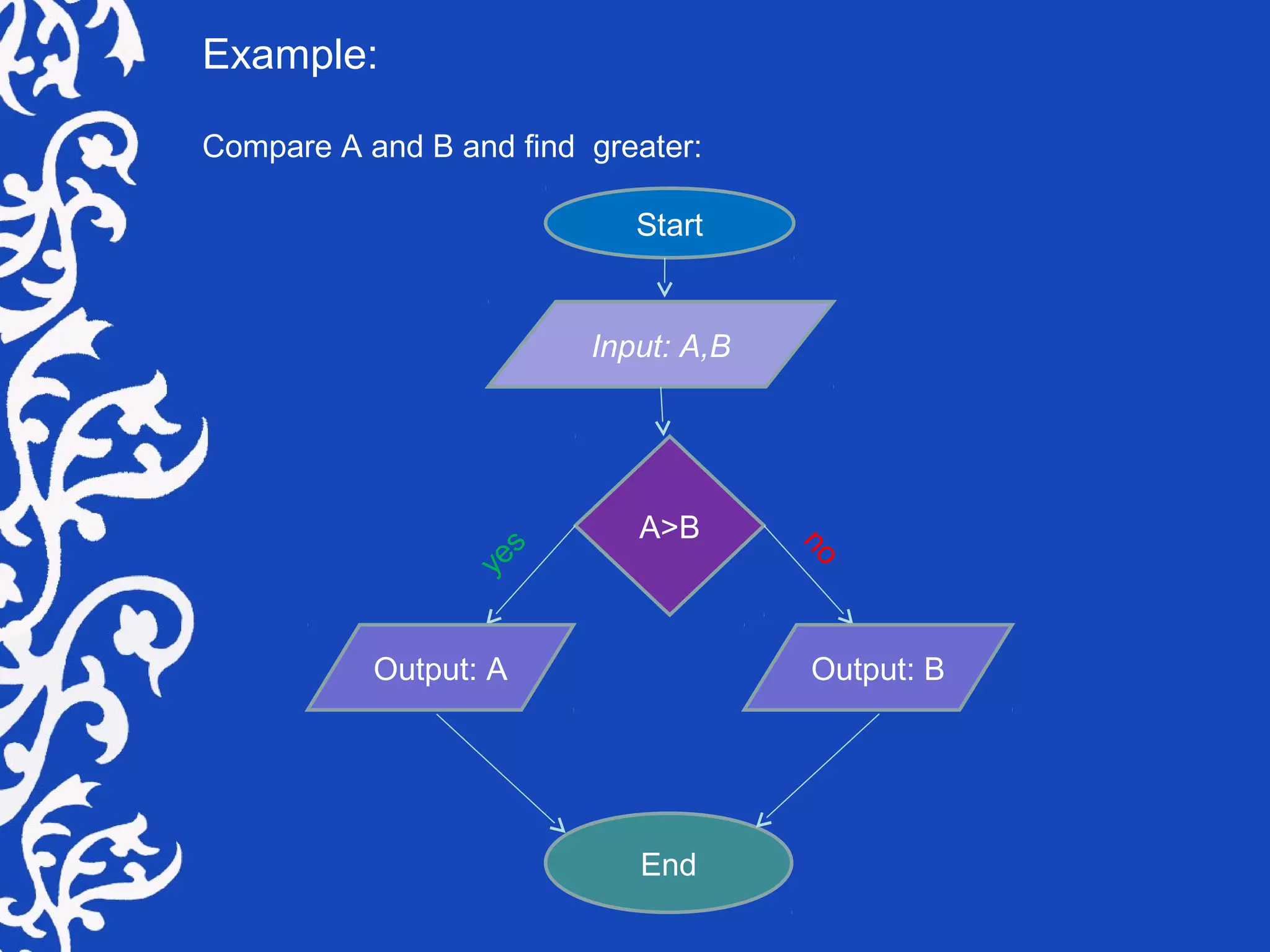
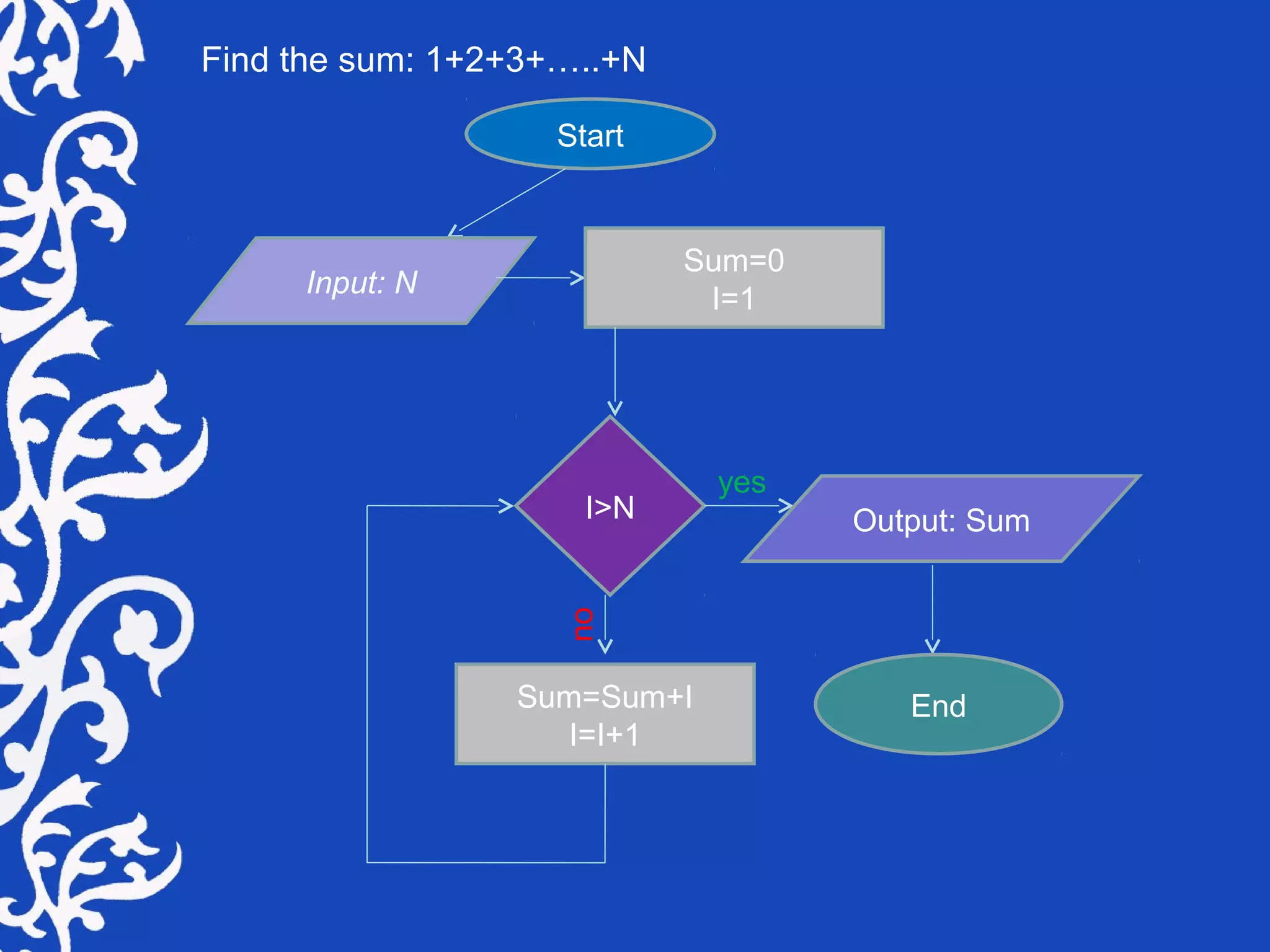
A flowchart is a visual representation of steps to solve problems, complete tasks, or illustrate system components, primarily used in programming and process documentation. It employs various symbols to represent processes, inputs, outputs, and decisions, offering a clear and concise overview of logic flows. Despite a decline in use with the rise of object-oriented programming, flowcharts remain valuable for modeling complex logic and documenting processes.