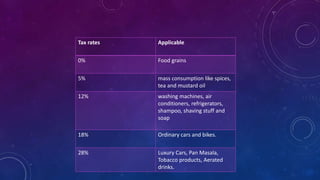
The document discusses the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India, which consolidates multiple indirect taxes into a single value-added tax to reduce tax cascading effects and simplify the taxation system. It highlights the advantages of GST, such as ease of doing business, increased foreign investment, and reductions in compliance burdens and inventory costs. Additionally, it outlines GST tax rates and its impact on various sectors, including economic growth and consumer prices.