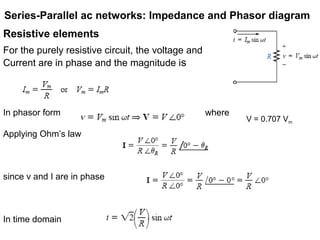
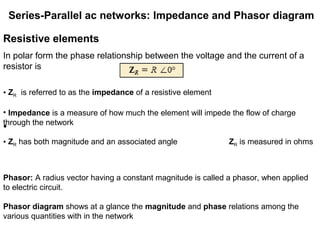
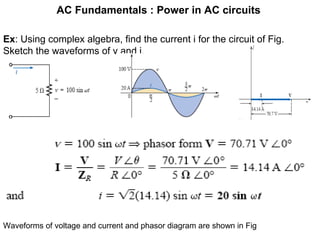
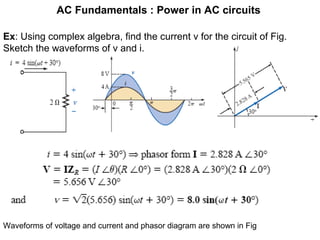
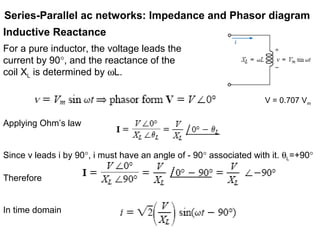
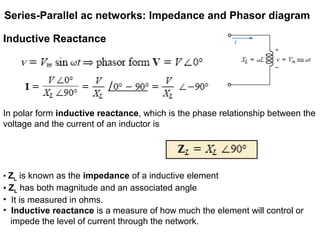
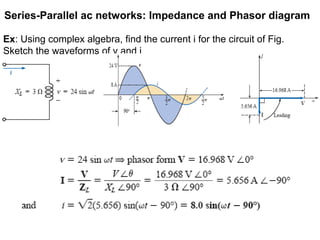
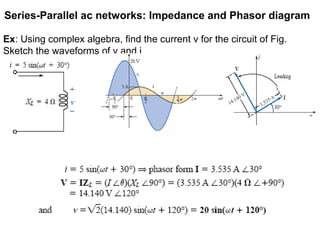
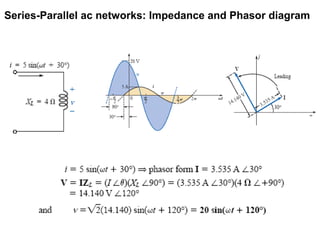
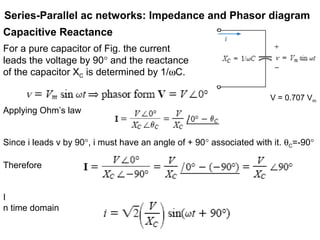
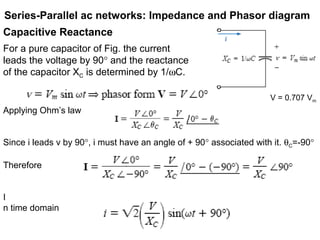
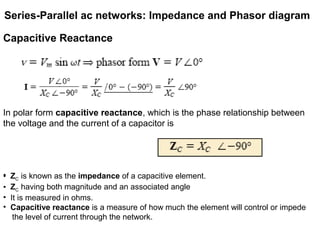
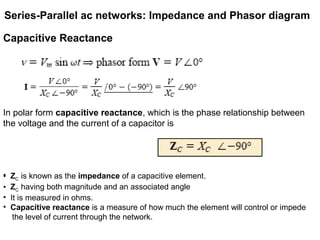
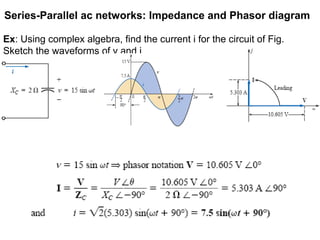
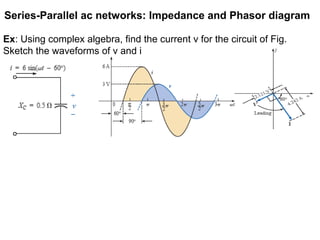
The document discusses series-parallel AC networks, focusing on impedance and phasor diagrams for resistive, inductive, and capacitive elements. It explains the phase relationships between voltage and current in these circuits, utilizing complex algebra for calculations. Additionally, it outlines how impedance affects current flow and describes the measurement units involved.