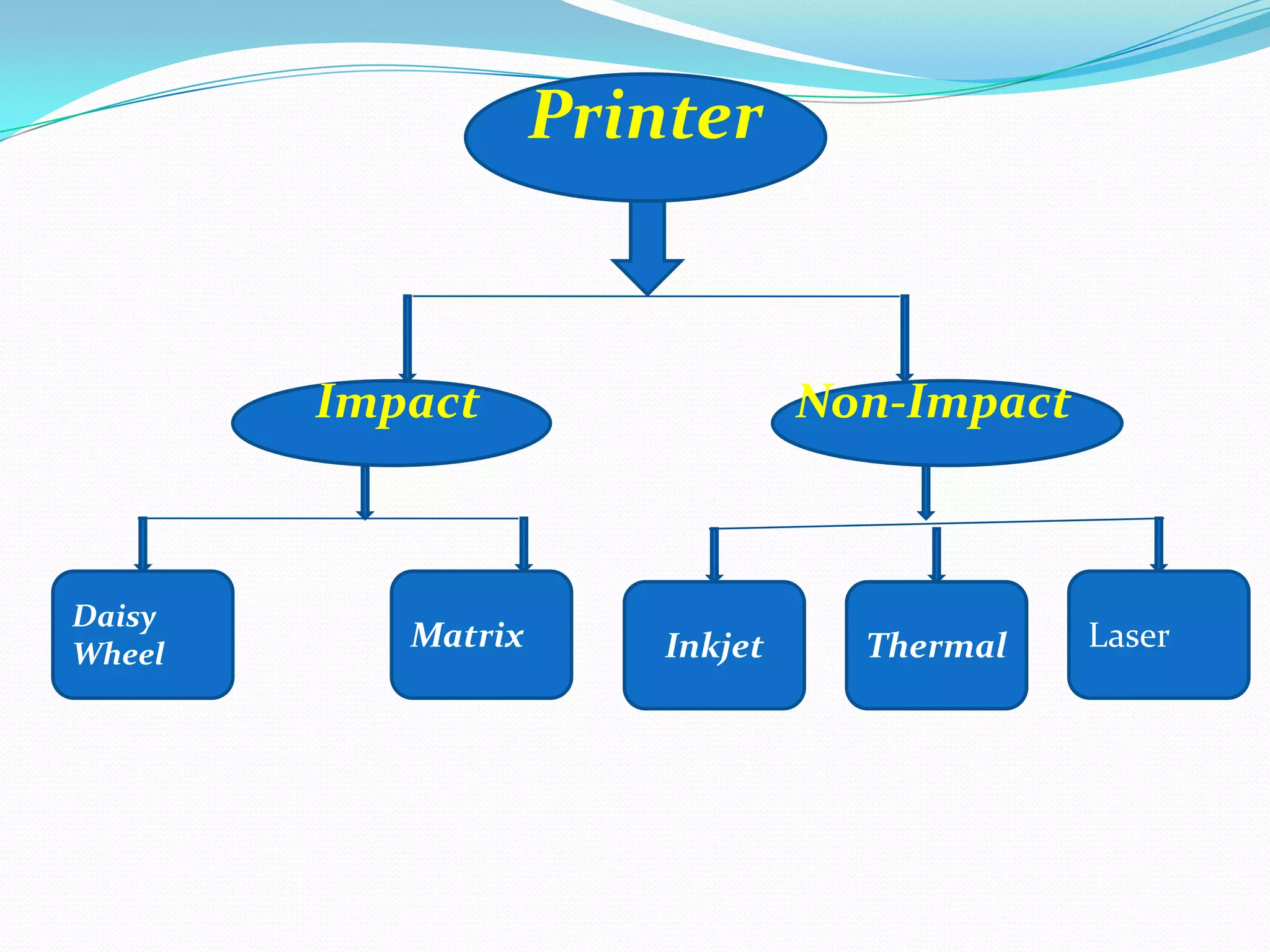
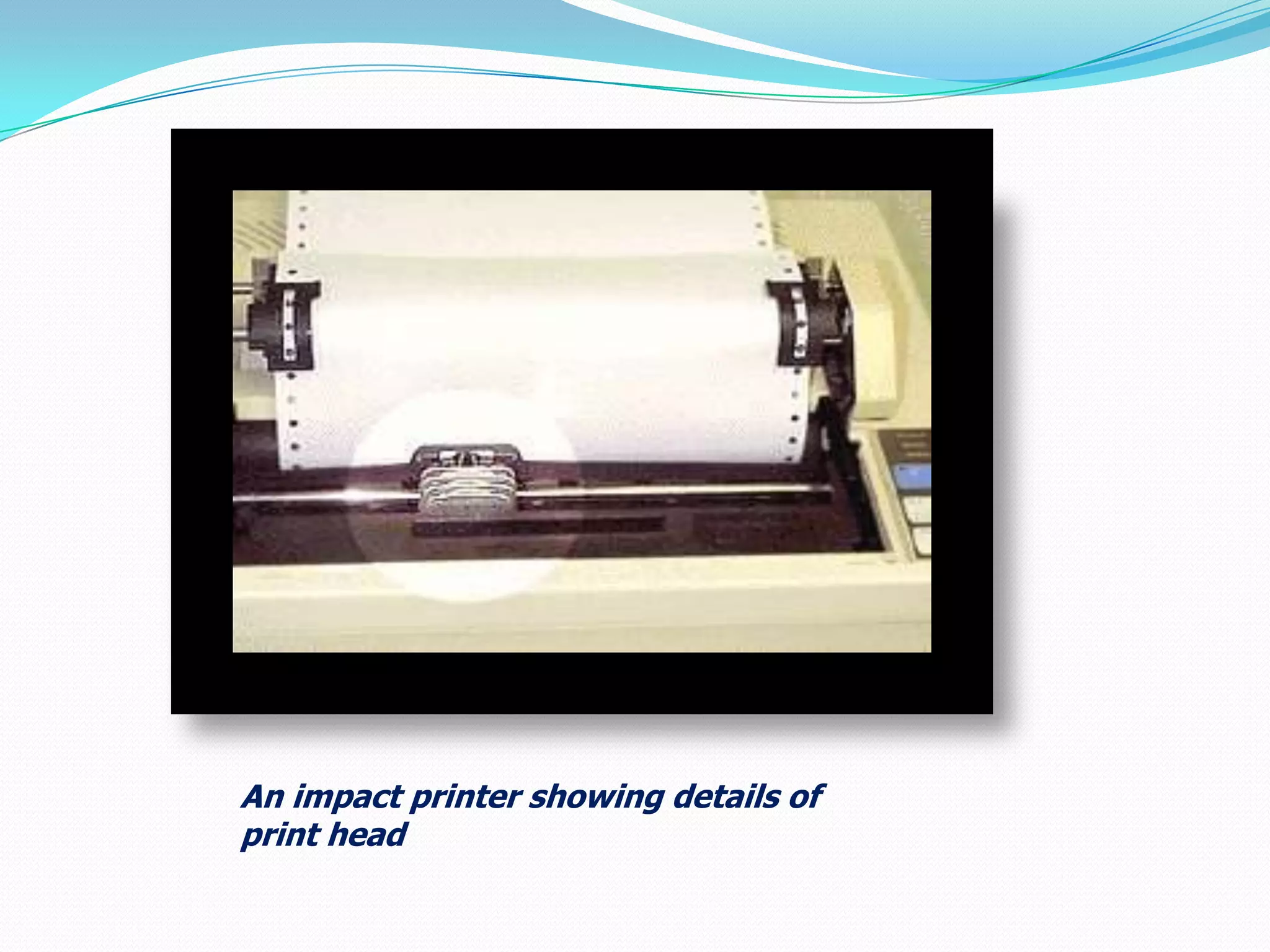
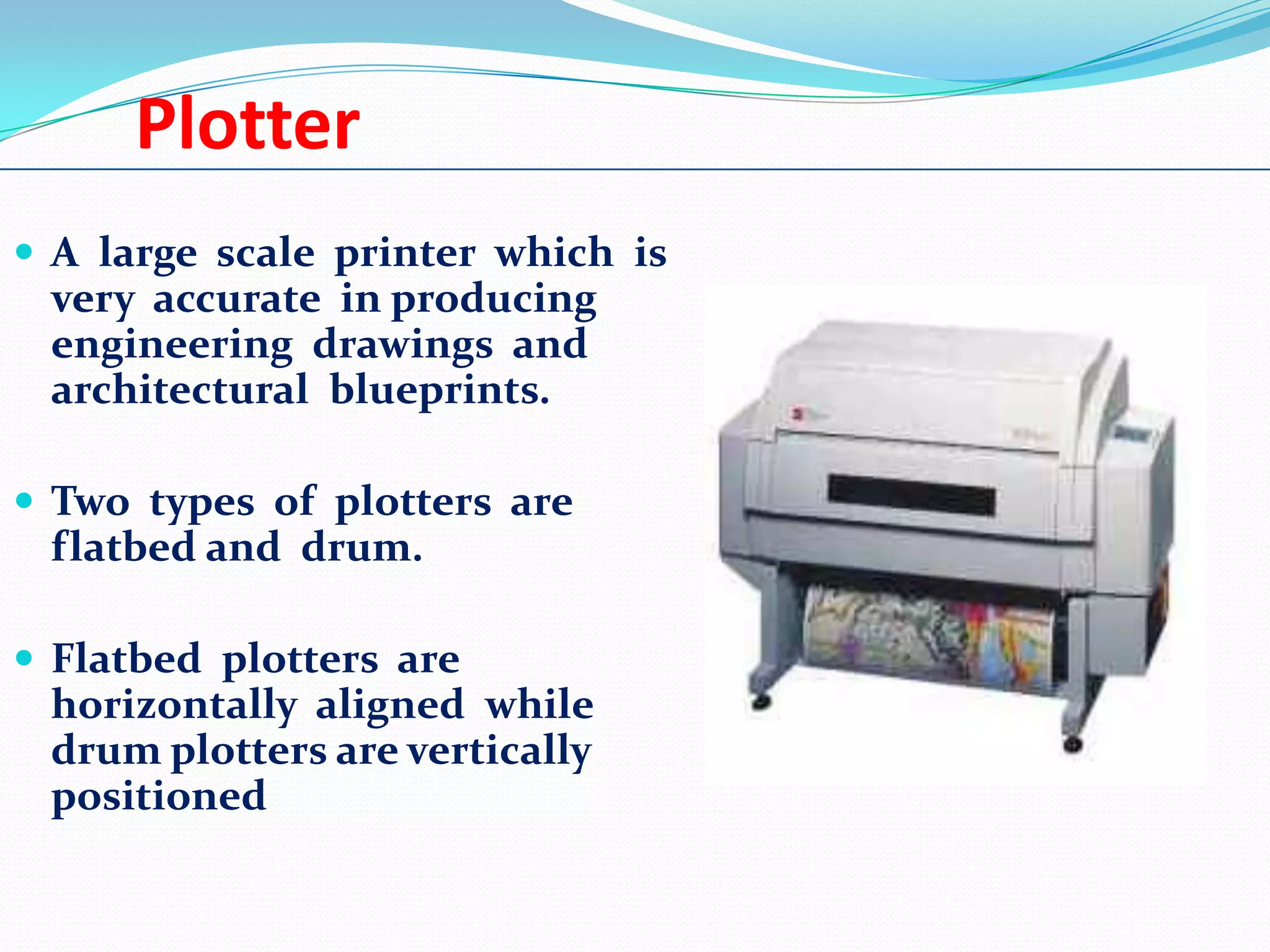
This document provides an overview of different types of printers. It begins by discussing the history of printing, including the invention of electrophotography in 1938 and the first high-speed printer for computers in 1953. The document then defines printers and categorizes them as either impact or non-impact. Specific impact printers discussed include dot matrix, daisy wheel, and thermal printers. Non-impact printers covered are inkjet, laser, multi-function, and 3D printers. The document concludes by emphasizing the importance of printers for utilizing computer resources.