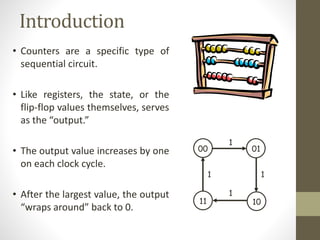
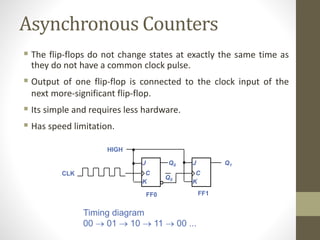
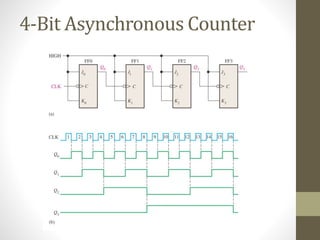
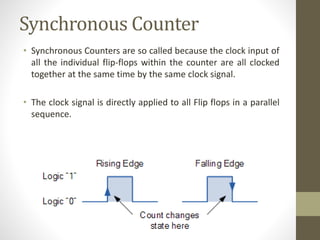
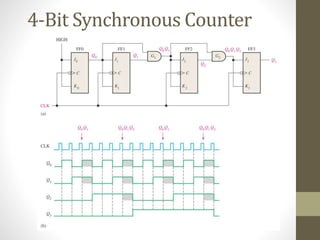
This document discusses counters in digital electronics. It begins by introducing counters as sequential circuits that increment their output value by one each clock cycle, wrapping back to 0 after their maximum count. There are two main types of counters: asynchronous and synchronous. Asynchronous counters have their flip-flops clocked one after another by the previous flip-flop's output, causing a ripple effect. Synchronous counters clock all flip-flops simultaneously with a common clock signal. Examples of 4-bit asynchronous and synchronous counters are also provided with their respective timing diagrams.