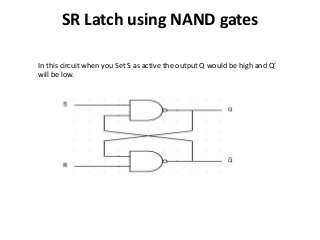
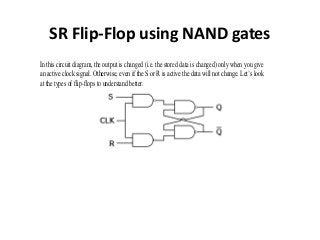
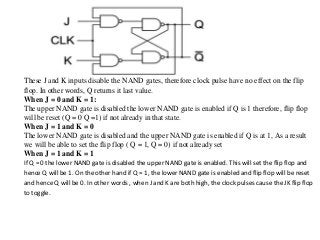
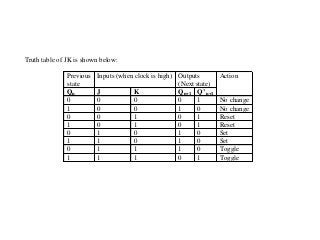
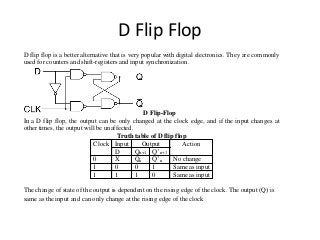
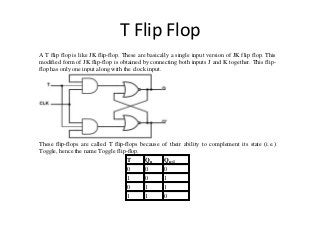
This document discusses different types of flip-flops including SR, JK, D, and T flip-flops. Flip-flops are fundamental building blocks of digital electronics that can store binary data in one of two stable states. They are used as data storage elements in computers and other electronic systems. The different types of flip-flops have inputs like Set, Reset, J, K, D, and T that determine how the output state changes based on their truth tables when a clock signal is applied.