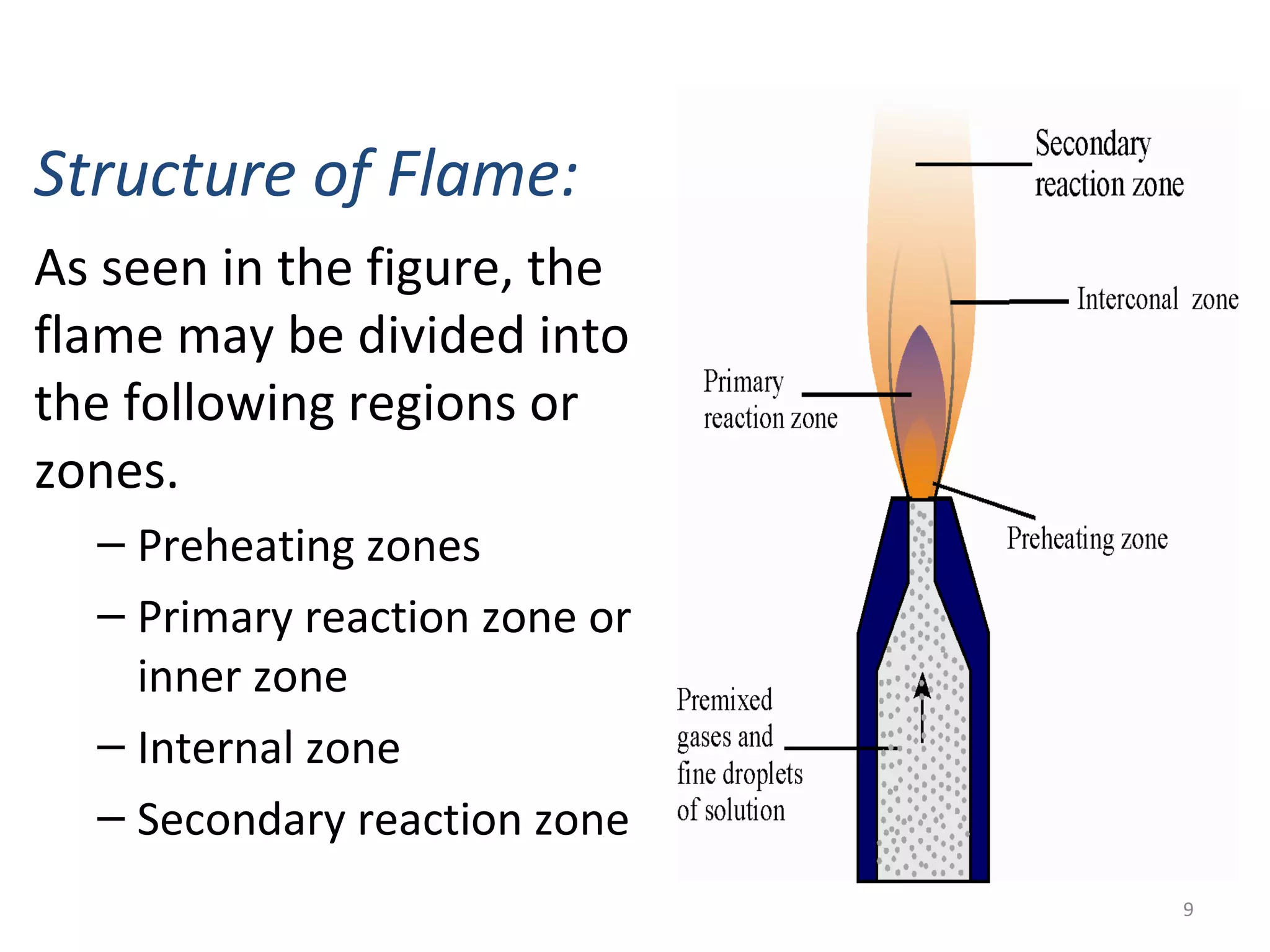
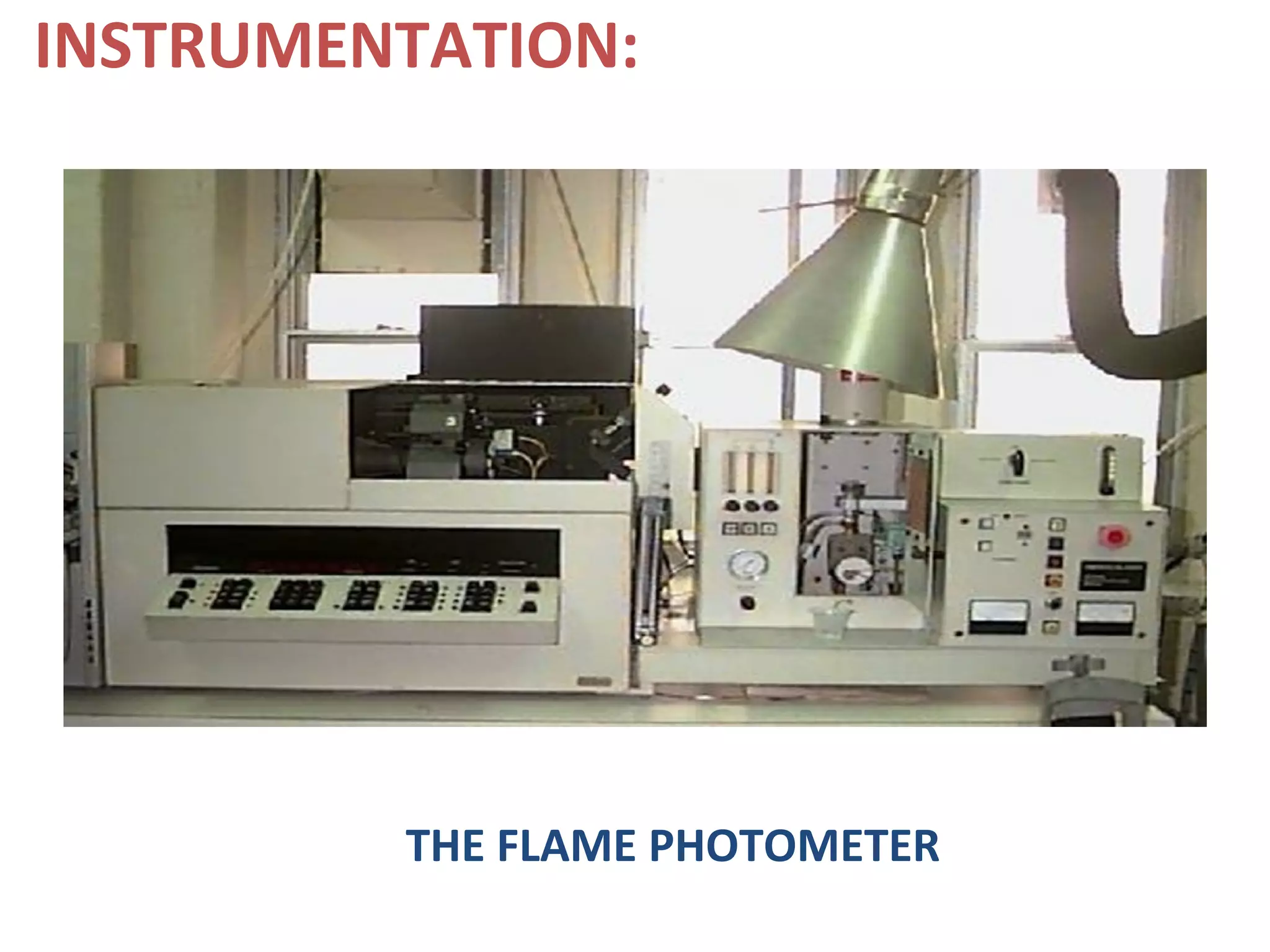
Flame photometry, a branch of atomic emission spectrometry, utilizes a photoelectric flame photometer to measure the concentration of specific metal ions by analyzing the intensity of light emitted when these metals are subjected to a flame. The process involves atomizing the metal salt solution, exciting the atoms, and measuring the emitted photons, which is proportional to the concentration of the metal. Applications include determining levels of alkali and alkaline earth metals in biological fluids, as well as measuring certain metals in various materials, despite potential interferences affecting accuracy.